Abstract
Objective: To investigate whether polymorphism in the transforming growth factor ß1 (TGFß1) gene is associated with disease outcome in rheumatoid arthritis.
Methods: 208 patients with established rheumatoid arthritis were genotyped for the TGFß1 T869C polymorphism using an amplification refractory mutation system–polymerase chain reaction (ARMS-PCR) method. Disease severity was assessed by measuring radiographic damage by Larsen score and functional outcome by the health assessment questionnaire (HAQ). Patients were tracked on the NHS central register for notification of death, and the relation between TGFß1 polymorphism and mortality was analysed using Cox proportional hazards regression.
Results: Patients carrying a TGFß1 T allele had a higher mean HAQ score than those without this allele (1.60 v 1.22, p = 0.04). The T allele was also associated with higher five year mean area under the curve (MAUC) erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and nodular disease. Larsen score was higher in patients with the TT genotype compared with CC + CT genotypes, although this was not significant after correction for disease duration. There was a trend of increasing mortality risk with T allele dose after adjustment for age, sex, and disease duration (hazard ratio = 1.6 (95% confidence interval, 1.1 to 2.4), p = 0.01).
Conclusions: TGFß1 T869C gene polymorphism is associated with disease outcome in rheumatoid arthritis. Carriage of the T allele (putatively associated with decreased TGFß1 production) was associated with increased inflammatory activity and poor functional outcome, while increasing T allele dose was associated with worse survival.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (83.9 KB).
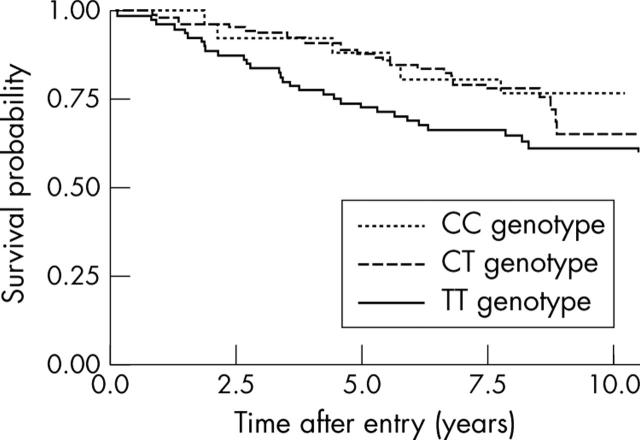
Figure 1.
Kaplan–Meier survival probability curve illustrating the poorer survival of individuals with the TGFß1 TT genotype compared with those carrying CC or CT genotypes.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arkwright P. D., Laurie S., Super M., Pravica V., Schwarz M. J., Webb A. K., Hutchinson I. V. TGF-beta(1) genotype and accelerated decline in lung function of patients with cystic fibrosis. Thorax. 2000 Jun;55(6):459–462. doi: 10.1136/thorax.55.6.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baugh J. A., Chitnis S., Donnelly S. C., Monteiro J., Lin X., Plant B. J., Wolfe F., Gregersen P. K., Bucala R. A functional promoter polymorphism in the macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) gene associated with disease severity in rheumatoid arthritis. Genes Immun. 2002 May;3(3):170–176. doi: 10.1038/sj.gene.6363867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobe G. C., Schiemann W. P., Lodish H. F. Role of transforming growth factor beta in human disease. N Engl J Med. 2000 May 4;342(18):1350–1358. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200005043421807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan F. M., Chantry D., Turner M., Foxwell B., Maini R., Feldmann M. Detection of transforming growth factor-beta in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue: lack of effect on spontaneous cytokine production in joint cell cultures. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Aug;81(2):278–285. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb03331.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun Johan G., Madland Tor M., Vedeler Christian A. Immunoglobulin G fc-receptor (FcgammaR) IIA, IIIA, and IIIB polymorphisms related to disease severity in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2002 Jun;29(6):1135–1140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchs N., di Giovine F. S., Silvestri T., Vannier E., Duff G. W., Miossec P. IL-1B and IL-1Ra gene polymorphisms and disease severity in rheumatoid arthritis: interaction with their plasma levels. Genes Immun. 2001 Jun;2(4):222–228. doi: 10.1038/sj.gene.6363766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantagrel A., Navaux F., Loubet-Lescoulié P., Nourhashemi F., Enault G., Abbal M., Constantin A., Laroche M., Mazières B. Interleukin-1beta, interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, interleukin-4, and interleukin-10 gene polymorphisms: relationship to occurrence and severity of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Jun;42(6):1093–1100. