Abstract
Objective: To investigate changes in prescription practice during the first 3 years of post-marketing use of biological drugs, and to determine the proportion of patients who would not have received tumour necrosis factor (TNF) blocking agents if the prescription guidelines of the UK and the Netherlands had been applied.
Methods: Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) receiving TNF blocking agents from Denmark (n = 823, median age 56.0, 72.2% women) and Norway (n = 371, median age 52.5, 75.4% women) were studied. Prescription guidelines in the UK and the Netherlands were applied to the data.
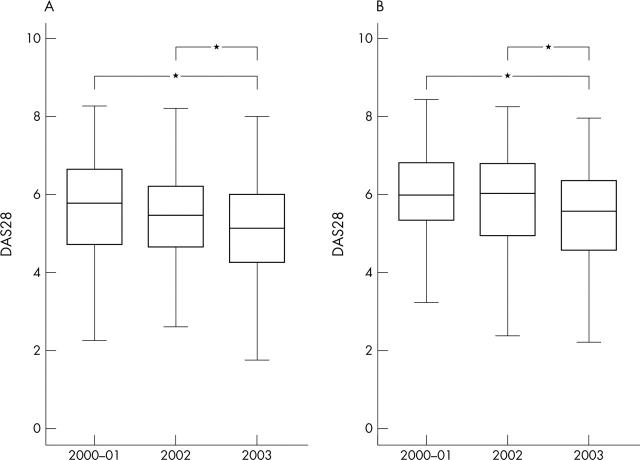
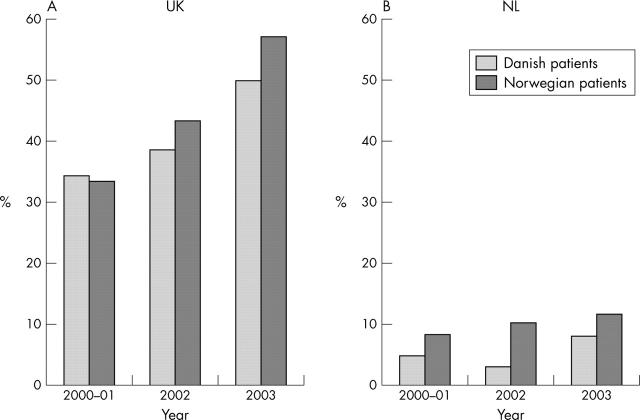
Results: Baseline disease activity and number of previous DMARDs declined significantly during the 3 years (median baseline DAS28 decreased from 5.8 to 5.2 in Denmark (p<0.001) and from 6.0 to 5.6 in Norway (p<0.01)). 47.9% and 41.3% of the Norwegian and Danish patients, respectively, did not meet the UK criteria for using TNF blocking agents, and 10.5% and 5.7% did not meet the Dutch criteria.
Conclusion: Danish and Norwegian prescription practices of biological treatments in RA were similar, and became less stringent from 2000 to 2003. Prescriptions agreed well with the Dutch guidelines, but almost half the patients did not meet the UK guidelines.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (64.0 KB).
Figure 1.
Median disease activity score of 28 joints (DAS28 CRP based) at treatment initiation presented as box plots with 25th and 75th centiles in years 1, 2, and 3 of post-marketing use of the biological drugs. *p<0.05 (Mann-Whitney). (A) Denmark, (B) Norway.
Figure 2.
Percentage of Danish and Norwegian patients who would not have been treated in: (A) the United Kingdom (UK); (B) The Netherlands (NL).