Abstract
Objective: To evaluate a low field dedicated extremity MRI unit for detection of bone erosions, synovitis, and bone marrow oedema in wrist and metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints, with a high field MRI unit as the standard reference.
Methods: In 37 patients with RA and 28 healthy controls MRI of the wrist and 2nd–5th MCP joints was performed on a low field MRI unit (0.2 T Esaote Artoscan) and a high field MRI unit (1.0 T Siemens Impact) on 2 subsequent days. MRI was performed and evaluated according to OMERACT recommendations. Additionally, conventional x ray, clinical, and biochemical examinations were performed. In an initial low field MRI "sequence selection phase", based on a subset of 10 patients and 10 controls, sequences for comparison with high field MRI were selected.
Results: With high field, spin echo MRI considered as the reference method, the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of low field 3D gradient echo MRI for erosions were 94%, 93%, 94%, while the corresponding values for x ray examination were 33%, 98%, and 83%. Sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of low field MRI for synovitis were 90%, 96%, and 94%, and for bone marrow oedema 39%, 99%, and 95%. Intraclass correlation coefficients between low field and high field scores were 0.936 (p<0.005) for bone erosions and 0.923 (p<0.05) for synovitis.
Conclusion: Low field MRI provides high accuracy for detection and grading of erosions and synovitis, with high field MRI as the standard reference. For bone marrow oedema, specificity is high, but sensitivity only moderate. Low cost, patient compliant, low field dedicated extremity MRI provides similar information on bone erosions and synovitis as expensive high field MRI units.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (357.6 KB).
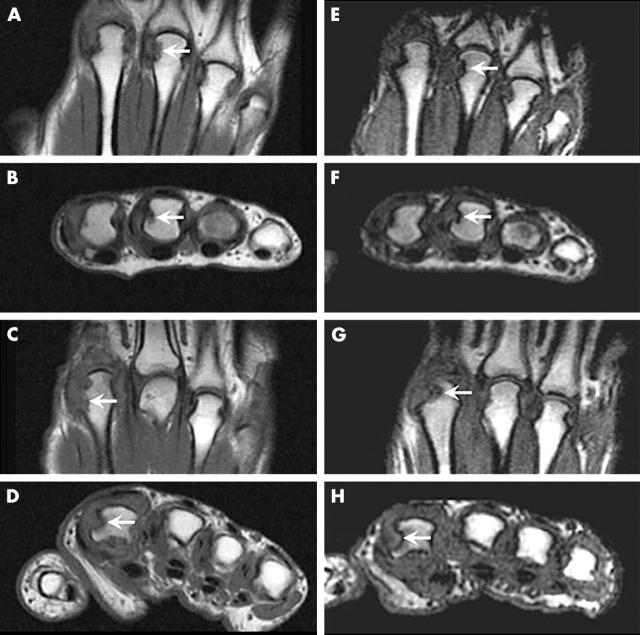
Figure 1.
Erosions in RA MCP joint bones visualised by high field and low field MRI. High field (A, B, C, D) and low field (E, F, G, H) coronal (A, C, E, G) and axial (B, D, F, H) images of the 2nd–5th MCP joints. On high field MRI as well as low field MRI, an erosion (OMERACT grade 2) (arrows) is depicted in the 3rd metacarpal head (A, B, E, F) in patient 1 (upper four images). In patient 2 (lower four images) an erosion (OMERACT grade 3) (arrows) is depicted in the 2nd metacarpal head at both field strengths. All displayed images were obtained before contrast injection.
Figure 2.
