Abstract
Objective: To examine the effect of contrast agents on Doppler ultrasound findings in the synovial membrane in the wrist and fingers of healthy volunteers.
Material and methods: Eleven healthy subjects were included in the study (5 women and 6 men, mean age 38 years, range (20–60)). They had no clinical signs of inflammatory or degenerative joint diseases. A total of 66 joints were examined—6 joints for each subject: wrist and metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints 1–5—before contrast injection and after Levovist and SonoVue injection with a 30 minute interval.
Results: Colour Doppler activity was detected in 10/55 (18%) MCP joints before contrast injection and in 29/55 (53%) and 28/55 (51%) joints after Levovist (p<0.0001) and SonoVue injection (p = 0.0001), respectively. A significant increase in Doppler activity in the radial (p<0.05) and ulnar (p = 0.01) parts of the wrist joint was detected only after SonoVue injections. With spectral Doppler no difference was found in the resistive index (RI) in the vessels measured before as compared with those only detected after contrast injection.
Conclusion: The number of joints with colour Doppler activity in healthy volunteers was increased by the use of contrast agents. No changes in RI were detected. The value of contrast agents remains to be demonstrated in inflammatory diagnostics.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (94.4 KB).
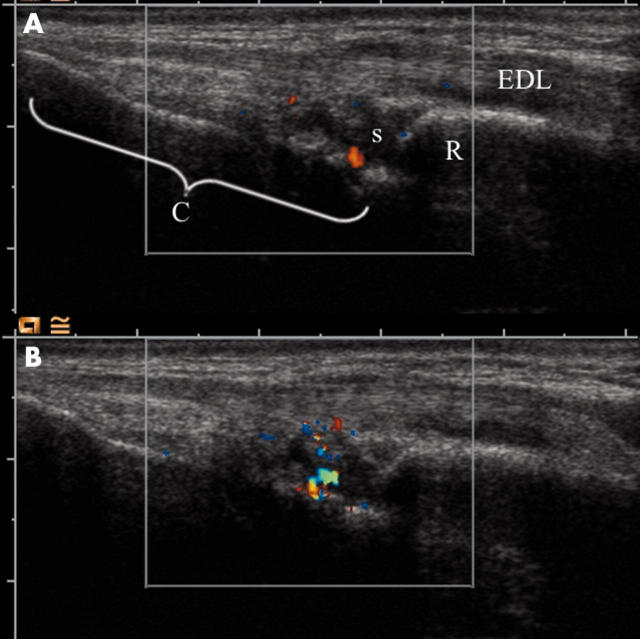
Figure 1.
Colour Doppler in the wrist before and after SonoVue injection. The images are longitudinal through the extensor digitorum longus tendon (EDL). The surface of the radius (R) and carpal bones (C) are seen as bright reflectors. The synovium of the radiocarpal joint(s) is seen as a anechoic/hypoechoic mass with extensions that are synovial duplications. (A) Before contrast injection. A single Doppler focus is visible inside the synovium. (B) After contrast injection. A larger Doppler focus is visible.
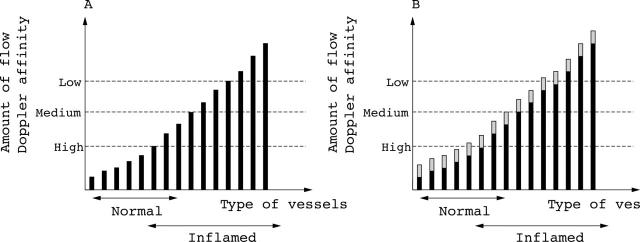
Figure 2.
