Abstract
Background: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is increasingly used to detect inflammation in the spine of patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS).
Objectives: To detect differentially the presence and extent of inflammation in the three spinal segments of patients with AS by MRI.
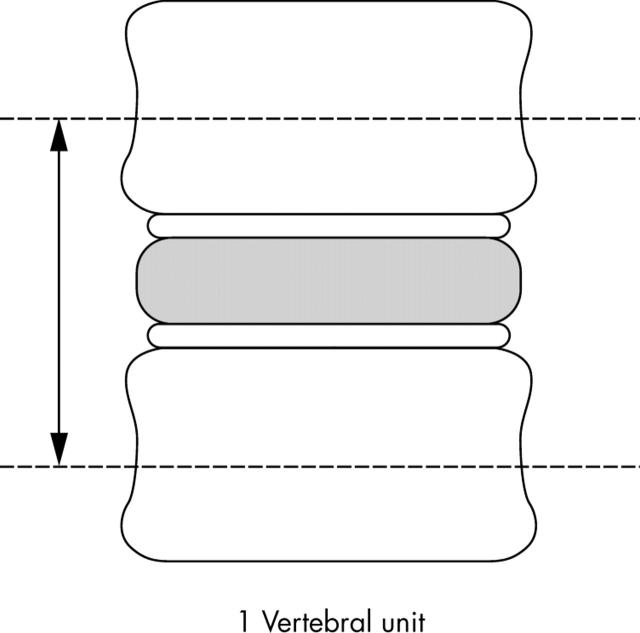
Methods: In 38 patients with active AS, acute spinal lesions were assessed by T1 weighted, gadolinium enhanced, spin echo MRI (T1/Gd-DTPA) and short τ inversion recovery (STIR) sequences. MRI was quantified by the validated scoring system ASspiMRI-a. Acute spinal lesions were detected in the whole spine and in each spinal segment. One vertebral unit (VU) was defined as the region between two virtual lines drawn through the middle of each vertebral body.
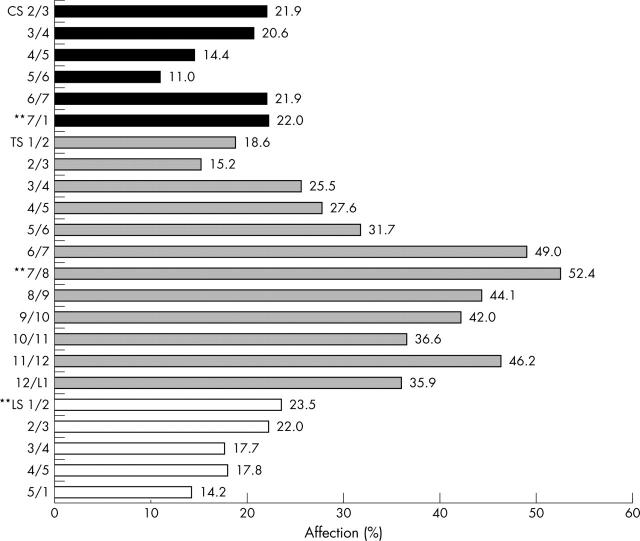
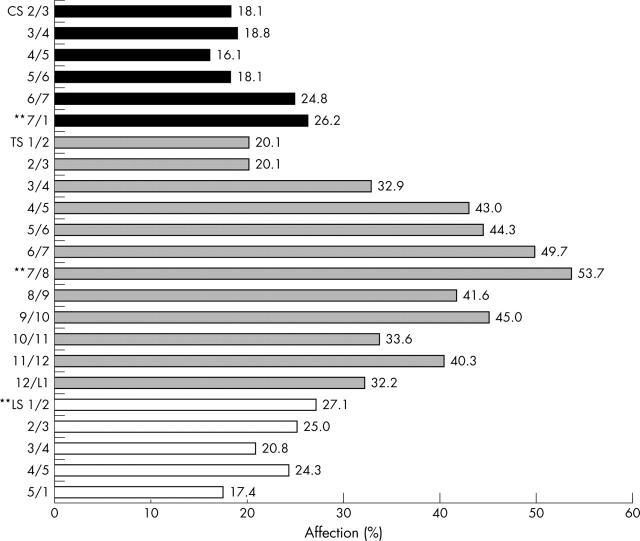
Results: A greater number of inflammatory spinal lesions were found by the STIR sequence than by Gd-DTPA: inflammation was present in 30.6% of the VUs as assessed by STIR, compared with 26.8% of the same VUs assessed by T1/Gd-DTPA. Inflammation was found more commonly in the thoracic spine (TS) than in the cervical (CS) or the lumbar spine (LS) with both techniques. When STIR was used, spinal inflammation in the CS, the TS, and LS was detected in 10/38 (26%), 28/38 (74%), and 9/38 (24%) patients, respectively. The VU T7/8 was found to be the VU most often affected by both techniques (27.8% by T1/Gd-DTPA and 34.5% by STIR).
