Abstract
Methods: Skin biopsy specimens from 17 patients with SSc were analysed by immunohistochemistry using the indirect peroxidase method and monoclonal antibodies for CD3 (T cell marker), CD69 (early T cell activation marker), and CD68 (macrophage marker).
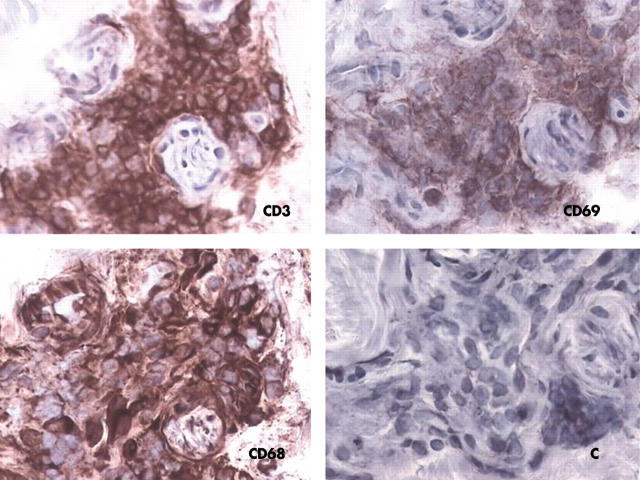
Results: Mononuclear cells, containing mostly T cells and macrophages, were increased in SSc skin lesions and were present in perivascular areas. CD69 was expressed in these mononuclear cells. There was no correlation between the number of CD3+, CD69+, or CD68+ cells and the Rodnan skin score or disease duration.
Conclusions: The expression of early T cell activation antigen CD69 in skin lesions suggests that T cells may actively participate in cell-cell contact with fibroblasts to promote fibrosis.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (118.2 KB).
Figure 1.
Immunoperoxidase staining of a skin lesion from a patient with SSc. Sequential sections were stained with anti-CD3, anti-CD69, anti-CD68 monoclonal antibody or with IgG1 (control).