Abstract
Objectives: To determine the changes in body weight, body composition, and bone turnover in patients with spondyloarthropathy (SpA) treated with anti-tumour necrosis factor α (TNFα).
Patients and methods: 19 patients with SpA (2 women, 17 men), aged 21–71 years, were studied in a 1 year prospective open study. 17 patients received infliximab: 3 or 5 mg/kg/infusion at weeks 0, 2, 6 and infusions in the case of a relapse (n = 14) or systematically (n = 3); 2 patients received etanercept (25 mg twice a week). Body weight, body composition (lean mass, fat mass), and bone mineral density (BMD; using dual energy x ray absorptiometry) were measured at baseline and at months 6 and 12. Serum insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), bone markers (carboxy terminal telopeptide of collagen I (CTX) and procollagen type I N terminal propeptide (PINP)) were measured at baseline and months 3, 6, and 12.
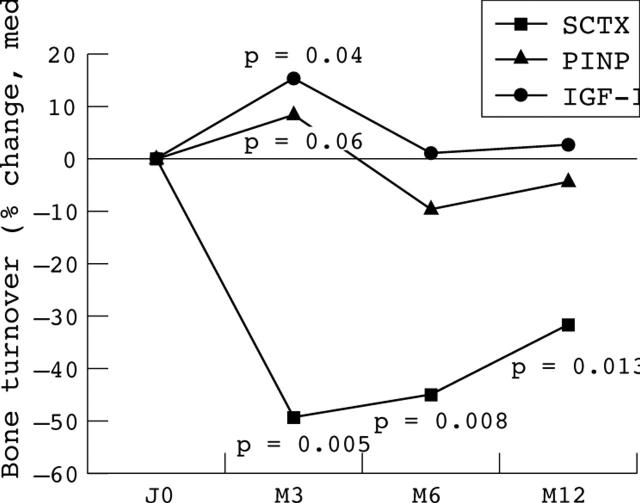
Results: In 1 year there was a significant increase in body weight (mean (SD) 2.24 (3.1) kg, p = 0.0004), and in lean mass (1.4 (1.69) kg, p = 0.005), but no changes in fat mass. BMD increased at the spine (5.6%, p = 0.0005) and total femur (2.6%, p = 0.01). CTX decreased from the third month (–50%, p = 0.005) up to 1 year (–30%, p = 0.012), and a trend for an increase in PINP (10%, p = 0.06) and in IGF-I (15%, p = 0.04) was seen at month 3.
Conclusion: These data confirm that treatment with anti-TNFα in SpA is associated with an increase of BMD, which results from a decrease of bone resorption. Increase in body weight and lean mass is observed in parallel with an increase in IGF-1.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (75.7 KB).
Figure 1.
Effect of anti-TNF on bone turnover and IGF-I in 15 patients with SpA.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allali F., Breban M., Porcher R., Maillefert J. F., Dougados M., Roux C. Increase in bone mineral density of patients with spondyloarthropathy treated with anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Apr;62(4):347–349. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.4.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aloia J. F., Vaswani A., Ma R., Flaster E. To what extent is bone mass determined by fat-free or fat mass? Am J Clin Nutr. 1995 May;61(5):1110–1114. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/61.4.1110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreassen T. T., Oxlund H. Local anabolic effects of growth hormone on intact bone and healing fractures in rats. Calcif Tissue Int. 2003 Sep;73(3):258–264. doi: 10.1007/s00223-002-2074-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouillon R. Growth hormone and bone. Horm Res. 1991;36 (Suppl 1):49–55. doi: 10.1159/000182189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppack S. W. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and adipose tissue. Proc Nutr Soc. 2001 Aug;60(3):349–356. doi: 10.1079/pns2001110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costelli P., Carbó N., Tessitore L., Bagby G. J., Lopez-Soriano F. J., Argilés J. M., Baccino F. M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediates changes in tissue protein turnover in a rat cancer cachexia model. J Clin Invest. 1993 Dec;92(6):2783–2789. doi: 10.1172/JCI116897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewys W. D., Begg C., Lavin P. T., Band P. R., Bennett J. M., Bertino J. R., Cohen M. H., Douglass H. O., Jr, Engstrom P. F., Ezdinli E. Z. Prognostic effect of weight loss prior to chemotherapy in cancer patients. Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am J Med. 1980 Oct;69(4):491–497. doi: 10.1016/s0149-2918(05)80001-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein S. L., Barrett-Connor E. Relation between body size and bone mineral density in elderly men and women. Am J Epidemiol. 1993 Aug 1;138(3):160–169. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El Maghraoui A., Borderie D., Cherruau B., Edouard R., Dougados M., Roux C. Osteoporosis, body composition, and bone turnover in ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol. 1999 Oct;26(10):2205–2209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnero P., Tsouderos Y., Marton I., Pelissier C., Varin C., Delmas P. D. Effects of intranasal 17beta-estradiol on bone turnover and serum insulin-like growth factor I in postmenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999 Jul;84(7):2390–2397. doi: 10.1210/jcem.84.7.5848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen M. D., Kanaley J. A., Roust L. R., O'Brien P. C., Braun J. S., Dunn W. L., Wahner H. W. Assessment of body composition with use of dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry: evaluation and comparison with other methods. Mayo Clin Proc. 1993 Sep;68(9):867–873. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)60695-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotler D. P., Wang J., Pierson R. N. Body composition studies in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am J Clin Nutr. 1985 Dec;42(6):1255–1265. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/42.6.1255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzo-Ortega H., McGonagle D., Haugeberg G., Green M. J., Stewart S. P., Emery P. Bone mineral density improvement in spondyloarthropathy after treatment with etanercept. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Oct;62(10):1020–1021. