Abstract
Background: Severe neurological involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus (NPSLE) is one of the most dreadful complications of the disease.
Objective: To identify the best drug, dose, and treatment.
Patients and methods: The study was a controlled clinical trial at two tertiary care centres of patients with SLE according to the ACR criteria, with incident (no more than 15 days) onset of severe NP manifestations such as seizures, optic neuritis, peripheral or cranial neuropathy, coma, brainstem disease, or transverse myelitis. Induction treatment with 3 g of IV methylprednisolone (MP) followed by either IV monthly cyclophosphamide (Cy) versus IV MP bimonthly every 4 months for 1 year and then IV Cy or IV MP every 3 months for another year. The primary end point was response to treatment: at least 20% improvement from basal conditions on clinical, laboratory, or specific neurological testing variables.
Results: Overall, a response rate of 75% was observed. Of the 32 patients studied, 18/19 receiving Cy and 7/13 receiving MP responded to treatment (p<0.03).
Conclusions: Cy seems to be more effective than MP in the treatment of acute, severe NPSLE.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (82.2 KB).
Figure 1.
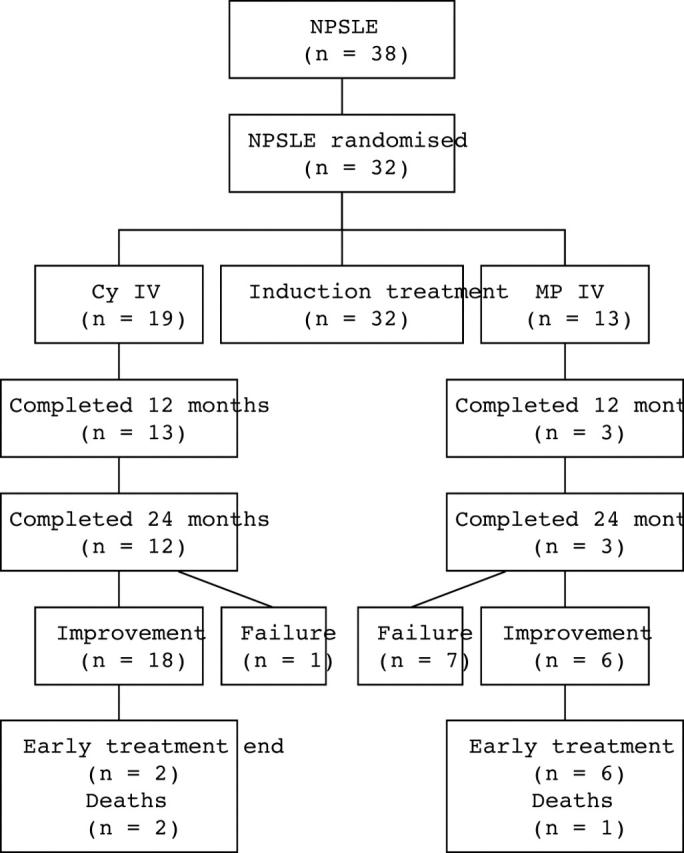
Patient's outcome throughout follow up.
Figure 2.
Mean number of seizures/month in (A) MP group; (B) Cy group.
Figure 3.
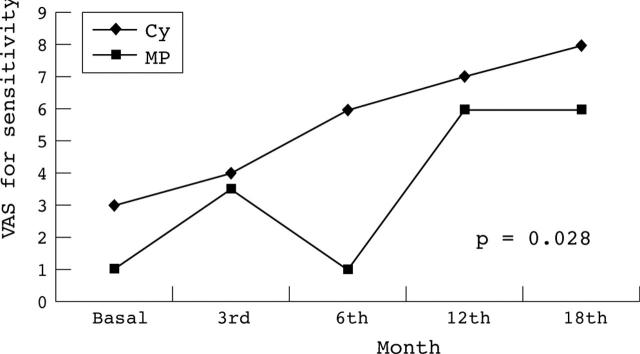
Changes in visual analogue scale for sensitivity in transverse myelitis and peripheral neuropathy.
Figure 4.
