Abstract
Objective: To assess the changes in inflammatory lesions of the spine and the sacroiliac (SI) joints as detected by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis (uSpA) with predominant axial symptoms during treatment with etanercept.
Methods: MRI of the spine and/or the SI joints of patients with active AS or axial uSpA was performed at baseline (TP0, n = 25), after 6 weeks (TP1, n = 20), and after 24 weeks of continuous treatment with etanercept (TP2, n = 12). T1 weighted spin echo pre -(T1), post-gadolinium (T1/Gd-DTPA) and short tau inversion recovery (STIR) MRI sequences were used to assess chronic and active spinal lesions using the scoring system ASspiMRI. Active and chronic SI lesions were assessed using a simple scoring system.
Results: By use of the definite STIR sequence, significant regression of spinal inflammation was already seen already after 6 weeks in the patients treated with etanercept (mean (SD) 11.2 (13.8) at TP0 v 6.8 (7.9) at TP1; p = 0.023) but not in patients treated with placebo. Continuous treatment with etanercept for 24 weeks reduced active spinal changes by 69% (p = 0.012). T1/Gd-DTPA sequences gave similar results. There was only a trend for a decrease of active inflammatory lesions of the SI joints.
Conclusions: Etanercept treatment in patients with active AS and uSpA leads to regression of active inflammatory lesions of the spine as depicted by MRI. The potential role of etanercept on deceleration of chronic spinal changes needs further study.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (212.8 KB).
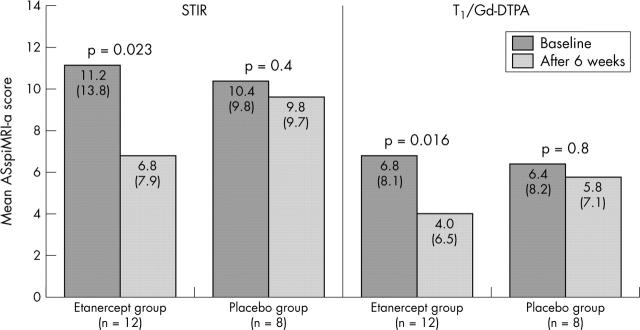
Figure 1.
Mean improvement of active spinal lesions as assessed by MRI using the STIR and T1/Gd-DTPA technique and quantified by the ASspiMRI-a score at baseline and after 6 weeks of etanercept or placebo treatment, respectively. Significant differences were found for the patients treated with etanercept (in the STIR sequence and in the T1/Gd-DTPA sequence) but not for patients treated with placebo.
Figure 2.
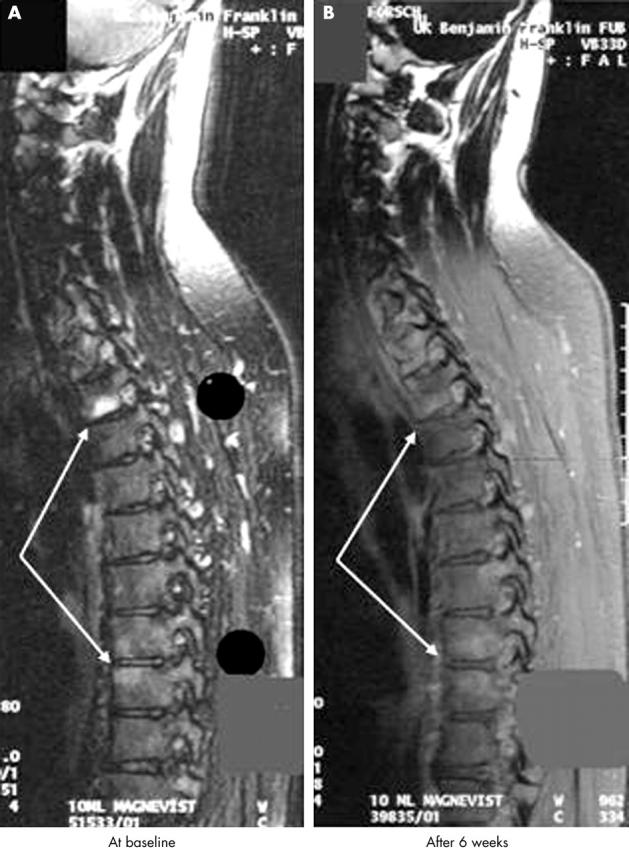
Improvement of inflammatory spinal lesions in a patient with AS before and after application of T1/Gd-DTPA. The hyperintensity of the signal in the vertebra is no longer detectable after 6 weeks of treatment with etanercept.
