Abstract
Background: Increased apoptosis may induce autoimmune conditions. Apoptosis is induced by binding of death receptor ligands, members of the tumour necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily, to their cognate receptors. The Fas–Fas ligand pathway has been studied extensively in relation to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). However, other death pathways are also considered important. TNF related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL), another ligand of the TNF superfamily, induces apoptosis in sensitive cells.
Objective: To assess soluble (s) TRAIL concentrations in sera of SLE patients.
Methods: 40 SLE patients were studied (20 with active and 20 with inactive disease). Serum sTRAIL concentrations were measured by a solid phase sandwich enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Levels in SLE patients were compared with those in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (n = 20), Wegener's granulomatosis (n = 20), and healthy controls (n = 20).
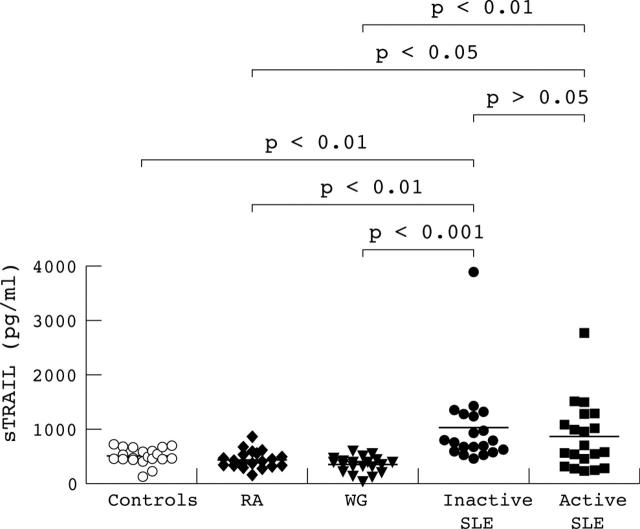
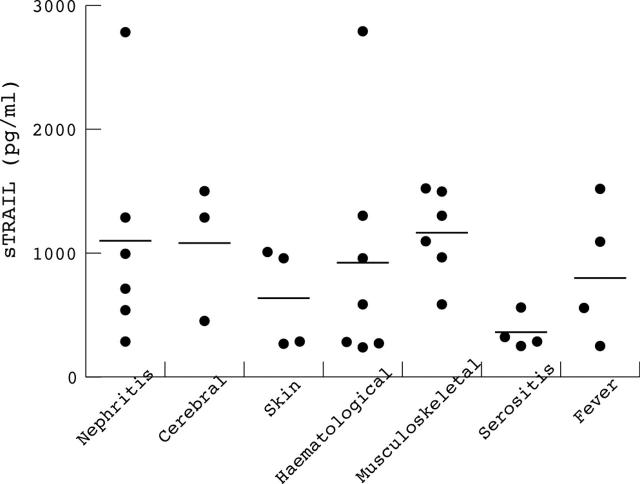
Results: Mean (SEM) serum sTRAIL concentration in SLE patients (936.0 (108.2) pg/ml) was higher than in healthy controls (509.4 (33.8) pg/ml; p<0.01) or in disease control patients with rheumatoid arthritis (443.8 (36.1) pg/ml, p<0.001) or Wegener's granulomatosis (357.1 (32.2) pg/ml; p<0.001). The mean serum sTRAIL concentration was 1010.2 (168.0) pg/ml for patients with inactive disease and 861.8 (138.7) pg/ml for those with active disease. sTRAIL values were not correlated with specific manifestations of the disease, such as leucopenia or lymphopenia, or with SLE disease activity index.
Conclusions: Serum sTRAIL concentrations are increased SLE patients. This seems to be disease specific and could indicate a role for TRAIL in SLE pathophysiology.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (81.7 KB).
Figure 1.
Serum soluble TNF related apoptosis inducing ligand (sTRAIL) concentrations (pg/ml) in SLE patients with inactive disease (n = 20), SLE patients with active disease (n = 20), disease control patients with rheumatoid arthritis (n = 20), disease control patients with Wegener's granulomatosis (n = 20), and healthy controls (n = 20). The horizontal lines give the mean sTRAIL value.
