Abstract
Objective: To assess whether anti-TNF therapy modifies the cardiovascular risk profile in patients with RA.
Methods: The lipoprotein spectrum and the inflammation markers CRP and IL6 were investigated in 33 patients with RA treated with human anti-TNF monoclonal antibodies (D2E7, adalimumab, Humira) and 13 patients with RA given placebo, before and after 2 weeks' treatment.
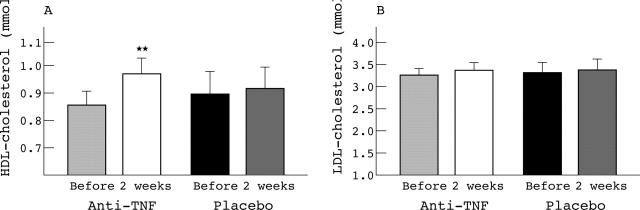
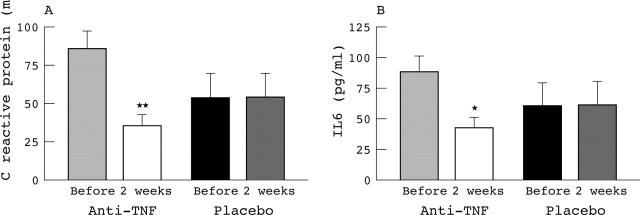
Results: In the anti-TNF treated group, the mean (SD) concentrations of HDL-cholesterol were significantly higher after 2 weeks' treatment (0.86 (0.30) mmol/l v 0.98 (0.33) mmol/l, p<0.01), whereas LDL and triglyceride levels were not significantly changed. Additionally, a significant decrease in CRP (86.1 (54.4) mg/l v 35.4 (35.0) mg/l, p<0.0001), and IL6 (88.3 (60.5) pg/ml v 42.3 (40.7) pg/ml, p<0.001) concentrations was seen in this group. No changes in lipid profile, IL6, or CRP levels were seen in the placebo group.
Conclusions: TNF neutralisation with monoclonal anti-TNF antibodies increased HDL-cholesterol levels and decreased CRP and IL6 levels after 2 weeks. Therefore this treatment may improve the cardiovascular risk profile of patients with RA.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (196.4 KB).
Figure 1.
Concentrations of HDL-cholesterol (A) and LDL-cholesterol (B) in 33 patients with RA before and 2 weeks after treatment with a fully human anti-TNF monoclonal antibody or with placebo. **p<0.0001.
Figure 2.
CRP (A) and IL6 (B) concentrations in 33 patients with RA treated with anti-TNF monoclonal human antibodies and with placebo, before and after 2 weeks' treatment. *p<0.001; **p<0.0001.