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199906)42:6<1093::AID-ANR5>3.0.CO;2-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chehata J. C., Hassell A. B., Clarke S. A., Mattey D. L., Jones M. A., Jones P. W., Dawes P. T. Mortality in rheumatoid arthritis: relationship to single and composite measures of disease activity. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2001 Apr;40(4):447–452. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/40.4.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantin Arnaud, Lauwers-Cancès Valérie, Navaux Frédérique, Abbal Michel, van Meerwijk Joost, Mazières Bernard, Cambon-Thomsen Anne, Cantagrel Alain. Stromelysin 1 (matrix metalloproteinase 3) and HLA-DRB1 gene polymorphisms: Association with severity and progression of rheumatoid arthritis in a prospective study. Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Jul;46(7):1754–1762. doi: 10.1002/art.10336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crilly A., Hamilton J., Clark C. J., Jardine A., Madhok R. Analysis of transforming growth factor beta1 gene polymorphisms in patients with systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Aug;61(8):678–681. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.8.678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick I. M., Devine A., Li S., Dhaliwal S. S., Prince R. L. The T869C TGF beta polymorphism is associated with fracture, bone mineral density, and calcaneal quantitative ultrasound in elderly women. Bone. 2003 Sep;33(3):335–341. doi: 10.1016/s8756-3282(03)00158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunning Alison M., Ellis Peter D., McBride Simon, Kirschenlohr Heidi L., Healey Catherine S., Kemp Paul R., Luben Robert N., Chang-Claude Jenny, Mannermaa Arto, Kataja Vesa. A transforming growth factorbeta1 signal peptide variant increases secretion in vitro and is associated with increased incidence of invasive breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2003 May 15;63(10):2610–2615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fava R., Olsen N., Keski-Oja J., Moses H., Pincus T. Active and latent forms of transforming growth factor beta activity in synovial effusions. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):291–296. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries J. F., Spitz P., Kraines R. G., Holman H. R. Measurement of patient outcome in arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Feb;23(2):137–145. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grainger D. J., Heathcote K., Chiano M., Snieder H., Kemp P. R., Metcalfe J. C., Carter N. D., Spector T. D. Genetic control of the circulating concentration of transforming growth factor type beta1. Hum Mol Genet. 1999 Jan;8(1):93–97. doi: 10.1093/hmg/8.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen P. K., Silver J., Winchester R. J. The shared epitope hypothesis. An approach to understanding the molecular genetics of susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Nov;30(11):1205–1213. doi: 10.1002/art.1780301102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassell A. B., Davis M. J., Fowler P. D., Clarke S., Fisher J., Shadforth M. F., Jones P. W., Dawes P. T. The relationship between serial measures of disease activity and outcome in rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med. 1993 Sep;86(9):601–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinke V., Seck T., Clanget C., Scheidt-Nave C., Ziegler R., Pfeilschifter J. Association of transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGFbeta1) T29 --> C gene polymorphism with bone mineral density (BMD), changes in BMD, and serum concentrations of TGF-beta1 in a population-based sample of postmenopausal german women. Calcif Tissue Int. 2001 Dec;69(6):315–320. doi: 10.1007/s002230020024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hishida Asahi, Iwata Hiroji, Hamajima Nobuyuki, Matsuo Keitaro, Mizutani Mitsuhiro, Iwase Takuji, Miura Shigeto, Emi Nobuhiko, Hirose Kaoru, Tajima Kazuo. Transforming growth factor B1 T29C polymorphism and breast cancer risk in Japanese women. Breast Cancer. 2003;10(1):63–69. doi: 10.1007/BF02967627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaijzel E. L., van Dongen H., Bakker A. M., Breedveld F. C., Huizinga T. W. J., Verweij C. L. Relationship of polymorphisms of the Interleukin-1 gene cluster to occurrence and severity of rheumatoid arthritis. Tissue Antigens. 2002 Feb;59(2):122–126. