Abstract
Objectives: To study the incidence and clinical picture of Shigella associated reactive arthritis (ReA) and the arthritogenicity of various Shigella species in the population.
Methods: A questionnaire on enteric and extraintestinal, especially musculoskeletal, symptoms was sent to 278 consecutive patients with Shigella positive stool culture and to 597 controls. Analysis of self reported musculoskeletal symptoms was supplemented with clinical examination of those subjects with recent symptoms.
Results: Of the patients, 14/211 (7%) had ReA, and a further 4/211 (2%) other reactive musculoskeletal symptoms (tendonitis, enthesopathy, or bursitis). Of the 14 patients with ReA, all adults, 10 had S sonnei, three S flexneri, and one S dysenteriae infection. HLA-B27 was positive in 36% of the patients with ReA. One control subject had ReA. In the patients with Shigella infection, the odds ratio for developing ReA was 16.2 (95% confidence interval 2.1 to 123.9), p = 0.001.
Conclusions: ReA occurred in 7% of patients after Shigella infection, with an annual incidence of 1.3/1 000 000 in Finland. Besides S flexneri, S sonnei and S dysenteriae can also trigger ReA.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (81.0 KB).
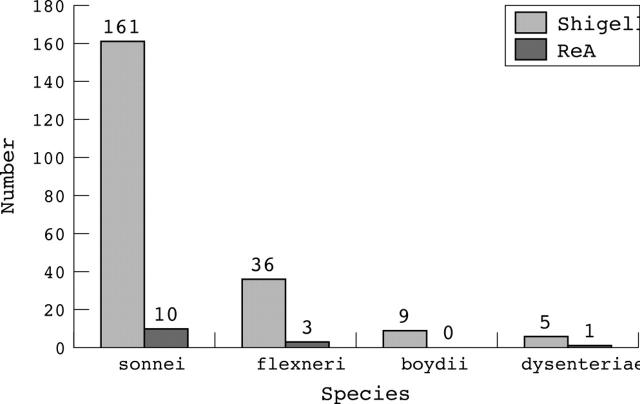
Figure 1.
Occurrence of Shigella species and reactive arthritis among the 211 Shigella patients with a positive stool culture.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calin A., Fries J. F. An "experimental" epidemic of Reiter's syndrome revisited. Follow-up evidence on genetic and environmental factors. Ann Intern Med. 1976 May;84(5):564–566. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-5-564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M., Delpech V., O'Sullivan B., Donovan B. Shigella sonnei: another cause of sexually acquired reactive arthritis. Int J STD AIDS. 2002 Feb;13(2):135–136. doi: 10.1258/0956462021924640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies N. E., Haverty J. R., Boatwright M. Reiter's disease associated with shigellosis. South Med J. 1969 Aug;62(8):1011–1014. doi: 10.1097/00007611-196908000-00027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch M., Rodey G., Lawrence D., Blake P. Epidemic Reiter's syndrome following an outbreak of shigellosis. Eur J Epidemiol. 1986 Mar;2(1):26–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00152713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannu T., Mattila L., Rautelin H., Pelkonen P., Lahdenne P., Siitonen A., Leirisalo-Repo M. Campylobacter-triggered reactive arthritis: a population-based study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2002 Mar;41(3):312–318. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/41.3.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman R. D., Johnston M. E., Hodge M., Falk J., Helewa A. Postdysenteric reactive arthritis. A clinical and immunogenetic study following an outbreak of salmonellosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Nov;31(11):1377–1383. doi: 10.1002/art.1780311106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaslow R. A., Ryder R. W., Calin A. Search for Reiter's syndrome after an outbreak of Shigella sonnei dysentery. J Rheumatol. 1979 Sep-Oct;6(5):562–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauhio A., Lähdevirta J., Janes R., Kontiainen S., Repo H. Reactive arthritis associated with Shigella sonnei infection. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Sep;31(9):1190–1193. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leirisalo M., Skylv G., Kousa M., Voipio-Pulkki L. M., Suoranta H., Nissilä M., Hvidman L., Nielsen E. D., Svejgaard A., Tilikainen A. Followup study on patients with Reiter's disease and reactive arthritis, with special reference to HLA-B27. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Mar;25(3):249–259. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. B. The absence of reactive arthritis after Shigella sonnei infection. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Oct;25(10):1267–1267. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattila L., Leirisalo-Repo M., Koskimies S., Granfors K., Siitonen A. Reactive arthritis following an outbreak of Salmonella infection in Finland. Br J Rheumatol. 1994 Dec;33(12):1136–1141. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/33.12.1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazumder R. N., Salam M. A., Ali M., Bhattacharya M. K. Reactive arthritis associated with Shigella dysenteriae type 1 infection. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1997 Mar;15(1):21–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse H. G., Rate R. G., Bonnell M. D., Kuberski T. T. Reiter's syndrome in a five-year-old girl. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Aug;23(8):960–961. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noer H. R. An "experimental" epidemic of Reiter's syndrome. JAMA. 1966 Nov 14;198(7):693–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon D. G., Kaslow R. A., Rosenbaum J., Kaye R. L., Calin A. Reiter's syndrome following epidemic shigellosis. J Rheumatol. 1981 Nov-Dec;8(6):969–973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson G. T., Alfa M., Orr K., Thomson B. R., Olson N. Secretory immune response and clinical sequelae of Salmonella infection in a point source cohort. J Rheumatol. 1994 Jan;21(1):132–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toivanen A., Granfors K., Lahesmaa-Rantala R., Leino R., Ståhlberg T., Vuento R. Pathogenesis of Yersinia-triggered reactive arthritis: immunological, microbiological and clinical aspects. Immunol Rev. 1985 Aug;86:47–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Bohemen C. G., Lionarons R. J., van Bodegom P., Dinant H. J., Landheer J. E., Nabbe A. J., Grumet F. C., Zanen H. C. Susceptibility and HLA-B27 in post-dysenteric arthropathies. Immunology. 1985 Oct;56(2):377–379. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]