Abstract
Background: Previous work identified synovial sublining macrophage numbers as a potential biomarker for clinical efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis.
Objective: To investigate the association between changes in infiltration of synovial macrophages and clinical improvement after antirheumatic treatment.
Methods: 88 patients who participated in various clinical trials were studied. All patients underwent serial arthroscopy before initiation of treatment and after different time intervals. Immunohistochemical and digital image analysis were performed according to standardised procedures to detect changes in CD68+ synovial sublining macrophages in relationship to changes in the 28 joint count Disease Activity Score (DAS28). Statistical analysis was performed using one way analysis of variance, the independent samples t test, linear regression, and the standardised response mean (SRM).
Results: For good, moderate, and non-responders, according to the DAS28 response criteria, there was a significant difference in the change in sublining macrophages (mean (SEM) cells/mm2 –643 (124), –270 (64), and –95 (60), respectively; p<0.0003). There was a significant correlation between the change in the number of macrophages and the change in DAS28 (Pearson correlation 0.874, p<0.01). The change in sublining macrophages explained 76% of the variation in the change in DAS28 (p<0.02). The sensitivity to change of the biomarker was high in patients treated actively (SRM >0.8), whereas the ability to detect changes in placebo treated patients was weak (SRM <0.3).
Conclusion: The results suggest that changes in synovial sublining macrophages can be used to predict possible efficacy of antirheumatic treatment.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (79.8 KB).
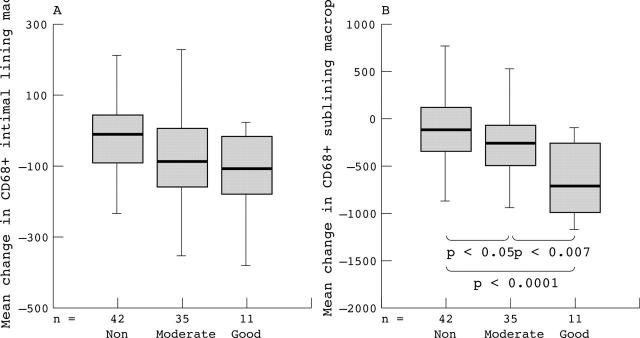
Figure 1.
Mean values of the change compared with baseline in (A) the number of CD68+ macrophages in the intimal lining layer and (B) the synovial sublining for, respectively, non-responders, moderate responders, and good responders according to the DAS28 response criteria in the total study group.
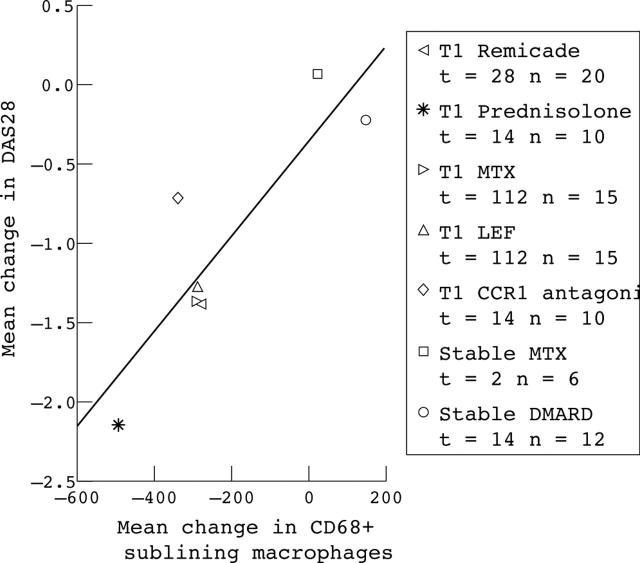
Figure 2.
Correlation between the mean change for each substudy in the number of CD68+ sublining macrophages and the mean change in DAS28 (p<0.01, Pearson correlation 0.874, weighted linear regression p<0.02, R2 = 0.755, 95% confidence interval (95% CI) 0.001 to 0.005). t, interval between the first and second measurement, n, number of patients; TI, treatment initiation.