Conclusions: Spinal inflammation is a common manifestation in patients with AS, and appears more frequently in the TS. The scoring system ASspiMRI-a can be used for evaluation of acute spinal changes in AS.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (103.6 KB).
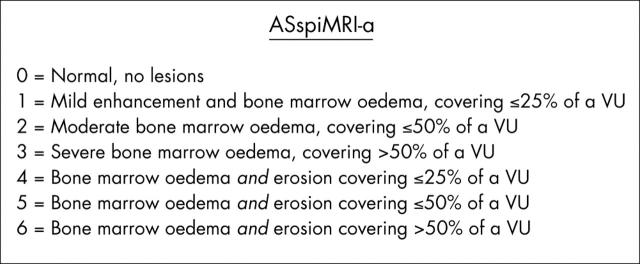
Figure 1.
The new scoring system ASspiMRI-a for evaluation of acute spinal lesions in patients with ankylosing spondylitis as assessed by Gd-DTPA and STIR MRI.
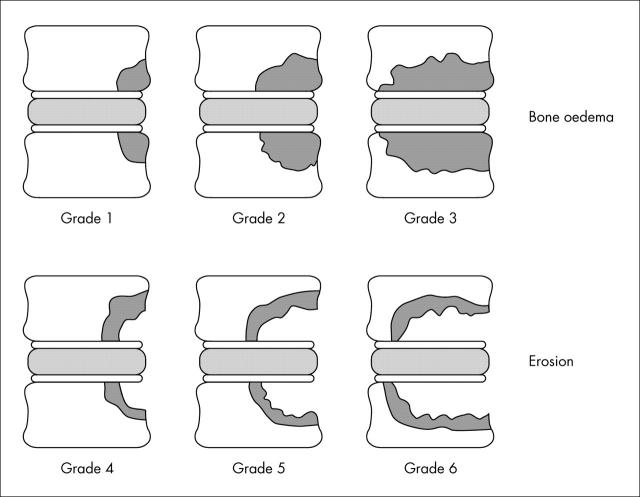
Figure 2.
The ASspiMRI-a scoring system in detail. Grades 1–3 indicate only erosion with differentiation of the range of inflammation (in the Gd-DTPA sequence) or oedema (in the STIR sequence). Grades 4–6 indicates inflammation with erosion, in relation to the extent of the erosion in the assessed VU.
Figure 3.
Definition of the VU for using the ASspiMRI score in the evaluation of MR images in the spine of patients with AS.
Figure 6.
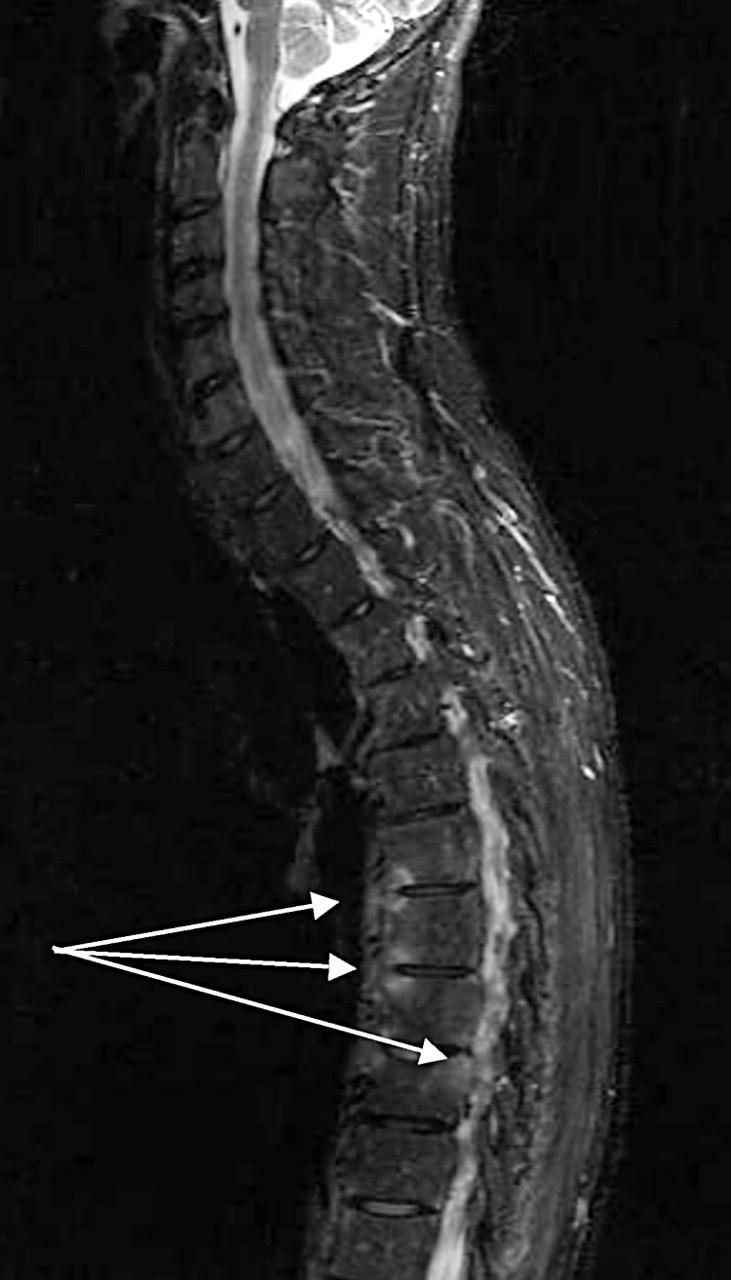
Spondylitis anterior in T6/7 and T7/8 and spondylitis posterior in T8/9 as seen in the STIR MRI sequence. Inflammation is seen as a spot in the vertebra (arrows).
