Abstract
Objective: To study the characteristics of the haemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelets (HELLP) syndrome in the antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and its influence on the subsequent pregnancies.
Methods: This was a retrospective analysis of 16 episodes of HELLP complicating APS in 15 women.
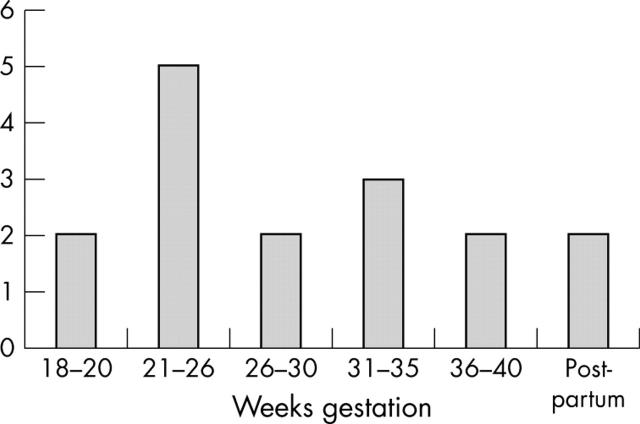
Results: HELLP was complete in 10 cases and partial in six. It occurred during the second trimester in seven cases (the earliest at 18 weeks' gestation), the third trimester in seven cases, and the day following delivery in two cases. Pre-eclampsia was present in six cases and eclampsia in five. Outcome of pregnancies was: live birth (n = 8), stillbirth (n = 2) and fetal death (n = 6). APS was primary in nine women and secondary to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in six. HELLP revealed primary APS in six cases. Seven women were not treated. Low dose aspirin was empirically prescribed in one woman whose APS had been undiagnosed despite a history of two fetal deaths. In the other women, therapy consisted of aspirin (n = 8), low molecular weight heparin with a dose varying between 3000 and 12 000 U daily (n = 5), and high dose immunoglobulin every 4 weeks (n = 2), hydroxychloroquine (n = 4), and prednisone (n = 6). Six women had seven subsequent pregnancies, 3–6 years after the complicated pregnancy. HELLP recurred at 33 weeks' gestation in one woman with SLE treated with prednisone, hydroxychloroquine, aspirin, and enoxaparin, and pregnancy ended in live birth. One woman became pregnant after in vitro fertilisation and embryo transfer, but pregnancy ended in fetal death despite prednisone, hydroxychloroquine, and enoxaparin. Four women had five uneventful pregnancies with 100 mg daily aspirin and heparin.
Conclusions: APS may be revealed by HELLP. In APS, HELLP is associated with pre-eclampsia/eclampsia in most cases and seems to occur earlier than in the general population. Heparin plus aspirin may prevent obstetric complications in the subsequent pregnancies.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (243.6 KB).
Figure 1.
Date of HELLP onset in APS.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alsulyman O. M., Castro M. A., Zuckerman E., McGehee W., Goodwin T. M. Preeclampsia and liver infarction in early pregnancy associated with the antiphospholipid syndrome. Obstet Gynecol. 1996 Oct;88(4 Pt 2):644–646. doi: 10.1016/0029-7844(96)00098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amant F., Spitz B., Arnout J., Van Assche F. A. Hepatic necrosis and haemorrhage in pregnant patients with antiphospholipid antibodies. Lupus. 1997;6(6):552–555. doi: 10.1177/096120339700600615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asherson R. A., Cervera R., Piette J. C., Shoenfeld Y., Espinosa G., Petri M. A., Lim E., Lau T. C., Gurjal A., Jedryka-Góral A. Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome: clues to the pathogenesis from a series of 80 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2001 Nov;80(6):355–377. doi: 10.1097/00005792-200111000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audibert F., Friedman S. A., Frangieh A. Y., Sibai B. M. Clinical utility of strict diagnostic criteria for the HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets) syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1996 Aug;175(2):460–464. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(96)70162-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backos M., Rai R., Baxter N., Chilcott I. T., Cohen H., Regan L. Pregnancy complications in women with recurrent miscarriage associated with antiphospholipid antibodies treated with low dose aspirin and heparin. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1999 Feb;106(2):102–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1999.tb08208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasch J., Carmona F., López-Soto A., Font J., Creus M., Fábregues F., Ingelmo M., Vanrell J. A. Low-dose aspirin for prevention of pregnancy losses in women with primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Hum Reprod. 1993 Dec;8(12):2234–2239. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a138009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branch D. W. Antiphospholipid antibodies and reproductive outcome: the current state of affairs. J Reprod Immunol. 1998 Apr;38(1):75–87. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0378(98)00003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branch D. W., Peaceman A. M., Druzin M., Silver R. K., El-Sayed Y., Silver R. M., Esplin M. S., Spinnato J., Harger J. A multicenter, placebo-controlled pilot study of intravenous immune globulin treatment of antiphospholipid syndrome during pregnancy. The Pregnancy Loss Study Group. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000 Jan;182(1 Pt 1):122–127. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(00)70500-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branch D. W., Silver R. M., Blackwell J. L., Reading J. C., Scott J. R. Outcome of treated pregnancies in women with antiphospholipid syndrome: an update of the Utah experience. Obstet Gynecol. 