Figure 2.
Serum soluble TNF related apoptosis inducing ligand (sTRAIL) concentrations (pg/ml) in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who had active disease (n = 20) divided by clinical disease manifestation (n = 35). One patient could have different manifestations of SLE; thus 35 disease manifestations were found in 20 patients. The horizontal lines give the mean sTRAIL value.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett Lynda, Palucka A. Karolina, Arce Edsel, Cantrell Victoria, Borvak Josef, Banchereau Jacques, Pascual Virginia. Interferon and granulopoiesis signatures in systemic lupus erythematosus blood. J Exp Med. 2003 Mar 17;197(6):711–723. doi: 10.1084/jem.20021553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijl M., Horst G., Limburg P. C., Kallenberg C. G. Anti-CD3-induced and anti-Fas-induced apoptosis in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Clin Exp Immunol. 2001 Jan;123(1):127–132. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01418.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijl M., Horst G., Limburg P. C., Kallenberg C. G. Fas expression on peripheral blood lymphocytes in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): relation to lymphocyte activation and disease activity. Lupus. 2001;10(12):866–872. doi: 10.1191/096120301701548517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bombardier C., Gladman D. D., Urowitz M. B., Caron D., Chang C. H. Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The Committee on Prognosis Studies in SLE. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Jun;35(6):630–640. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng J., Zhou T., Liu C., Shapiro J. P., Brauer M. J., Kiefer M. C., Barr P. J., Mountz J. D. Protection from Fas-mediated apoptosis by a soluble form of the Fas molecule. Science. 1994 Mar 25;263(5154):1759–1762. doi: 10.1126/science.7510905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Famularo G., Nucera E., Marcellini S., De Simone C. Fas/Fas ligand on the road: an apoptotic pathway common to AIDS, autoimmunity, lymphoproliferation and transplantation. Med Hypotheses. 1999 Jul;53(1):50–62. doi: 10.1054/mehy.1997.0712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith T. S., Wiley S. R., Kubin M. Z., Sedger L. M., Maliszewski C. R., Fanger N. A. Monocyte-mediated tumoricidal activity via the tumor necrosis factor-related cytokine, TRAIL. J Exp Med. 1999 Apr 19;189(8):1343–1354. doi: 10.1084/jem.189.8.1343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halaas O., Vik R., Ashkenazi A., Espevik T. Lipopolysaccharide induces expression of APO2 ligand/TRAIL in human monocytes and macrophages. Scand J Immunol. 2000 Mar;51(3):244–250. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.2000.00671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilliard B., Wilmen A., Seidel C., Liu T. S., Göke R., Chen Y. Roles of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 2001 Jan 15;166(2):1314–1319. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.2.1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang W-X, Huang M. P., Gomes M. A., Hillert J. Apoptosis mediators fasL and TRAIL are upregulated in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in MS. Neurology. 2000 Oct 10;55(7):928–934. doi: 10.1212/wnl.55.7.928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan Mariana J., Lewis Emily E., Shelden Eric A., Somers Emily, Pavlic Robert, McCune William J., Richardson Bruce C. The apoptotic ligands TRAIL, TWEAK, and Fas ligand mediate monocyte death induced by autologous lupus T cells. J Immunol. 2002 Nov 15;169(10):6020–6029. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.10.6020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley S. K., Harris L. A., Xie D., Deforge L., Totpal K., Bussiere J., Fox J. A. Preclinical studies to predict the disposition of Apo2L/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in humans: characterization of in vivo efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and safety. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001 Oct;299(1):31–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar-Sinha Chandan, Varambally Sooryanarayana, Sreekumar Arun, Chinnaiyan Arul M. Molecular cross-talk between the TRAIL and interferon signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2001 Oct 24;277(1):575–585. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M107795200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamhamedi-Cherradi Salah-Eddine, Zheng Shi-Jun, Maguschak Kimberly A., Peschon Jacques, Chen Youhai H. Defective thymocyte apoptosis and accelerated autoimmune diseases in TRAIL-/- mice. Nat Immunol. 