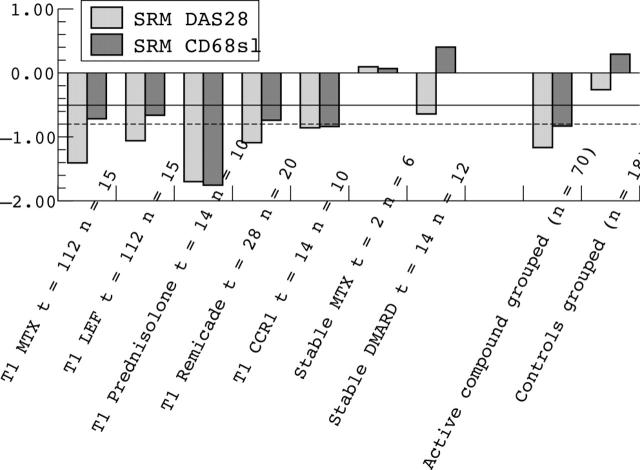
Figure 3.
Standardised response mean (SRM) of the change in DAS28 (SRM DAS28) and the number of CD68+ macrophages in the sublining (SRM CD68sl) for the individual studies (t, interval between the first and second measurement; n, number of patients, TI, treatment initiation) and grouped for patients who received initiation of an active compound (n = 70) and placebo (n = 18). The solid line indicates the 0.5 SRM cut off point (moderate), the dotted line indicates the 0.8 SRM cut off point (high).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boers M., Verhoeven A. C., Markusse H. M., van de Laar M. A., Westhovens R., van Denderen J. C., van Zeben D., Dijkmans B. A., Peeters A. J., Jacobs P. Randomised comparison of combined step-down prednisolone, methotrexate and sulphasalazine with sulphasalazine alone in early rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1997 Aug 2;350(9074):309–318. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(97)01300-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnihan B., Tak P. P., Emery P., Klareskog L., Breedveld F. Synovial biopsy in arthritis research: five years of concerted European collaboration. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Jul;59(7):506–511. doi: 10.1136/ard.59.7.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choy E. H. S., Isenberg D. A., Garrood T., Farrow S., Ioannou Y., Bird H., Cheung N., Williams B., Hazleman B., Price R. Therapeutic benefit of blocking interleukin-6 activity with an anti-interleukin-6 receptor monoclonal antibody in rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Dec;46(12):3143–3150. doi: 10.1002/art.10623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunnane G., Madigan A., Murphy E., FitzGerald O., Bresnihan B. The effects of treatment with interleukin-1 receptor antagonist on the inflamed synovial membrane in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2001 Jan;40(1):62–69. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/40.1.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer Jean-Michel, Bresnihan Barry. Targeting interleukin-1 in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Mar;46(3):574–578. doi: 10.1002/art.10168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolhain R. J., Tak P. P., Dijkmans B. A., De Kuiper P., Breedveld F. C., Miltenburg A. M. Methotrexate reduces inflammatory cell numbers, expression of monokines and of adhesion molecules in synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1998 May;37(5):502–508. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/37.5.502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein W. V. Expectation bias in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials. The anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody experience. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Nov;39(11):1773–1780. doi: 10.1002/art.1780391102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann M., Maini R. N. Anti-TNF alpha therapy of rheumatoid arthritis: what have we learned? Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:163–196. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestein Gary S. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003 May 15;423(6937):356–361. doi: 10.1038/nature01661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlag Danielle M., Haringman Jasper J., Smeets Tom J. M., Zwinderman A. H., Kraan Maarten C., Laud Peter J., Morgan Shethah, Nash Anthony F. P., Tak Paul P. Effects of oral prednisolone on biomarkers in synovial tissue and clinical improvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004 Dec;50(12):3783–3791. doi: 10.1002/art.20664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haringman J. J., Kraan M. C., Smeets T. J. M., Zwinderman K. H., Tak P. P. Chemokine blockade and chronic inflammatory disease: proof of concept in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Aug;62(8):715–721. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.8.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazis L. E., Anderson J. J., Meenan R. F. Effect sizes for interpreting changes in health status. Med Care. 1989 Mar;27(3 Suppl):S178–S189. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198903001-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinne R. W., Bräuer R., Stuhlmüller B., Palombo-Kinne E., Burmester G. R. Macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. 2000 Apr 12;2(3):189–202. doi: 10.1186/ar86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraan M. C., Haringman J. J., Ahern M. J., Breedveld F. C., Smith M. D., Tak P. P. Quantification of the cell infiltrate in synovial tissue by digital image analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2000 Jan;39(1):43–49. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/39.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraan M. C., Reece R. J., Barg E. C., Smeets T. J., Farnell J., Rosenburg R., Veale D. J., Breedveld F. C., Emery P., Tak P. P. Modulation of inflammation and metalloproteinase expression in synovial tissue by leflunomide and methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Findings in a prospective, randomized, double-blind, parallel-design clinical trial in thirty-nine patients at two centers. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Aug;43(8):1820–1830. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200008)43:8<1820::AID-ANR18>3.0.CO;2-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraan M. C., Versendaal H., Jonker M., Bresnihan B., Post W. J., t Hart B. A., Breedveld F. C., Tak P. P. Asymptomatic synovitis precedes clinically manifest arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Aug;41(8):1481–1488. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199808)41:8<1481::AID-ART19>3.0.CO;2-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulherin D., Fitzgerald O., Bresnihan B. Synovial tissue macrophage populations and articular damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Jan;39(1):115–124. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettit A. R., Weedon H., Ahern M., Zehntner S., Frazer I. H., Slavotinek J., Au V., Smith M. D., Thomas R. Association of clinical, radiological and synovial immunopathological responses to anti-rheumatic treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2001 Nov;40(11):1243–1255. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/40.11.1243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeets T. J. M., Barg E. C., Kraan M. C., Smith M. D., Breedveld F. C., Tak P. P. Analysis of the cell infiltrate and expression of proinflammatory cytokines and matrix metalloproteinases in arthroscopic synovial biopsies: comparison with synovial samples from patients with end stage, destructive rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Jul;62(7):635–638. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.7.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeets T. J., Kraan M. C., Versendaal J., Breedveld F. C., Tak P. P. Analysis of serial synovial biopsies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: description of a control group without clinical improvement after treatment with interleukin 10 or placebo. J Rheumatol. 1999 Oct;26(10):2089–2093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeets Tom J. M., Kraan Maarten C., van Loon Marieke E., Tak Paul-Peter. Tumor necrosis factor alpha blockade reduces the synovial cell infiltrate early after initiation of treatment, but apparently not by induction of apoptosis in synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Aug;48(8):2155–2162. doi: 10.1002/art.11098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. D., Kraan M. C., Slavotinek J., Au V., Weedon H., Parker A., Coleman M., Roberts-Thomson P. J., Ahern M. J. Treatment-induced remission in rheumatoid arthritis patients is characterized by a reduction in macrophage content of synovial biopsies. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2001 Apr;40(4):367–374. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/40.4.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tak P. P., Smeets T. J., Daha M. R., Kluin P. M., Meijers K. A., Brand R., Meinders A. E., Breedveld F. C. Analysis of the synovial cell infiltrate in early rheumatoid synovial tissue in relation to local disease activity. Arthritis Rheum. 1997 Feb;40(2):217–225. doi: 10.1002/art.1780400206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tak P. P., van der Lubbe P. A., Cauli A., Daha M. R., Smeets T. J., Kluin P. M., Meinders A. E., Yanni G., Panayi G. S., Breedveld F. C. Reduction of synovial inflammation after anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody treatment in early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Oct;38(10):1457–1465. doi: 10.1002/art.1780381012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. C., Peters A. M., Paleolog E., Chapman P. T., Elliott M. J., McCloskey R., Feldmann M., Maini R. N. Reduction of chemokine levels and leukocyte traffic to joints by tumor necrosis factor alpha blockade in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Jan;43(1):38–47. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200001)43:1<38::AID-ANR6>3.0.CO;2-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vervoordeldonk Margriet J. B. M., Tak Paul P. Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2002 Jun;4(3):208–217. doi: 10.1007/s11926-002-0067-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanni G., Nabil M., Farahat M. R., Poston R. N., Panayi G. S. Intramuscular gold decreases cytokine expression and macrophage numbers in the rheumatoid synovial membrane. Ann Rheum Dis. 1994 May;53(5):315–322. doi: 10.1136/ard.53.5.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Riel P. L., van Gestel A. M., van de Putte L. B. Development and validation of response criteria in rheumatoid arthritis: steps towards an international consensus on prognostic markers. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Sep;35 (Suppl 2):4–7. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.suppl_2.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]