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.10.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro R., Capell H. Prevalence of low body mass in rheumatoid arthritis: association with the acute phase response. Ann Rheum Dis. 1997 May;56(5):326–329. doi: 10.1136/ard.56.5.326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quartier Pierre, Taupin Pierre, Bourdeaut Franck, Lemelle Irène, Pillet Pascal, Bost Michel, Sibilia Jean, Koné-Paut Isabelle, Gandon-Laloum Sylvie, LeBideau Marc. Efficacy of etanercept for the treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis according to the onset type. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Apr;48(4):1093–1101. doi: 10.1002/art.10885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall L. C., Rosen C. J., Dolnikowski G., Hartman W. J., Lundgren N., Abad L. W., Dinarello C. A., Roubenoff R. Protein metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis and aging. Effects of muscle strength training and tumor necrosis factor alpha. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Jul;39(7):1115–1124. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall L. C., Roubenoff R. Body composition, metabolism, and resistance exercise in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 1996 Apr;9(2):151–156. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199604)9:2<151::aid-anr1790090212>3.0.co;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravn P., Cizza G., Bjarnason N. H., Thompson D., Daley M., Wasnich R. D., McClung M., Hosking D., Yates A. J., Christiansen C. Low body mass index is an important risk factor for low bone mass and increased bone loss in early postmenopausal women. Early Postmenopausal Intervention Cohort (EPIC) study group. J Bone Miner Res. 1999 Sep;14(9):1622–1627. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.1999.14.9.1622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubenoff R., Rall L. C. Humoral mediation of changing body composition during aging and chronic inflammation. Nutr Rev. 1993 Jan;51(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1993.tb03045.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubenoff R., Roubenoff R. A., Cannon J. G., Kehayias J. J., Zhuang H., Dawson-Hughes B., Dinarello C. A., Rosenberg I. H. Rheumatoid cachexia: cytokine-driven hypermetabolism accompanying reduced body cell mass in chronic inflammation. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jun;93(6):2379–2386. doi: 10.1172/JCI117244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubenoff R., Roubenoff R. A., Ward L. M., Holland S. M., Hellmann D. B. Rheumatoid cachexia: depletion of lean body mass in rheumatoid arthritis. Possible association with tumor necrosis factor. J Rheumatol. 1992 Oct;19(10):1505–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svendsen O. L., Haarbo J., Hassager C., Christiansen C. Accuracy of measurements of body composition by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry in vivo. Am J Clin Nutr. 1993 May;57(5):605–608. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/57.5.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toussirot E., Michel F., Wendling D. Bone density, ultrasound measurements and body composition in early ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2001 Aug;40(8):882–888. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/40.8.882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vis M., Wolbink G. J., Lodder M. C., Kostense P. J., van de Stadt R. J., de Koning M. H. M. T., Dijkmans B. A. C., Lems W. F. Early changes in bone metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with infliximab. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Oct;48(10):2996–2997. doi: 10.1002/art.11292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhovens R., Nijs J., Taelman V., Dequeker J. Body composition in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1997 Apr;36(4):444–448. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/36.4.444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhouse L. J., Asa S. L., Thomas S. G., Ezzat S. Measures of submaximal aerobic performance evaluate and predict functional response to growth hormone (GH) treatment in GH-deficient adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999 Dec;84(12):4570–4577. doi: 10.1210/jcem.84.12.6196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D., Hopper J. L., Nowson C. A., Green R. M., Sherwin A. J., Kaymakci B., Smid M., Guest C. S., Larkins R. G., Wark J. D. Determinants of bone mass in 10- to 26-year-old females: a twin study. J Bone Miner Res. 1995 Apr;10(4):558–567. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650100408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamir O., Hasselgren P. O., Kunkel S. L., Frederick J., Higashiguchi T., Fischer J. E. Evidence that tumor necrosis factor participates in the regulation of muscle proteolysis during sepsis. Arch Surg. 1992 Feb;127(2):170–174. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1992.01420020052008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamir O., Hasselgren P. O., O'Brien W., Thompson R. C., Fischer J. E. Muscle protein breakdown during endotoxemia in rats and after treatment with interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra). Ann Surg. 1992 Sep;216(3):381–387. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199209000-00018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]