Abstract
Methods: 35 patients with AS with mean (SD) age 42.5 (12.6) years and mean (SD) disease duration 14.5 (8.0) years were studied for 2 years. Patients entering the study had a negative tuberculin skin test, were fully informed about the treatment, and were followed up regularly. Infliximab, 5 mg/kg weight, was given intravenously at weeks 0, 2, 6, and every 8 weeks thereafter. Data concerning infliximab tolerability, adverse events, interval, and drug discontinuation were all recorded. Clinical improvement according to the BASDAI and the Ankylosing Spondylitis Assessment Study group (ASAS) 20%, 40%, and ASAS 5/6 response criteria were recorded.
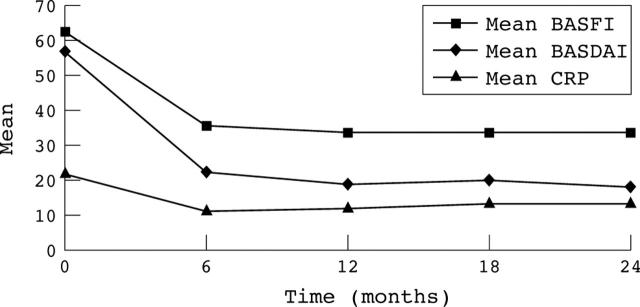
Results: After 1 year, 20 (57%) patients achieved the BASDAI 50% response criteria, 25 (71%) achieved ASAS 20%, 23 (66%) reached ASAS 40%, and 18 (51%) attained ASAS 5/6. After 2 years' treatment, 11 (31%) patients achieved BASDAI 50% response criteria, 14 (40%) ASAS 20%, 11 (31%) ASAS 40%, and 9 (26%) ASAS 5/6. Clinical improvement was associated with an improved BASFI and reduction of CRP. After 2 years' treatment, "infliximab survival" was 89%. Treatment was well tolerated and adverse events were mild; 3 patients discontinued the study.
Conclusion: Infliximab was effective, safe, and well tolerated in patients with AS.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (68.1 KB).
Figure 1.
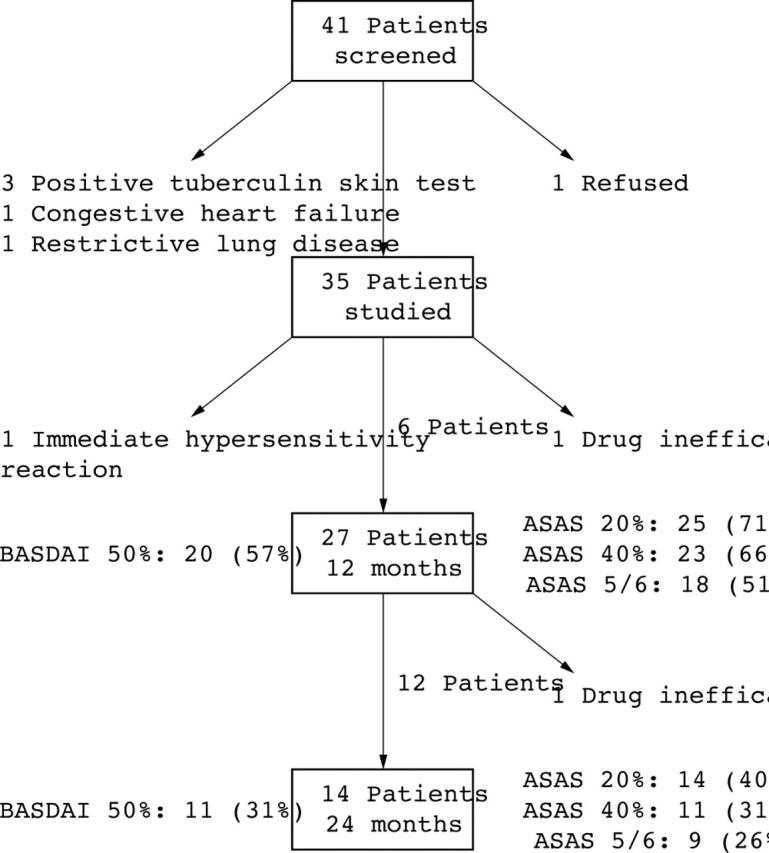
Study profile and response to treatment. The lateral arrows represent the patients who did not meet entry criteria or discontinued the study. The middle arrows represent the patients who continued infliximab treatment but were not followed up for a full 1 or 2 years. Percentages of response are calculated on the basis of 35 patients presented at entry.
Figure 2.
Improvement of the BASDAI and BASFI and reduction of CRP.