Hypothetical model for the interaction between Doppler ultrasound and amount of synovial flow. (A) The synovial vessels are ranked on the x axis with increasing ability to be detected by Doppler to the right. An overlap between vessels of the normal synovium and inflamed synovium is expected. Thresholds for detection of flow for low, medium, and high sensitivity Doppler are shown with dashed lines. In this model only high sensitivity Doppler will detect flow in a normal synovium and then will detect only a few vessels. (B) After contrast injection, all vessels have an increased ability to be detected by Doppler. The bars have increased in height and some vessels have crossed the Doppler thresholds. According to the model no Doppler activity will be found in normal joints before or after contrast injection if a medium sensitivity Doppler is used. Also, if a contrast study on patients with rheumatoid arthritis does not include mildly inflamed joints, then contrast injection will not result in additional joints becoming Doppler positive.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carotti M., Salaffi F., Manganelli P., Salera D., Simonetti B., Grassi W. Power Doppler sonography in the assessment of synovial tissue of the knee joint in rheumatoid arthritis: a preliminary experience. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Oct;61(10):877–882. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.10.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hau M., Schultz H., Tony H. P., Keberle M., Jahns R., Haerten R., Jenett M. Evaluation of pannus and vascularization of the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints in rheumatoid arthritis by high-resolution ultrasound (multidimensional linear array). Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Nov;42(11):2303–2308. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199911)42:11<2303::AID-ANR7>3.0.CO;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klauser Andrea, Frauscher Ferdinand, Schirmer Michael, Halpern Ethan, Pallwein Leo, Herold Manfred, Helweg Gernot, ZurNedden Dieter. The value of contrast-enhanced color Doppler ultrasound in the detection of vascularization of finger joints in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Mar;46(3):647–653. doi: 10.1002/art.10136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magarelli N., Guglielmi G., Di Matteo L., Tartaro A., Mattei P. A., Bonomo L. Diagnostic utility of an echo-contrast agent in patients with synovitis using power Doppler ultrasound: a preliminary study with comparison to contrast-enhanced MRI. Eur Radiol. 2001;11(6):1039–1046. doi: 10.1007/s003300000650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midiri M., Iovane A., Finazzo M., Brancatelli G., Gallo C., Lagalla R. L'eco color Doppler nell'artrite reumatoide con localizzazione extra-articolare. Esperienza preliminare. Radiol Med. 1999 Sep;98(3):123–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qvistgaard E., Røgind H., Torp-Pedersen S., Terslev L., Danneskiold-Samsøe B., Bliddal H. Quantitative ultrasonography in rheumatoid arthritis: evaluation of inflammation by Doppler technique. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001 Jul;60(7):690–693. doi: 10.1136/ard.60.7.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W. A., Völker L., Zacher J., Schläfke M., Ruhnke M., Gromnica-Ihle E. Colour Doppler ultrasonography to detect pannus in knee joint synovitis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2000 Jul-Aug;18(4):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szkudlarek Marcin, Court-Payen Michel, Strandberg Charlotte, Klarlund Mette, Klausen Tom, Østergaard Mikkel. Contrast-enhanced power Doppler ultrasonography of the metacarpophalangeal joints in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur Radiol. 2002 Jul 18;13(1):163–168. doi: 10.1007/s00330-002-1459-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terslev L., Torp-Pedersen S., Qvistgaard E., Danneskiold-Samsoe B., Bliddal H. Estimation of inflammation by Doppler ultrasound: quantitative changes after intra-articular treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Nov;62(11):1049–1053. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.11.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terslev L., Torp-Pedersen S., Qvistgaard E., von der Recke P., Bliddal H. Doppler ultrasound findings in healthy wrists and finger joints. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004 Jun;63(6):644–648. doi: 10.1136/ard.2003.009548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torp-Pedersen Tobias, Torp-Pedersen Sorren, Bliddal Henning. Diagnostic value of ultrasonography in epicondylitis. Ann Intern Med. 2002 May 21;136(10):781–782. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-136-10-200205210-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther M., Harms H., Krenn V., Radke S., Faehndrich T. P., Gohlke F. Correlation of power Doppler sonography with vascularity of the synovial tissue of the knee joint in patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Feb;44(2):331–338. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200102)44:2<331::AID-ANR50>3.0.CO;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]