Abstract
Objective: To investigate antibodies to complement 1q (anti-C1q) and investigate the correlation between anti-C1q titres and renal disease in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Methods: 151 SLE patients were studied. In patients with biopsy proven lupus nephritis (n = 77), activity of renal disease was categorised according to the BILAG renal score. Sera were tested for anti-C1q by enzyme immunoassay. Serum samples were randomly selected from 83 SLE patients who had no history of renal disease, and the positive and negative predictive value of the antibodies was studied.
Results: Patients with active lupus nephritis (BILAG A or B) had a higher prevalence of anti-C1q than those with no renal disease (74% v 32%; relative risk (RR) = 2.3 (95% confidence interval, 1.6 to 3.3)) (p<0.0001). There was no significant difference in anti-C1q prevalence between SLE without nephritis and SLE with non-active nephritis (BILAG C or D) (32% v 53%, p = 0.06) or between active and non-active nephritis (74% v 53%, p = 0.06). Patients with nephritis had higher anti-C1q levels than those without nephritis (36.0 U/ml (range 4.9 to 401.0) v 7.3 U/ml (4.9 to 401.0)) (p<0.001). Anti-C1q were found in 33 of 83 patients (39%) without history of renal disease. Nine of the 33 patients with anti-C1q developed lupus nephritis. The median renal disease-free interval was nine months. One patient with positive anti-C1q was diagnosed as having hypocomplementaemic urticarial vasculitis syndrome during follow up.
Conclusions: Anti-C1q in SLE are associated with renal involvement. Monitoring anti-C1q and their titres in SLE patients could be important for predicting renal flares.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (79.7 KB).
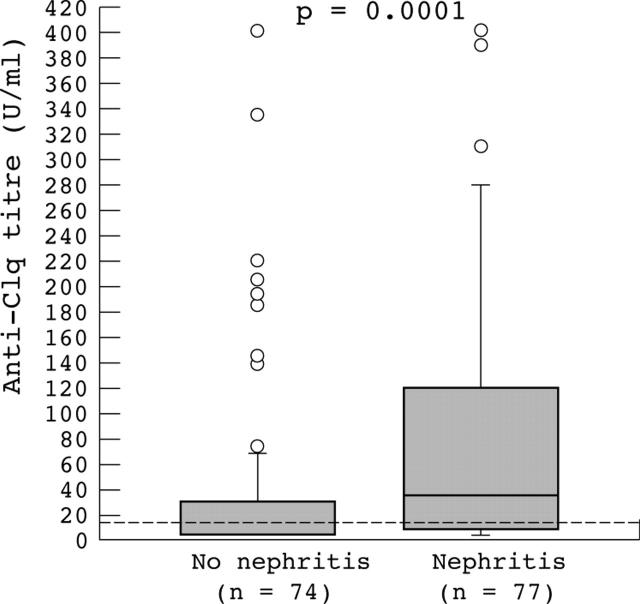
Figure 1.
Anti-C1q antibody titres in 151 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Dashed lines indicate cut off for positivity. This graph shows the median, first to third quartiles (box), interquartile range (whiskers), and outliers (circles). Higher titres of anti-C1q were found in patients with v without renal involvement; the difference was significant.
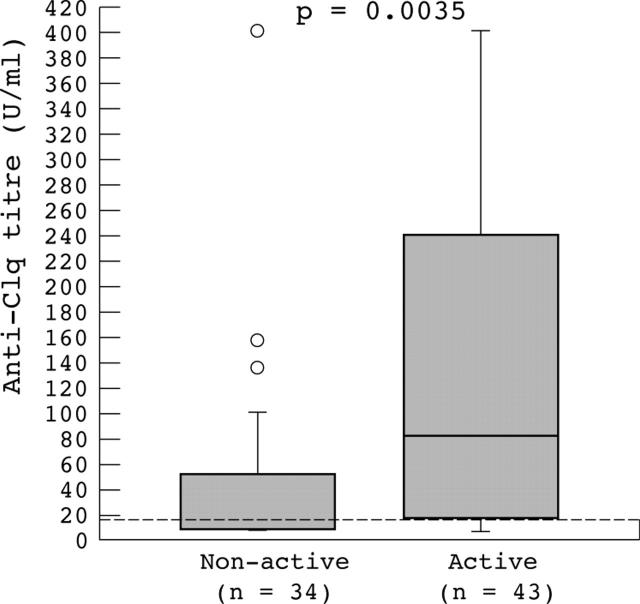
Figure 2.