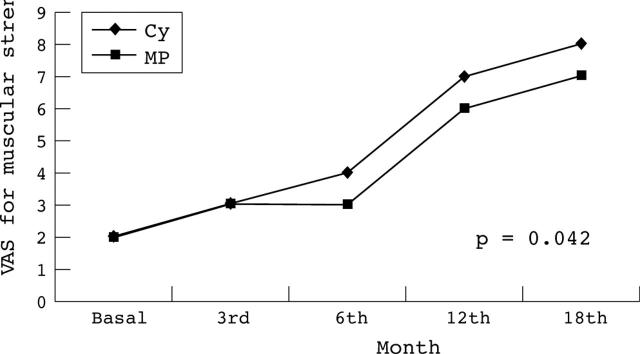
Changes in visual analogue scale for muscular strength in transverse myelitis and peripheral neuropathy.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alarcón-Segovia D., Cabral A. R. The antiphospholipid/cofactor syndromes. J Rheumatol. 1996 Aug;23(8):1319–1322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barile L., Lavalle C. Transverse myelitis in systemic lupus erythematosus--the effect of IV pulse methylprednisolone and cyclophosphamide. J Rheumatol. 1992 Mar;19(3):370–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bombardier C., Gladman D. D., Urowitz M. B., Caron D., Chang C. H. Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The Committee on Prognosis Studies in SLE. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Jun;35(6):630–640. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boumpas D. T., Austin H. A., 3rd, Vaughn E. M., Klippel J. H., Steinberg A. D., Yarboro C. H., Balow J. E. Controlled trial of pulse methylprednisolone versus two regimens of pulse cyclophosphamide in severe lupus nephritis. Lancet. 1992 Sep 26;340(8822):741–745. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92292-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boumpas D. T., Yamada H., Patronas N. J., Scott D., Klippel J. H., Balow J. E. Pulse cyclophosphamide for severe neuropsychiatric lupus. Q J Med. 1991 Dec;81(296):975–984. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/81.3.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buyse M. Interim analyses, stopping rules and data monitoring in clinical trials in Europe. Stat Med. 1993 Mar;12(5-6):509–520. doi: 10.1002/sim.4780120517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan K. F., Boey M. L. Transverse myelopathy in SLE: clinical features and functional outcomes. Lupus. 1996 Aug;5(4):294–299. doi: 10.1177/096120339600500409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricchione G. L., Kaufman L. D., Gruber B. L., Fink M. Electroconvulsive therapy and cyclophosphamide in combination for severe neuropsychiatric lupus with catatonia. Am J Med. 1990 Apr;88(4):442–443. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(90)90509-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jara L. J., Capin N. R., Lavalle C. Hyperviscosity syndrome as the initial manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1989 Feb;16(2):225–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennekens F. G. I., Kater L. The central nervous system in systemic lupus erythematosus. Part 1. Clinical syndromes: a literature investigation. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2002 Jun;41(6):605–618. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/41.6.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazatchkine M. D., Kaveri S. V. Immunomodulation of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases with intravenous immune globulin. N Engl J Med. 2001 Sep 6;345(10):747–755. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra993360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K., Tsiatis A. A. Study duration for clinical trials with survival response and early stopping rule. Biometrics. 1990 Mar;46(1):81–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang M. H., Corzillius M., Bae S. C., Fortin P., Esdaile J. M., Abrahamowicz M. A conceptual framework for clinical trials in SLE and other multisystem diseases. Lupus. 1999;8(8):570–580. doi: 10.1191/096120399680411290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune W. J., Golbus J., Zeldes W., Bohlke P., Dunne R., Fox D. A. Clinical and immunologic effects of monthly administration of intravenous cyclophosphamide in severe systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 2;318(22):1423–1431. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806023182203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meroni P. L., Tincani A., Sepp N., Raschi E., Testoni C., Corsini E., Cavazzana I., Pellegrini S., Salmaggi A. Endothelium and the brain in CNS lupus. Lupus. 2003;12(12):919–928. doi: 10.1191/0961203303lu503oa. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mok C. C., Lau C. S., Chan E. Y., Wong R. W. Acute transverse myelopathy in systemic lupus erythematosus: clinical presentation, treatment, and outcome. J Rheumatol. 1998 Mar;25(3):467–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuwelt C. M., Lacks S., Kaye B. R., Ellman J. B., Borenstein D. G. Role of intravenous cyclophosphamide in the treatment of severe neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1995 Jan;98(1):32–41. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9343(99)80078-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos P. C., Mendez M. J., Ames P. R., Khamashta M. A., Hughes G. R. Pulse cyclophosphamide in the treatment of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1996 May-Jun;14(3):295–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito K., Nawata M., Nakayamada S., Tokunaga M., Tsukada J., Tanaka Y. Successful treatment with anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (rituximab) of life-threatening refractory systemic lupus erythematosus with renal and central nervous system involvement. Lupus. 2003;12(10):798–800. doi: 10.1191/0961203303lu450xx. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanna G., Bertolaccini M. L., Mathieu A. Central nervous system lupus: a clinical approach to therapy. Lupus. 2003;12(12):935–942. doi: 10.1191/0961203303lu505oa. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanna Giovanni, Bertolaccini Maria L., Cuadrado Maria J., Laing Hana, Khamashta Munther A., Mathieu Alessandro, Hughes Graham R. V. Neuropsychiatric manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus: prevalence and association with antiphospholipid antibodies. J Rheumatol. 2003 May;30(5):985–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sastre-Garriga J., Montalban X. APS and the brain. Lupus. 2003;12(12):877–882. doi: 10.1191/0961203303lu496oa. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder J. O., Euler H. H. Treatment combining plasmapheresis and pulse cyclophosphamide in severe systemic lupus erythematosus. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1989;260:203–213. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-5718-6_21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherer Y., Levy Y., Langevitz P., Lorber M., Fabrizzi F., Shoenfeld Y. Successful treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus cerebritis with intravenous immunoglobulin. Clin Rheumatol. 1999;18(2):170–173. doi: 10.1007/s100670050079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tincani A., Spatola L., Cinquini M., Cattaneo R., Meroni P., Balestrieri G. Anti beta2-glycoprotein I antibodies: clinical significance. Lupus. 1998;7 (Suppl 2):S107–S109. doi: 10.1177/096120339800700224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trevisani V. F., Castro A. A., Neves Neto J. F., Atallah A. N. Cyclophosphamide versus methylprednisolone for the treatment of neuropsychiatric involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(3):CD002265–CD002265. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valesini G., Priori R., Francia A., Balestrieri G., Tincani A., Airo P., Cattaneo R., Zambruni A., Troianello B., Chofflon M. Central nervous system involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus: a new therapeutic approach with intrathecal dexamethasone and methotrexate. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1994;16(2-3):313–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00197524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw D. A., Spangenberg J. J., Rickman R., Hugo F. H., Roberts M. The association between the antiphospholipid antibody syndrome and neuropsychological impairment in SLE. Lupus. 1999;8(6):444–448. doi: 10.1177/096120339900800606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]