Figure 4.
Relative involvement of each single VU in the assessment of inflammation by the Gd-DTPA MRI sequence and evaluation with the ASspiMRI-a scoring system. Values are shown as percentage of VU affected. **VU most commonly affected in each spinal segment.
Figure 5.
Relative involvement of each single VU in the assessment of inflammation by the STIR MRI sequence and evaluation with the ASspiMRI-a scoring system. Values are shown as percentage of VU affected. **VU most commonly affected in each spinal segment.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brandt J., Haibel H., Cornely D., Golder W., Gonzalez J., Reddig J., Thriene W., Sieper J., Braun J. Successful treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with the anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody infliximab. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Jun;43(6):1346–1352. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200006)43:6<1346::AID-ANR18>3.0.CO;2-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt J., Khariouzov A., Listing J., Haibel H., Sörensen H., Grassnickel L., Rudwaleit M., Sieper J., Braun J. Six-month results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of etanercept treatment in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Jun;48(6):1667–1675. doi: 10.1002/art.11017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Baraliakos X., Golder W., Brandt J., Rudwaleit M., Listing J., Bollow M., Sieper J., Van Der Heijde D. Magnetic resonance imaging examinations of the spine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, before and after successful therapy with infliximab: evaluation of a new scoring system. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Apr;48(4):1126–1136. doi: 10.1002/art.10883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Baraliakos X., Golder W., Hermann K-G, Listing J., Brandt J., Rudwaleit M., Zuehlsdorf S., Bollow M., Sieper J. Analysing chronic spinal changes in ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic comparison of conventional x rays with magnetic resonance imaging using established and new scoring systems. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004 Apr 5;63(9):1046–1055. doi: 10.1136/ard.2003.019968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Bollow M., Remlinger G., Eggens U., Rudwaleit M., Distler A., Sieper J. Prevalence of spondylarthropathies in HLA-B27 positive and negative blood donors. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Jan;41(1):58–67. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199801)41:1<58::AID-ART8>3.0.CO;2-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Bollow M., Sieper J. Radiologic diagnosis and pathology of the spondyloarthropathies. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1998 Nov;24(4):697–735. doi: 10.1016/s0889-857x(05)70038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Brandt J., Listing J., Zink A., Alten R., Burmester G., Gromnica-Ihle E., Kellner H., Schneider M., Sörensen H. Two year maintenance of efficacy and safety of infliximab in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004 Sep 23;64(2):229–234. doi: 10.1136/ard.2004.025130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Brandt J., Listing J., Zink A., Alten R., Golder W., Gromnica-Ihle E., Kellner H., Krause A., Schneider M. Treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with infliximab: a randomised controlled multicentre trial. Lancet. 2002 Apr 6;359(9313):1187–1193. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(02)08215-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., van der Heijde D. Imaging and scoring in ankylosing spondylitis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2002 Sep;16(4):573–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calin A., Porta J., Fries J. F., Schurman D. J. Clinical history as a screening test for ankylosing spondylitis. JAMA. 1977 Jun 13;237(24):2613–2614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis John C., Jr, Van Der Heijde Désirée, Braun Jurgen, Dougados Maxime, Cush John, Clegg Daniel O., Kivitz Alan, Fleischmann Roy, Inman Robert, Tsuji Wayne. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor receptor (etanercept) for treating ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Nov;48(11):3230–3236. doi: 10.1002/art.11325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frei Hanspeter, Oxland Thomas R., Nolte Lutz P. Thoracolumbar spine mechanics contrasted under compression and shear loading. J Orthop Res. 2002 Nov;20(6):1333–1338. doi: 10.1016/S0736-0266(02)00058-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton L. J., 3rd, Kan S. H., Frye M. A., Wahner H. W., O'Fallon W. M., Riggs B. L. Epidemiology of vertebral fractures in women. Am J Epidemiol. 1989 May;129(5):1000–1011. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spoorenberg Anneke, de Vlam Kurt, van der Linden Sjef, Dougados Maxime, Mielants Herman, van de Tempel Hille, van der Heijde Désirée. Radiological scoring methods in ankylosing spondylitis. Reliability and change over 1 and 2 years. J Rheumatol. 2004 Jan;31(1):125–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]