Abstract
Methods: 120 patients participating in a randomised trial comparing 3 weeks' treatment in a spa resort in Austria or in the Netherlands with a control group completed a WTP questionnaire before and after spa treatment. Patients indicated on a payment card the maximal co-payment they wanted to contribute for three scenarios that included (a) two levels of improvement in pain and stiffness and (b) two treatment environments: a rehabilitation hospital and a spa resort.
Results: At baseline, patients wanted to contribute more for the same improvement after treatment in a spa resort compared with a rehabilitation hospital (p<0.003), and were prepared to pay more when expected effects were higher (p<0.001). No differences were found between men and women, pain, or income. After the trial none of the treatment groups showed a change in their WTP.
Conclusion: The WTP of patients with AS for inpatient treatment is influenced by the treatment environment and the expected improvement. Experiencing treatment in a spa resort does not influence the co-payment.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (79.5 KB).
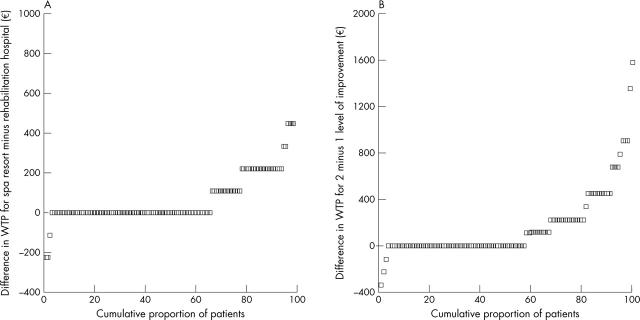
Figure 1.
(A) Difference in WTP for improvement through a stay in a rehabilitation hospital as opposed to a spa resort (y axis) plotted against the cumulative proportion of patients reporting that difference in WTP (x axis). (B) Difference in WTP for a spa treatment for two levels of improvement in pain compared with one level (on a scale from 0 to 4) (y axis) plotted against the cumulative proportion of patients reporting that difference in WTP(x axis).
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.