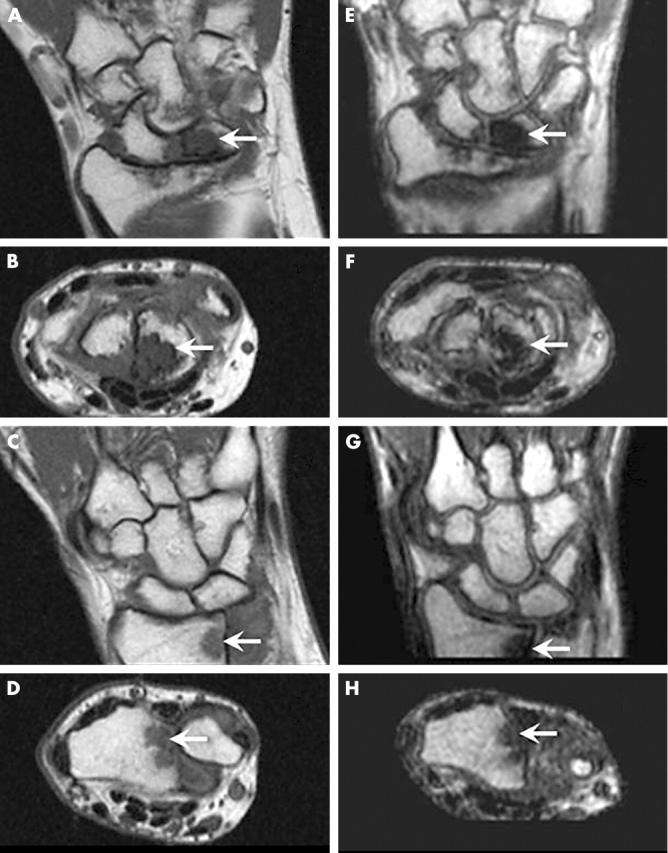
Erosions in RA wrist joint bones visualised by high field and low field MRI. High field (A, B, C, D) and low field (E, F, G, H) coronal (A, C, E, G) and axial (B, D, F, H) images of the wrist joints. On high field MRI as well as low field MRI, an erosion (OMERACT grade 5) (arrows) is depicted in the lunate (A, B, E, F) in patient 1 (upper four images). In patient 2 (lower four images) an erosion (OMERACT grade 1) (arrows) is depicted in radius (C, D, G, H) at both field strengths. All displayed images were obtained before contrast injection.
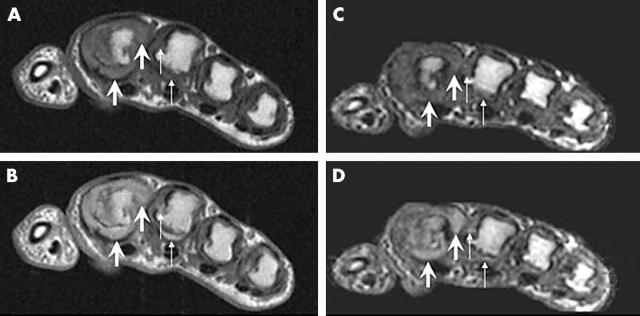
Figure 3.
Synovitis in RA MCP joints visualised by high field and low field MRI. High field (A, B) and low field (C, D) axial images of the 2nd-5th MCP joints before (A, C) and after (B, D) intravenous contrast injection. Post-contrast images show high grade synovitis (OMERACT grade 3) (arrows) in the 2nd MCP joint on high field MRI as well as on low field MRI, while low grade synovitis (OMERACT grade 1) (thin arrows) is seen in the 3rd MCP joint on images obtained at both field strengths.
Figure 4.