Anti-C1q titres and activity of renal disease in 77 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and renal involvement. This graph shows the median, first and third quartiles (box), interquartile range (whiskers), and outliers (circles). Higher titres of anti-C1q were found in patients with v without renal involvement; the difference was significant.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amoura Z., Koutouzov S., Chabre H., Cacoub P., Amoura I., Musset L., Bach J. F., Piette J. C. Presence of antinucleosome autoantibodies in a restricted set of connective tissue diseases: antinucleosome antibodies of the IgG3 subclass are markers of renal pathogenicity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Jan;43(1):76–84. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200001)43:1<76::AID-ANR10>3.0.CO;2-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amoura Z., Koutouzov S., Piette J. C. The role of nucleosomes in lupus. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2000 Sep;12(5):369–373. doi: 10.1097/00002281-200009000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin H. A., 3rd, Muenz L. R., Joyce K. M., Antonovych T. T., Balow J. E. Diffuse proliferative lupus nephritis: identification of specific pathologic features affecting renal outcome. Kidney Int. 1984 Apr;25(4):689–695. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berden J. H. Lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 1997 Aug;52(2):538–558. doi: 10.1038/ki.1997.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowness P., Davies K. A., Norsworthy P. J., Athanassiou P., Taylor-Wiedeman J., Borysiewicz L. K., Meyer P. A., Walport M. J. Hereditary C1q deficiency and systemic lupus erythematosus. QJM. 1994 Aug;87(8):455–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns A., Bläss S., Hausdorf G., Burmester G. R., Hiepe F. Nucleosomes are major T and B cell autoantigens in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Oct;43(10):2307–2315. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200010)43:10<2307::AID-ANR19>3.0.CO;2-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coremans I. E., Daha M. R., van der Voort E. A., Muizert Y., Halma C., Breedveld F. C. Antibodies against C1q in anti-glomerular basement membrane nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Feb;87(2):256–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb02984.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coremans I. E., Spronk P. E., Bootsma H., Daha M. R., van der Voort E. A., Kater L., Breedveld F. C., Kallenberg C. G. Changes in antibodies to C1q predict renal relapses in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Kidney Dis. 1995 Oct;26(4):595–601. doi: 10.1016/0272-6386(95)90595-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egner W. The use of laboratory tests in the diagnosis of SLE. J Clin Pathol. 2000 Jun;53(6):424–432. doi: 10.1136/jcp.53.6.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frémeaux-Bacchi V., Weiss L., Demouchy C., Blouin J., Kazatchkine M. D. Autoantibodies to the collagen-like region of C1q are strongly associated with classical pathway-mediated hypocomplementemia in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 1996 Jun;5(3):216–220. doi: 10.1177/096120339600500309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frémeaux-Bacchi Véronique, Noël Laure Hélène, Schifferli Jürg A. No lupus nephritis in the absence of antiC1q autoantibodies? Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2002 Dec;17(12):2041–2043. doi: 10.1093/ndt/17.12.2041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnarsson I., Rönnelid J., Huang Y. H., Rogberg S., Nilsson B., Lundberg I., Klareskog L. Association between ongoing anti-C1q antibody production in peripheral blood and proliferative nephritis in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. Br J Rheumatol. 1997 Jan;36(1):32–37. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/36.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnarsson Iva, Sundelin Birgitta, Heimbürger Mikael, Forslid Jan, van Vollenhoven Ronald, Lundberg Ingrid, Jacobson Stefan H. Repeated renal biopsy in proliferative lupus nephritis--predictive role of serum C1q and albuminuria. J Rheumatol. 2002 Apr;29(4):693–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H. Antibodies to DNA. N Engl J Med. 1998 May 7;338(19):1359–1368. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199805073381906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseley L. A., Wisnieski J. J., Denburg M. R., Michael-Grossman A. R., Ginzler E. M., Gourley M. F., Hoffman J. H., Kimberly R. P., Salmon J. E. Antibodies to C1q in systemic lupus erythematosus: characteristics and relation to Fc gamma RIIA alleles. Kidney Int. 1997 Nov;52(5):1375–1380. doi: 10.1038/ki.1997.464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay E. M., Bacon P. A., Gordon C., Isenberg D. A., Maddison P., Snaith M. L., Symmons D. P., Viner N., Zoma A. The BILAG index: a reliable and valid instrument for measuring clinical disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Q J Med. 1993 Jul;86(7):447–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horváth L., Czirják L., Fekete B., Jakab L., Pozsonyi T., Kalabay L., Romics L., Miklós K., Varga L., Prohászka Z. High levels of antibodies against Clq are associated with disease activity and nephritis but not with other organ manifestations in SLE patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2001 Nov-Dec;19(6):667–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg D. A., Ravirajan C. T., Rahman A., Kalsi J. The role of antibodies to DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus--a review and introduction to an international workshop on DNA antibodies held in London, May 1996. Lupus. 1997;6(3):290–304. doi: 10.1177/096120339700600316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson H., Sturfelt G., Mårtensson U., Truedsson L., Sjöholm A. G. Prospective analysis of C1 dissociation and complement activation in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1995 Sep-Oct;13(5):573–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowith J. B., Gilkeson G. S. Nephritogenic autoantibodies in lupus: current concepts and continuing controversies. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Jun;39(6):894–903. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd W., Schur P. H. Immune complexes, complement, and anti-DNA in exacerbations of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Medicine (Baltimore) 1981 May;60(3):208–217. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198105000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannik M., Wener M. H. Deposition of antibodies to the collagen-like region of C1q in renal glomeruli of patients with proliferative lupus glomerulonephritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Aug;40(8):1504–1511. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroni G., Trendelenburg M., Del Papa N., Quaglini S., Raschi E., Panzeri P., Testoni C., Tincani A., Banfi G., Balestrieri G. Anti-C1q antibodies may help in diagnosing a renal flare in lupus nephritis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001 Mar;37(3):490–498. doi: 10.1053/ajkd.2001.22071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering M. C., Walport M. J. Links between complement abnormalities and systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2000 Feb;39(2):133–141. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/39.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rönnelid J., Huang Y. H., Norrlander T., Rogberg S., Nilsson B., Gustafsson R., Klareskog L. Short-term kinetics of the humoral anti-C1q response in SLE using the ELISPOT method: fast decline in production in response to steroids. Scand J Immunol. 1994 Aug;40(2):243–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1994.tb03457.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegert C. E., Daha M. R., Halma C., van der Voort E. A., Breedveld F. C. IgG and IgA autoantibodies to C1q in systemic and renal diseases. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1992 Jan-Feb;10(1):19–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegert C. E., Daha M. R., Tseng C. M., Coremans I. E., van Es L. A., Breedveld F. C. Predictive value of IgG autoantibodies against C1q for nephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Dec;52(12):851–856. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.12.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegert C. E., Kazatchkine M. D., Sjöholm A., Würzner R., Loos M., Daha M. R. Autoantibodies against C1q: view on clinical relevance and pathogenic role. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999 Apr;116(1):4–8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00867.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegert C., Daha M., Westedt M. L., van der Voort E., Breedveld F. IgG autoantibodies against C1q are correlated with nephritis, hypocomplementemia, and dsDNA antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1991 Feb;18(2):230–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaak A. J., Aarden L. A., Statius van Eps L. W., Feltkamp T. E. Anti-dsDNA and complement profiles as prognostic guides in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Mar;22(3):226–235. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaak A. J., Groenwold J., Bronsveld W. Predictive value of complement profiles and anti-dsDNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 May;45(5):359–366. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.5.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trendelenburg M., Marfurt J., Gerber I., Tyndall A., Schifferli J. A. Lack of occurrence of severe lupus nephritis among anti-C1q autoantibody-negative patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Jan;42(1):187–188. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199901)42:1<187::AID-ANR24>3.0.CO;2-U. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trouw L. A., Seelen M. A., Duijs J. M. G. J., Benediktsson H., Van Kooten C., Daha M. R. Glomerular deposition of C1q and anti-C1q antibodies in mice following injection of antimouse C1q antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 2003 Apr;132(1):32–39. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2003.02108.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uwatoko S., Aotsuka S., Okawa M., Egusa Y., Yokohari R., Aizawa C., Suzuki K. Characterization of C1q-binding IgG complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 Jan;30(1):104–116. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(84)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walport M. J. Complement. First of two parts. N Engl J Med. 2001 Apr 5;344(14):1058–1066. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200104053441406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walport M. J. Complement. Second of two parts. N Engl J Med. 2001 Apr 12;344(15):1140–1144. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200104123441506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wener M. H., Uwatoko S., Mannik M. Antibodies to the collagen-like region of C1q in sera of patients with autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 May;32(5):544–551. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. A., Gharavi A. E., Koike T., Lockshin M. D., Branch D. W., Piette J. C., Brey R., Derksen R., Harris E. N., Hughes G. R. International consensus statement on preliminary classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome: report of an international workshop. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Jul;42(7):1309–1311. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199907)42:7<1309::AID-ANR1>3.0.CO;2-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisnieski J. J., Jones S. M. IgG autoantibody to the collagen-like region of Clq in hypocomplementemic urticarial vasculitis syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, and 6 other musculoskeletal or rheumatic diseases. J Rheumatol. 1992 Jun;19(6):884–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]