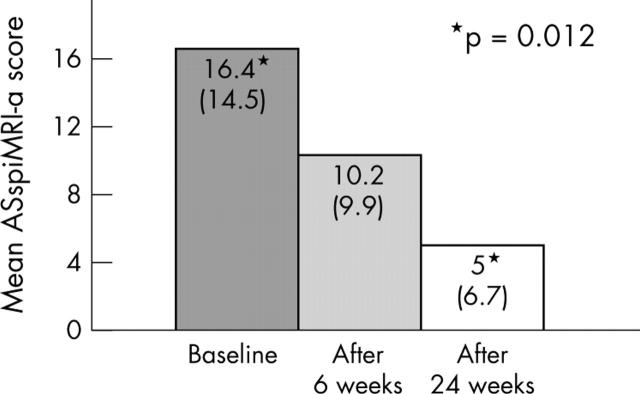
Figure 3.
Active inflammatory lesions of the spine (n = 12) as assessed by MRI using the STIR sequence and as quantified by the ASspiMRI-a at baseline (TP0), after 6 weeks (TP1), and after 24 weeks of treatment (TP2). *p = 0.001 refers to the comparison between TP0 and TP2.
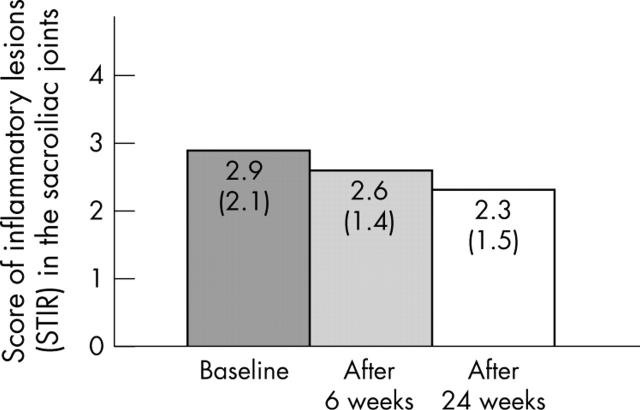
Figure 4.
Active inflammatory lesions of the SI joints (n = 15) as assessed by MRI using the STIR sequence and a simple score at baseline (TP0), after 6 weeks of treatment (TP1), and after 24 weeks of treatment (TP2).
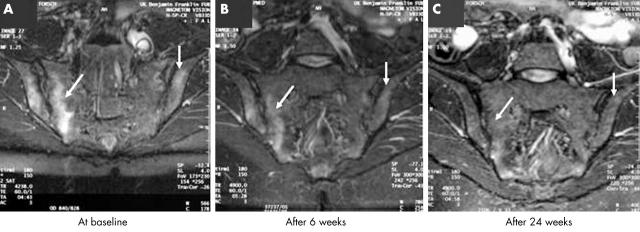
Figure 5.
An example of a patient with significant improvement of active inflammatory lesions of the SI joints over the treatment period. Improvement was already seen after 6 weeks of treatment.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baraliakos X., Davis J., Tsuji W., Braun J. Magnetic resonance imaging examinations of the spine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis before and after therapy with the tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor fusion protein etanercept. Arthritis Rheum. 2005 Apr;52(4):1216–1223. doi: 10.1002/art.20977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baraliakos X., Hermann K-G A., Landewé R., Listing J., Golder W., Brandt J., Rudwaleit M., Bollow M., Sieper J., van der Heijde D. Assessment of acute spinal inflammation in patients with ankylosing spondylitis by magnetic resonance imaging: a comparison between contrast enhanced T1 and short tau inversion recovery (STIR) sequences. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005 Jan 13;64(8):1141–1144. doi: 10.1136/ard.2004.031609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baraliakos X., Landewé R., Hermann K-G, Listing J., Golder W., Brandt J., Rudwaleit M., Bollow M., Sieper J., van der Heijde D. Inflammation in ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic description of the extent and frequency of acute spinal changes using magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004 Sep 30;64(5):730–734. doi: 10.1136/ard.2004.029298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollow M., Enzweiler C., Taupitz M., Golder W., Hamm B., Sieper J., Braun J. Use of contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging to detect spinal inflammation in patients with spondyloarthritides. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2002 Nov-Dec;20(6 Suppl 28):S167–S174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt J., Bollow M., Häberle J., Rudwaleit M., Eggens U., Distler A., Sieper J., Braun J. Studying patients with inflammatory back pain and arthritis of the lower limbs clinically and by magnetic resonance imaging: many, but not all patients with sacroiliitis have spondyloarthropathy. Rheumatology (Oxford) 1999 Sep;38(9):831–836. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/38.9.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt J., Khariouzov A., Listing J., Haibel H., Sörensen H., Grassnickel L., Rudwaleit M., Sieper J., Braun J. Six-month results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of etanercept treatment in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Jun;48(6):1667–1675. doi: 10.1002/art.11017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt J., Listing J., Haibel H., Sörensen H., Schwebig A., Rudwaleit M., Sieper J., Braun J. Long-term efficacy and safety of etanercept after readministration in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2004 Nov 23;44(3):342–348. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keh475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt Jan, Haibel Hildrun, Reddig Jaqueline, Sieper Joachim, Braun Jürgen. Successful short term treatment of severe undifferentiated spondyloarthropathy with the anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha monoclonal antibody infliximab. J Rheumatol. 2002 Jan;29(1):118–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt Jan, Khariouzov Andre, Listing Joachim, Haibel Hildrun, Sörensen Helmut, Rudwaleit Martin, Sieper Joachim, Braun Jurgen. Successful short term treatment of patients with severe undifferentiated spondyloarthritis with the anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha fusion receptor protein etanercept. J Rheumatol. 