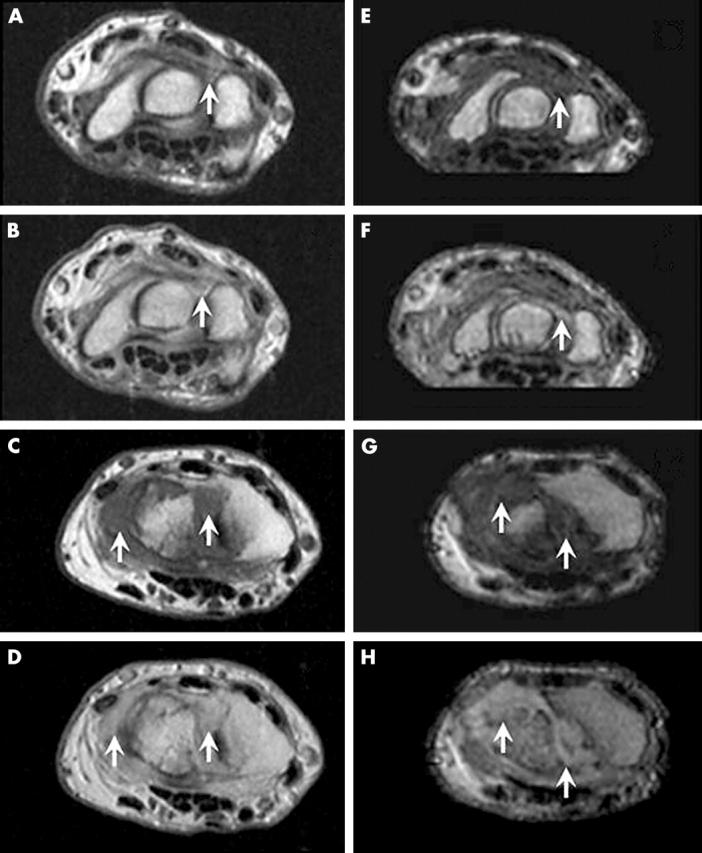
Synovitis in RA wrist joints visualised by high field and low field MRI. High field (A, B, C, D) and low field (E, F, G, H) axial images of the wrist joint before (A, C, E, G) and after (B, D, F, H) intravenous contrast injection. Post-contrast images in patient 1 (upper four images) show low grade synovitis (OMERACT grade 1) (arrows) in the intercarpal area of the wrist joint on high field MRI as well as on low field MRI, while high grade synovitis (OMERACT grade 3) (arrows) is seen in the radiocarpal area of the wrist joint in patient 2 (lower four images) on images obtained at both field strengths.
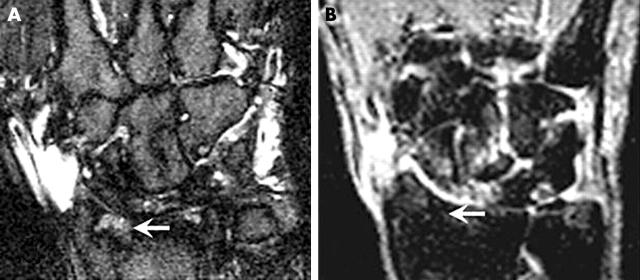
Figure 5.
Bone marrow oedema in RA wrist joint bones visualised by high field and low field MRI. High field (A) and low field (B) STIR images of the wrist. On high field MRI, a low grade bone marrow oedema (OMERACT grade 1) (arrow) is seen in the distal radius. The oedema at this site is not detected on low field MRI.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backhaus M., Kamradt T., Sandrock D., Loreck D., Fritz J., Wolf K. J., Raber H., Hamm B., Burmester G. R., Bollow M. Arthritis of the finger joints: a comprehensive approach comparing conventional radiography, scintigraphy, ultrasound, and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Rheum. 1999 Jun;42(6):1232–1245. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199906)42:6<1232::AID-ANR21>3.0.CO;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brower A. C. Use of the radiograph to measure the course of rheumatoid arthritis. The gold standard versus fool's gold. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Mar;33(3):316–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce Bonnie, Fries James F. The Stanford Health Assessment Questionnaire: dimensions and practical applications. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2003 Jun 9;1:20–20. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-1-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvetta A., Giovagnoni A., Baldelli S., Ercolani P., Pomponio G., Luchetti M. M., Rinaldi N., De Nigris E. MR imaging of rheumatoid hand lesions: comparison with conventional radiology in 31 patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1992 May-Jun;10(3):217–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crues John V., Shellock Frank G., Dardashti Siamak, James Timothy W., Troum Orrin M. Identification of wrist and metacarpophalangeal joint erosions using a portable magnetic resonance imaging system compared to conventional radiographs. J Rheumatol. 2004 Apr;31(4):676–685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ejbjerg Bo, Narvestad Eva, Rostrup Egill, Szkudlarek Marcin, Jacobsen Søren, Thomsen Henrik S., Østergaard Mikkel. Magnetic resonance imaging of wrist and finger joints in healthy subjects occasionally shows changes resembling erosions and synovitis as seen in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004 Apr;50(4):1097–1106. doi: 10.1002/art.20135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery P. The Roche Rheumatology Prize Lecture. The optimal management of early rheumatoid disease: the key to preventing disability. Br J Rheumatol. 1994 Aug;33(8):765–768. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/33.8.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foley-Nolan D., Stack J. P., Ryan M., Redmond U., Barry C., Ennis J., Coughlan R. J. Magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of rheumatoid arthritis--a comparison with plain film radiographs. Br J Rheumatol. 1991 Apr;30(2):101–106. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/30.2.