1992 Oct;80(4):614–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowchock F. S., Reece E. A., Balaban D., Branch D. W., Plouffe L. Repeated fetal losses associated with antiphospholipid antibodies: a collaborative randomized trial comparing prednisone with low-dose heparin treatment. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1992 May;166(5):1318–1323. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(92)91596-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehr T., Cathomas G., Weber C., Fontana A., Schaffner A. Foetal loss, liver necrosis and acute lupus erythematosus in a patient with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. Lupus. 2001;10(8):576–579. doi: 10.1191/096120301701549606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haram Kjell, Trovik Jone, Sandset Per Morten, Hordnes Knut. Severe syndrome of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelets (HELLP) in the 18th week of pregnancy associated with the antiphospholipid-antibody syndrome. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2003 Jul;82(7):679–680. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0412.2003.00181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa I., Takakuwa K., Goto S., Yamada K., Sekizuka N., Kanazawa K., Tanaka K. Effectiveness of prednisolone/aspirin therapy for recurrent aborters with antiphospholipid antibody. Hum Reprod. 1992 Feb;7(2):203–207. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a137617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochberg M. C. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Sep;40(9):1725–1725. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochfeld M., Druzin M. L., Maia D., Wright J., Lambert R. E., McGuire J. Pregnancy complicated by primary antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. Obstet Gynecol. 1994 May;83(5 Pt 2):804–805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huong D. L., Wechsler B., Bletry O., Vauthier-Brouzes D., Lefebvre G., Piette J. C. A study of 75 pregnancies in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome. J Rheumatol. 2001 Sep;28(9):2025–2030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilbery M., Jones A. R., Sampson J. Lupus anticoagulant and HELLP syndrome complicated by placental abruption, hepatic, dermal and adrenal infarction. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 1995 May;35(2):215–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-828x.1995.tb01877.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isler C. M., Barrilleaux P. S., Magann E. F., Bass J. D., Martin J. N., Jr A prospective, randomized trial comparing the efficacy of dexamethasone and betamethasone for the treatment of antepartum HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count) syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2001 Jun;184(7):1332–1339. doi: 10.1067/mob.2001.115051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita K. Hepatic infarction during pregnancy complicated by antiphospholipid syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993 Jul;169(1):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(93)90164-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutteh W. H. Antiphospholipid antibody-associated recurrent pregnancy loss: treatment with heparin and low-dose aspirin is superior to low-dose aspirin alone. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1996 May;174(5):1584–1589. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(96)70610-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lima F., Khamashta M. A., Buchanan N. M., Kerslake S., Hunt B. J., Hughes G. R. A study of sixty pregnancies in patients with the antiphospholipid syndrome. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1996 Mar-Apr;14(2):131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. N., Jr, Rinehart B. K., May W. L., Magann E. F., Terrone D. A., Blake P. G. The spectrum of severe preeclampsia: comparative analysis by HELLP (hemolysis, elevated liver enzyme levels, and low platelet count) syndrome classification. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999 Jun;180(6 Pt 1):1373–1384. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(99)70022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon L. P., Smith J. The HELLP syndrome at 16 weeks gestation: possible association with the antiphospholipid syndrome. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 1997 Aug;37(3):313–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-828x.1997.tb02417.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagayama K., Izumi N., Miyasaka Y., Saito K., Ono K., Noguchi O., Hoshino Y., Uchihara M., Miyake S., Enomoto N. Hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets syndrome associated with primary anti-phospholipid antibody syndrome. Intern Med. 1997 Sep;36(9):661–666. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.36.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuwelt C. M., Daikh D. I., Linfoot J. A., Pfister D. A., Young R. G., Webb R. L., London S. S., Asherson R. A. Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome: response to repeated plasmapheresis over three years. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Aug;40(8):1534–1539. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornstein M. H., Rand J. H. An association between refractory HELLP syndrome and antiphospholipid antibodies during pregnancy; a report of 2 cases. J Rheumatol. 1994 Jul;21(7):1360–1364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauzner R., Dulitzky M., Carp H., Mayan H., Kenett R., Farfel Z., Many A. Hepatic infarctions during pregnancy are associated with the antiphospholipid syndrome and in addition with complete or incomplete HELLP syndrome. J Thromb Haemost. 2003 Aug;1(8):1758–1763. doi: 10.1046/j.1538-7836.2003.00253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queyrel V., Ducloy-Bouthors A-S, Michon-Pasturel U., Hachulla E., Dubucquoi S., Caron C., Vallat A-S, Subtil D., Dufour P., Lambert M. Anticorps antiphospholipides au cours du syndrome HELLP: étude clinique et biologique à partir de 68 patientes. Rev Med Interne. 2003 Mar;24(3):158–164. doi: 10.1016/s0248-8663(02)00013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rai R. S., Clifford K., Cohen H., Regan L. High prospective fetal loss rate in untreated pregnancies of women with recurrent miscarriage and antiphospholipid antibodies. Hum Reprod. 1995 Dec;10(12):3301–3304. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a135907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G., Gordon M. M., Porter D., Jardine A. G., Gibson I. W. Acute renal failure complicating HELLP syndrome, SLE and anti-phospholipid syndrome: successful outcome using plasma exchange therapy. Lupus. 2003;12(4):251–257. doi: 10.1191/0961203303lu378xx. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosove M. H., Tabsh K., Wasserstrum N., Howard P., Hahn B. H., Kalunian K. C. Heparin therapy for pregnant women with lupus anticoagulant or anticardiolipin antibodies. Obstet Gynecol. 1990 Apr;75(4):630–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffatti A., Orsini A., Di Lenardo L., Nardelli G. B., Patrassi G. M., Truscia D., Brigato G., Grella P., Todesco S. A prospective study of fifty-three consecutive calcium heparin treated pregnancies in patients with antiphospholipid antibody-related fetal loss. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1997 Sep-Oct;15(5):499–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal S., Shenhav S., Segal O., Zohav E., Gemer O. Budd-Chiari syndrome complicating severe preeclampsia in a parturient with primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1996 Sep;68(1-2):227–229. doi: 10.1016/0301-2115(96)02495-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibai B. M., Ramadan M. K., Usta I., Salama M., Mercer B. M., Friedman S. A. Maternal morbidity and mortality in 442 pregnancies with hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets (HELLP syndrome) Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993 Oct;169(4):1000–1006. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(93)90043-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silveira L. H., Hubble C. L., Jara L. J., Saway S., Martínez-Osuna P., Seleznick M. J., Angel J., O'Brien W., Espinoza L. R. Prevention of anticardiolipin antibody-related pregnancy losses with prednisone and aspirin. Am J Med. 1992 Oct;93(4):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(92)90170-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. K., MacGregor S. N., Sholl J. S., Hobart J. M., Neerhof M. G., Ragin A. Comparative trial of prednisone plus aspirin versus aspirin alone in the treatment of anticardiolipin antibody-positive obstetric patients. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1993 Dec;169(6):1411–1417. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(93)90410-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha Jayashree, Chowdhry Iftikhar, Sedan Sarah, Barland Peter. Bone marrow necrosis and refractory HELLP syndrome in a patient with catastrophic antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. J Rheumatol. 2002 Jan;29(1):195–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. A., Gharavi A. E., Koike T., Lockshin M. D., Branch D. W., Piette J. C., Brey R., Derksen R., Harris E. N., Hughes G. R. International consensus statement on preliminary classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome: report of an international workshop. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Jul;42(7):1309–1311. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199907)42:7<1309::AID-ANR1>3.0.CO;2-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Tempelhoff G. F., Heilmann L., Spanuth E., Kunzmann E., Hommel G. Incidence of the factor V Leiden-mutation, coagulation inhibitor deficiency, and elevated antiphospholipid-antibodies in patients with preeclampsia or HELLP-syndrome. Hemolysis, elevated liver-enzymes, low platelets. Thromb Res. 2000 Nov 15;100(4):363–365. doi: 10.1016/s0049-3848(00)00312-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]