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0039.2002.590208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Yoon Jun, Lee Hyo-Suk, Im Jong Pil, Min Byung-Hoon, Kim Hyun-Dae, Jeong Ji Bong, Yoon Jung-Hwan, Kim Chung Yong, Kim Myung Soo, Kim Jun Yeon. Association of transforming growth factor-beta1 gene polymorphisms with a hepatocellular carcinoma risk in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Exp Mol Med. 2003 Jun 30;35(3):196–202. doi: 10.1038/emm.2003.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krippl Peter, Langsenlehner Uwe, Renner Wilfried, Yazdani-Biuki Babak, Wolf Gerald, Wascher Thomas C., Paulweber Bernhard, Bahadori Babak, Samonigg Hellmut. The L10P polymorphism of the transforming growth factor-beta 1 gene is not associated with breast cancer risk. Cancer Lett. 2003 Nov 25;201(2):181–184. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(03)00468-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Dale K., Eek M. Radiographic evaluation of rheumatoid arthritis and related conditions by standard reference films. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1977 Jul;18(4):481–491. doi: 10.1177/028418517701800415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Edith Ming Chu, Wong Samuel Yeung Shan, Li Martin, Ma Chun Hung, Lim Pak Leong, Woo Jean. Osteoporosis and transforming growth factor-beta-1 gene polymorphism in Chinese men and women. J Bone Miner Metab. 2004;22(2):148–152. doi: 10.1007/s00774-003-0463-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Marchand Loïc, Haiman Christopher A., van den Berg David, Wilkens Lynne R., Kolonel Laurence N., Henderson Brian E. T29C polymorphism in the transforming growth factor beta1 gene and postmenopausal breast cancer risk: the Multiethnic Cohort Study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004 Mar;13(3):412–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Zhenhua, Habuchi Tomonori, Tsuchiya Norihiko, Mitsumori Kenji, Wang Lizhong, Ohyama Chikara, Sato Kazunari, Kamoto Toshiyuki, Ogawa Osamu, Kato Tetsuro. Increased risk of prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia associated with transforming growth factor-beta 1 gene polymorphism at codon10. Carcinogenesis. 2003 Nov 6;25(2):237–240. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgg197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattey D. L., Hassell A. B., Dawes P. T., Jones P. W., Yengi L., Alldersea J., Strange R. C., Fryer A. A. Influence of polymorphism in the manganese superoxide dismutase locus on disease outcome in rheumatoid arthritis: evidence for interaction with glutathione S-transferase genes. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Apr;43(4):859–864. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200004)43:4<859::AID-ANR17>3.0.CO;2-Y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrey C., Turner S. J., Pravica V., Howell W. M., Hutchinson I. V. ARMS-PCR methodologies to determine IL-10, TNF-alpha, TNF-beta and TGF-beta 1 gene polymorphisms. Transpl Immunol. 1999 Jun;7(2):127–128. doi: 10.1016/s0966-3274(99)80030-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant M. J., Williams A. L., O'Sullivan M. M., Lewis P. A., Coles E. C., Jessop J. D. Relationship between time-integrated C-reactive protein levels and radiologic progression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Jul;43(7):1473–1477. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200007)43:7<1473::AID-ANR9>3.0.CO;2-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pokorny V., Chau J., Wu L., Yeoman S., Black P., McQueen F., McLean L. Transforming growth factor beta 1 gene (HSTGFB1) nucleotide T869C (codon 10) polymorphism is not associated with prevalence or severity of rheumatoid arthritis in a Caucasian population. Ann Rheum Dis. 2003 Sep;62(9):907–908. doi: 10.1136/ard.62.9.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez M. R., González-Escribano M. F., Aguilar F., Valenzuela A., García A., Núez-Roldán A. Association of NRAMP1 promoter gene polymorphism with the susceptibility and radiological severity of rheumatoid arthritis. Tissue Antigens. 2002 Apr;59(4):311–315. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0039.2002.590410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shu Xiao-Ou, Gao Yu-Tang, Cai Qiuyin, Pierce Larry, Cai Hui, Ruan Zhi-Xian, Yang Gong, Jin Fan, Zheng Wei. Genetic polymorphisms in the TGF-beta 1 gene and breast cancer survival: a report from the Shanghai Breast Cancer Study. Cancer Res. 2004 Feb 1;64(3):836–839. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-3492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman Eric S., Palmer Lyle J., Subramaniam Venkat, Hallock Arlene, Mathew Sheeba, Vallone Joseph, Faffe Debora S., Shikanai Toshiki, Raby Benjamin A., Weiss Scott T. Transforming growth factor-beta1 promoter polymorphism C-509T is associated with asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003 Nov 3;169(2):214–219. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200307-973OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura Y., Niimi T., Sato S., Yoshinouchi T., Banno S., Naniwa T., Maeda H., Shimizu S., Ueda R. Transforming growth factor beta1 gene polymorphism in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002 Sep;61(9):826–828. doi: 10.1136/ard.61.9.826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taketazu F., Kato M., Gobl A., Ichijo H., ten Dijke P., Itoh J., Kyogoku M., Rönnelid J., Miyazono K., Heldin C. H. Enhanced expression of transforming growth factor-beta s and transforming growth factor-beta type II receptor in the synovial tissues of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Lab Invest. 1994 May;70(5):620–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong Teresa Yuk Hwa, Poon Peter, Chow Kai Ming, Szeto Cheuk Chun, Cheung Man Kuen, Li Philip Kam Tao. Association of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) T869C (Leu 10Pro) gene polymorphisms with type 2 diabetic nephropathy in Chinese. Kidney Int. 2003 May;63(5):1831–1835. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L., Chau J., Young R. P., Pokorny V., Mills G. D., Hopkins R., McLean L., Black P. N. Transforming growth factor-beta1 genotype and susceptibility to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax. 2004 Feb;59(2):126–129. doi: 10.1136/thorax.2003.005769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Miyauchi A., Goto J., Takagi Y., Okuizumi H., Kanematsu M., Hase M., Takai H., Harada A., Ikeda K. Association of a polymorphism of the transforming growth factor-beta1 gene with genetic susceptibility to osteoporosis in postmenopausal Japanese women. J Bone Miner Res. 1998 Oct;13(10):1569–1576. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.1998.13.10.1569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota M., Ichihara S., Lin T. L., Nakashima N., Yamada Y. Association of a T29-->C polymorphism of the transforming growth factor-beta1 gene with genetic susceptibility to myocardial infarction in Japanese. Circulation. 2000 Jun 20;101(24):2783–2787. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.101.24.2783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapico I., Coto E., Rodríguez A., Alvarez C., Torre J. C., Alvarez V. A DNA polymorphism at the alpha2-macroglobulin gene is associated with the severity of rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2000 Oct;27(10):2308–2311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapico I., Coto E., Rodríguez A., Alvarez C., Torre J. C., Alvarez V. CCR5 (chemokine receptor-5) DNA-polymorphism influences the severity of rheumatoid arthritis. Genes Immun. 2000;1(4):288–289. doi: 10.1038/sj.gene.6363673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziv E., Cauley J., Morin P. A., Saiz R., Browner W. S. Association between the T29-->C polymorphism in the transforming growth factor beta1 gene and breast cancer among elderly white women: The Study of Osteoporotic Fractures. JAMA. 2001 Jun 13;285(22):2859–2863. doi: 10.1001/jama.285.22.2859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziv Elad, Kahn Arnold, Cauley Jane, Morin Phillip, Saiz Robert, Browner Warren. No association between the TGF-beta 1 Leu10Pro polymorphism and osteoporosis among white women in the United States. Am J Med. 2003 Feb 15;114(3):227–231. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(02)01393-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Krugten M. V., Huizinga T. W., Kaijzel E. L., Zanelli E., Drossaers-Bakker K. W., van de Linde P., Hazes J. M., Zwinderman A. H., Breedveld F. C., Verweij C. L. Association of the TNF +489 polymorphism with susceptibility and radiographic damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Genes Immun. 1999 Nov;1(2):91–96. doi: 10.1038/sj.gene.6363632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]