Abstract
Objectives: To compare the performance of two different MRI sequences—T1 weighted, fat saturated, spin echo after application of contrast medium, and short τ inversion recovery (STIR) sequences—to detect spinal inflammation in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS).
Methods: Both MRI sequences were performed in 38 patients with active AS and compared using the MRI activity scoring system, ASspiMRI-a. One vertebral unit (VU) was defined as the region between two virtual lines drawn through the middle of each vertebral body.
Results: Intraclass correlation coefficients were excellent—0.91 and 0.86 for the Gd-DTPA and STIR sequences, respectively. The overall correlation of the single MRI scores for both sequences was also good (r = 0.84, p = 0.01). The intrarater variance was 6.71 and 9.41 and the interrater variance was 13.16 and 19.04 for the Gd-DTPA and STIR sequences, respectively. The smallest detectable distance was 4.7 and 5.6 for the Gd-DTPA and STIR sequences, respectively. The concordance rate for both sequences was 83.5% (range 80.5–87.7% in the three spinal segments). Inflammatory spinal lesions were found in 10.1% of the VUs in the STIR sequence but not in the T1/Gd-DTPA sequence, while the T1/Gd-DTPA sequence showed inflammatory lesions in 6.4% of the VUs that were found normal by STIR.
Conclusions: Both MRI techniques can evaluate active spinal lesions in patients with AS. More spinal lesions are detected by the STIR sequence, but the reliability between readings and readers is better for the Gd-DTPA sequence. The ASspiMRI-a is a reliable instrument for evaluating acute spinal changes in AS.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (98.1 KB).
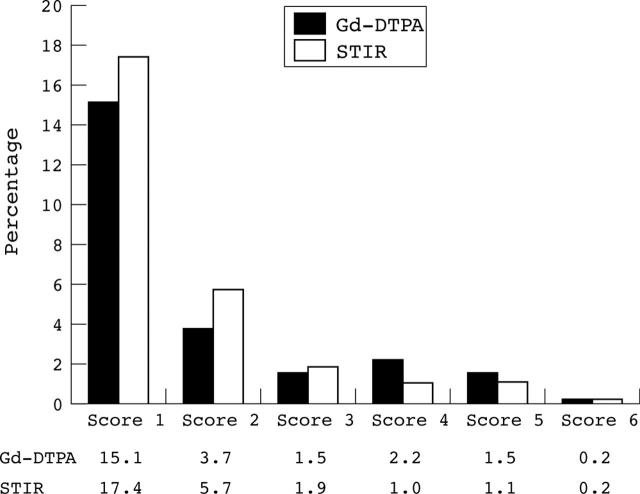
Figure 1.
Distribution of the percentage of the six positive MRI scores of the ASspiMRI-a on the basis of all VUs assessed in the whole spine for both sequences. The data suggest that 75.8% and 72.7% of the scores were negative (score = 0) for T1 Gd-DTPA and STIR, respectively.
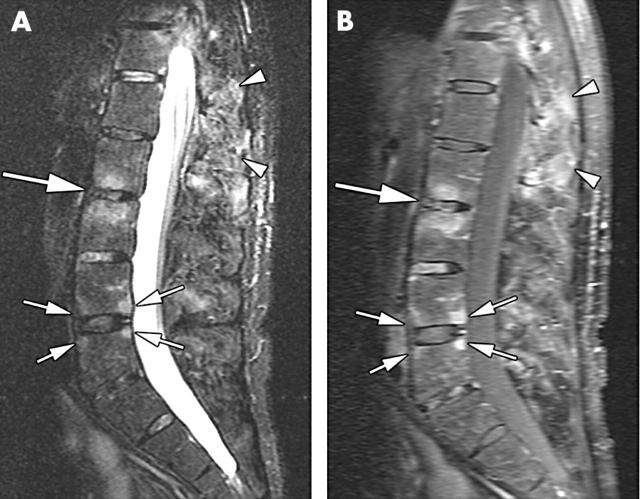
Figure 2.
(A) Sagittal STIR sequence; (B) sagittal T1 weighted sequence with fat saturation after administration of Gd-DTPA. Florid anterior and posterior spondylitis at the L4/5 level (small arrows) and spondylodiscitis at the L2/3 level (large arrow) as depicted by the two techniques. Additionally, there is severe enthesitis of the interspinal ligaments in the T12–L2 region (arrowheads).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boers M., Brooks P., Strand C. V., Tugwell P. The OMERACT filter for Outcome Measures in Rheumatology. J Rheumatol. 1998 Feb;25(2):198–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Baraliakos X., Golder W., Brandt J., Rudwaleit M., Listing J., Bollow M., Sieper J., Van Der Heijde D. Magnetic resonance imaging examinations of the spine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, before and after successful therapy with infliximab: evaluation of a new scoring system. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Apr;48(4):1126–1136. doi: 10.1002/art.10883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Bollow M., Sieper J. Radiologic diagnosis and pathology of the spondyloarthropathies. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1998 Nov;24(4):697–735. doi: 10.1016/s0889-857x(05)70038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., van der Heijde D. Imaging and scoring in ankylosing spondylitis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2002 Sep;16(4):573–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espinosa G., Bucciarelli S., Cervera R., Lozano M., Reverter J-C, de la Red G., Gil V., Ingelmo M., Font J., Asherson R. A. Thrombotic microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia and antiphospholipid antibodies. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004 Jun;63(6):730–736. doi: 10.1136/ard.2003.007245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGonagle D., Gibbon W., O'Connor P., Green M., Pease C., Emery P. Characteristic magnetic resonance imaging entheseal changes of knee synovitis in spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Apr;41(4):694–700. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199804)41:4<694::AID-ART17>3.0.CO;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spoorenberg Anneke, de Vlam Kurt, van der Linden Sjef, Dougados Maxime, Mielants Herman, van de Tempel Hille, van der Heijde Désirée. Radiological scoring methods in ankylosing spondylitis. Reliability and change over 1 and 2 years. J Rheumatol. 2004 Jan;31(1):125–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Linden S., Valkenburg H. A., Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Apr;27(4):361–368. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]