2003 Feb 10;4(3):255–260. doi: 10.1038/ni894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc H. N., Ashkenazi A. Apo2L/TRAIL and its death and decoy receptors. Cell Death Differ. 2003 Jan;10(1):66–75. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt R. Y., Fauci A. S., Bloch D. A., Michel B. A., Hunder G. G., Arend W. P., Calabrese L. H., Fries J. F., Lie J. T., Lightfoot R. W., Jr The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of Wegener's granulomatosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Aug;33(8):1101–1107. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura R., Umemiya K., Kagami M., Tomioka H., Tanabe E., Sugiyama T., Sueishi M., Kayagaki N., Yagita H., Okumura K. Expression of TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) on infiltrating cells and of TRAIL receptors on salivary glands in patients with Sjögren's syndrome. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2002 Nov-Dec;20(6):791–798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama Wataru, Yamamoto Masuki, Higashimoto Ikkou, Oonakahara Ken-ichi, Watanabe Masaki, Machida Kentarou, Yoshimura Teizo, Eiraku Nobutaka, Kawabata Masaharu, Osame Mitsuhiro. TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand is involved in neutropenia of systemic lupus erythematosus. Blood. 2004 Mar 4;104(1):184–191. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-12-4274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mevorach D., Zhou J. L., Song X., Elkon K. B. Systemic exposure to irradiated apoptotic cells induces autoantibody production. J Exp Med. 1998 Jul 20;188(2):387–392. doi: 10.1084/jem.188.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monleón I., Martínez-Lorenzo M. J., Monteagudo L., Lasierra P., Taulés M., Iturralde M., Piñeiro A., Larrad L., Alava M. A., Naval J. Differential secretion of Fas ligand- or APO2 ligand/TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-carrying microvesicles during activation-induced death of human T cells. J Immunol. 2001 Dec 15;167(12):6736–6744. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.12.6736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata S. Fas ligand-induced apoptosis. Annu Rev Genet. 1999;33:29–55. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.33.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozawa K., Kayagaki N., Tokano Y., Yagita H., Okumura K., Hasimoto H. Soluble Fas (APO-1, CD95) and soluble Fas ligand in rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Jun;40(6):1126–1129. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren Yi, Tang Jinling, Mok M. Y., Chan Albert W. K., Wu Adrian, Lau C. S. Increased apoptotic neutrophils and macrophages and impaired macrophage phagocytic clearance of apoptotic neutrophils in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Oct;48(10):2888–2897. doi: 10.1002/art.11237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rus Violeta, Atamas Sergei P., Shustova Valentina, Luzina Irina G., Selaru Florin, Magder Laurence S., Via Charles S. Expression of cytokine- and chemokine-related genes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from lupus patients by cDNA array. Clin Immunol. 2002 Mar;102(3):283–290. doi: 10.1006/clim.2001.5182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song K., Chen Y., Göke R., Wilmen A., Seidel C., Göke A., Hilliard B., Chen Y. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is an inhibitor of autoimmune inflammation and cell cycle progression. J Exp Med. 2000 Apr 3;191(7):1095–1104. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.7.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spronk P. E., Horst G., Van Der Gun B. T., Limburg P. C., Kallenberg C. G. Anti-dsDNA production coincides with concurrent B and T cell activation during development of active disease in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Clin Exp Immunol. 1996 Jun;104(3):446–453. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1996.44754.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White Sarah, Rosen Antony. Apoptosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2003 Sep;15(5):557–562. doi: 10.1097/00002281-200309000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley S. R., Schooley K., Smolak P. J., Din W. S., Huang C. P., Nicholl J. K., Sutherland G. R., Smith T. D., Rauch C., Smith C. A. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity. 1995 Dec;3(6):673–682. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90057-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]