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forslind K., Johanson A., Larsson E. M., Svensson B. Magnetic resonance imaging of the fifth metatarsophalangeal joint compared with conventional radiography in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 2003;32(3):131–137. doi: 10.1080/03009740310002452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffney K., Cookson J., Blake D., Coumbe A., Blades S. Quantification of rheumatoid synovitis by magnetic resonance imaging. Arthritis Rheum. 1995 Nov;38(11):1610–1617. doi: 10.1002/art.1780381113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen C., Cyteval C., Anaya J. M., Baron M. P., Lamarque J. L., Sany J. Sensitivity of magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist in very early rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1993 Mar-Apr;11(2):163–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klarlund M., Ostergaard M., Gideon P., Sørensen K., Jensen K. E., Lorenzen I. Wrist and finger joint MR imaging in rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Radiol. 1999 Jul;40(4):400–409. doi: 10.3109/02841859909177754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klarlund M., Ostergaard M., Jensen K. E., Madsen J. L., Skjødt H., Lorenzen I. Magnetic resonance imaging, radiography, and scintigraphy of the finger joints: one year follow up of patients with early arthritis. The TIRA Group. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000 Jul;59(7):521–528. doi: 10.1136/ard.59.7.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klarlund M., Ostergaard M., Lorenzen I. Finger joint synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis: quantitative assessment by magnetic resonance imaging. Rheumatology (Oxford) 1999 Jan;38(1):66–72. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/38.1.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König H., Sieper J., Wolf K. J. Rheumatoid arthritis: evaluation of hypervascular and fibrous pannus with dynamic MR imaging enhanced with Gd-DTPA. Radiology. 1990 Aug;176(2):473–477. doi: 10.1148/radiology.176.2.2367663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindegaard H., Vallø J., Hørslev-Petersen K., Junker P., Østergaard M. Low field dedicated magnetic resonance imaging in untreated rheumatoid arthritis of recent onset. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001 Aug;60(8):770–776. doi: 10.1136/ard.60.8.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen F. M., Stewart N., Crabbe J., Robinson E., Yeoman S., Tan P. L., McLean L. Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist in early rheumatoid arthritis reveals a high prevalence of erosions at four months after symptom onset. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998 Jun;57(6):350–356. doi: 10.1136/ard.57.6.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen F. M., Stewart N., Crabbe J., Robinson E., Yeoman S., Tan P. L., McLean L. Magnetic resonance imaging of the wrist in early rheumatoid arthritis reveals progression of erosions despite clinical improvement. Ann Rheum Dis. 1999 Mar;58(3):156–163. doi: 10.1136/ard.58.3.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQueen Fiona M., Benton Nick, Perry David, Crabbe Jeff, Robinson Elizabeth, Yeoman Sue, McLean Lachy, Stewart Neal. Bone edema scored on magnetic resonance imaging scans of the dominant carpus at presentation predicts radiographic joint damage of the hands and feet six years later in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Jul;48(7):1814–1827. doi: 10.1002/art.11162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norgaard F. Earliest roentgen changes in polyarthritis of the rheumatoid type. Continued investigations. Radiology. 1969 Feb;92(2):299–303. doi: 10.1148/92.2.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dell James R. Treating rheumatoid arthritis early: a window of opportunity? Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Feb;46(2):283–285. doi: 10.1002/art.10092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostendorf B., Peters R., Dann P., Becker A., Scherer A., Wedekind F., Friemann J., Schulitz K. P., Mödder U., Schneider M. Magnetic resonance imaging and miniarthroscopy of metacarpophalangeal joints: sensitive detection of morphologic changes in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Nov;44(11):2492–2502. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200111)44:11<2492::aid-art429>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard M., Gideon P., Sørensen K., Hansen M., Stoltenberg M., Henriksen O., Lorenzen I. Scoring of synovial membrane hypertrophy and bone erosions by MR imaging in clinically active and inactive rheumatoid arthritis of the wrist. Scand J Rheumatol. 1995;24(4):212–218. doi: 10.3109/03009749509100876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard M., Hansen M., Stoltenberg M., Lorenzen I. Quantitative assessment of the synovial membrane in the rheumatoid wrist: an easily obtained MRI score reflects the synovial volume. Br J Rheumatol. 1996 Oct;35(10):965–971. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/35.10.965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostergaard M., Stoltenberg M., Løvgreen-Nielsen P., Volck B., Sonne-Holm S., Lorenzen I. Quantification of synovistis by MRI: correlation between dynamic and static gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and microscopic and macroscopic signs of synovial inflammation. Magn Reson Imaging. 1998 Sep;16(7):743–754. doi: 10.1016/s0730-725x(98)00008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savnik A., Malmskov H., Thomsen H. S., Bretlau T., Graff L. B., Nielsen H., Danneskiold-Samsøe B., Boesen J., Bliddal H. MRI of the arthritic small joints: comparison of extremity MRI (0.2 T) vs high-field MRI (1.5 T). Eur Radiol. 2001;11(6):1030–1038. doi: 10.1007/s003300000709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savnik Anette, Malmskov Hanne, Thomsen Henrik S., Graff Lykke B., Nielsen Henrik, Danneskiold-Samsøe Bente, Boesen Jens, Bliddal Henning. MRI of the wrist and finger joints in inflammatory joint diseases at 1-year interval: MRI features to predict bone erosions. Eur Radiol. 2001 Sep 25;12(5):1203–1210. doi: 10.1007/s003300101114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto H., Takeda A., Masuyama J., Furuse M. Early-stage rheumatoid arthritis: diagnostic accuracy of MR imaging. Radiology. 1996 Jan;198(1):185–192. doi: 10.1148/radiology.198.1.8539375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Nobuyuki, Sakahashi Hisashi, Ishii Seiichi, Sato Eiichi, Hirose Kazuya, Ishima Takumi. Synovial membrane enhancement and bone erosion by magnetic resonance imaging for prediction of radiologic progression in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2003 Nov 27;25(2):103–107. doi: 10.1007/s00296-003-0404-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taouli Bachir, Zaim Souhil, Peterfy Charles G., Lynch John A., Stork Alexander, Guermazi Ali, Fan Bo, Fye Kenneth H., Genant Harry K. Rheumatoid arthritis of the hand and wrist: comparison of three imaging techniques. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004 Apr;182(4):937–943. doi: 10.2214/ajr.182.4.1820937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Østergaard Mikkel, Hansen Michael, Stoltenberg Michael, Jensen Karl Erik, Szkudlarek Marcin, Pedersen-Zbinden Brigitta, Lorenzen Ib. New radiographic bone erosions in the wrists of patients with rheumatoid arthritis are detectable with magnetic resonance imaging a median of two years earlier. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Aug;48(8):2128–2131. doi: 10.1002/art.11076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Østergaard Mikkel, Peterfy Charles, Conaghan Philip, McQueen Fiona, Bird Paul, Ejbjerg Bo, Shnier Ron, O'Connor Philip, Klarlund Mette, Emery Paul. OMERACT Rheumatoid Arthritis Magnetic Resonance Imaging Studies. Core set of MRI acquisitions, joint pathology definitions, and the OMERACT RA-MRI scoring system. J Rheumatol. 2003 Jun;30(6):1385–1386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]