2004 Mar;31(3):531–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Baraliakos X., Golder W., Brandt J., Rudwaleit M., Listing J., Bollow M., Sieper J., Van Der Heijde D. Magnetic resonance imaging examinations of the spine in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, before and after successful therapy with infliximab: evaluation of a new scoring system. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Apr;48(4):1126–1136. doi: 10.1002/art.10883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Baraliakos X., Golder W., Hermann K-G, Listing J., Brandt J., Rudwaleit M., Zuehlsdorf S., Bollow M., Sieper J. Analysing chronic spinal changes in ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic comparison of conventional x rays with magnetic resonance imaging using established and new scoring systems. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004 Apr 5;63(9):1046–1055. doi: 10.1136/ard.2003.019968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Bollow M., Eggens U., König H., Distler A., Sieper J. Use of dynamic magnetic resonance imaging with fast imaging in the detection of early and advanced sacroiliitis in spondylarthropathy patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1994 Jul;37(7):1039–1045. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Bollow M., Remlinger G., Eggens U., Rudwaleit M., Distler A., Sieper J. Prevalence of spondylarthropathies in HLA-B27 positive and negative blood donors. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Jan;41(1):58–67. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199801)41:1<58::AID-ART8>3.0.CO;2-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Bollow M., Sieper J. Radiologic diagnosis and pathology of the spondyloarthropathies. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1998 Nov;24(4):697–735. doi: 10.1016/s0889-857x(05)70038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Bollow M., Sieper J. Radiologic diagnosis and pathology of the spondyloarthropathies. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1998 Nov;24(4):697–735. doi: 10.1016/s0889-857x(05)70038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Sieper J. The sacroiliac joint in the spondyloarthropathies. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1996 Jul;8(4):275–287. doi: 10.1097/00002281-199607000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calin A., Porta J., Fries J. F., Schurman D. J. Clinical history as a screening test for ankylosing spondylitis. JAMA. 1977 Jun 13;237(24):2613–2614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougados M., van der Linden S., Juhlin R., Huitfeldt B., Amor B., Calin A., Cats A., Dijkmans B., Olivieri I., Pasero G. The European Spondylarthropathy Study Group preliminary criteria for the classification of spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Oct;34(10):1218–1227. doi: 10.1002/art.1780341003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobelt G., Andlin-Sobocki P., Brophy S., Jönsson L., Calin A., Braun J. The burden of ankylosing spondylitis and the cost-effectiveness of treatment with infliximab (Remicade). Rheumatology (Oxford) 2004 Jun 29;43(9):1158–1166. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keh271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzo-Ortega H., McGonagle D., O'Connor P., Emery P. Efficacy of etanercept in the treatment of the entheseal pathology in resistant spondylarthropathy: a clinical and magnetic resonance imaging study. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Sep;44(9):2112–2117. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200109)44:9<2112::AID-ART363>3.0.CO;2-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mau W., Zeidler H., Mau R., Majewski A., Freyschmidt J., Stangel W., Deicher H. Clinical features and prognosis of patients with possible ankylosing spondylitis. Results of a 10-year followup. J Rheumatol. 1988 Jul;15(7):1109–1114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puhakka K. Bøcker, Jurik A. G., Egund N., Schiottz-Christensen B., Stengaard-Pedersen K., van Overeem Hansen G., Christiansen J. Vallø. Imaging of sacroiliitis in early seronegative spondylarthropathy. Assessment of abnormalities by MR in comparison with radiography and CT. Acta Radiol. 2003 Mar;44(2):218–229. doi: 10.1080/j.1600-0455.2003.00034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Linden S., Valkenburg H. A., Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Apr;27(4):361–368. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.