Abstract
Objective: To compare growth and body composition in preterm infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) with normal healthy term infants during the first year of life.
Design: Twenty nine preterm infants with BPD (mean (SD) gestational age 27.1 (1.6) weeks; birth weight 852 (173) g) were followed prospectively. Anthropometry and body composition determined by total body electrical conductivity were measured and compared with those of healthy term infants at the same post-term age.
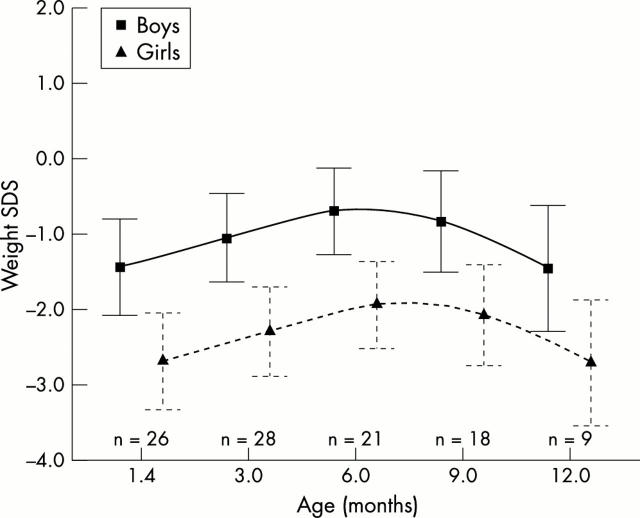
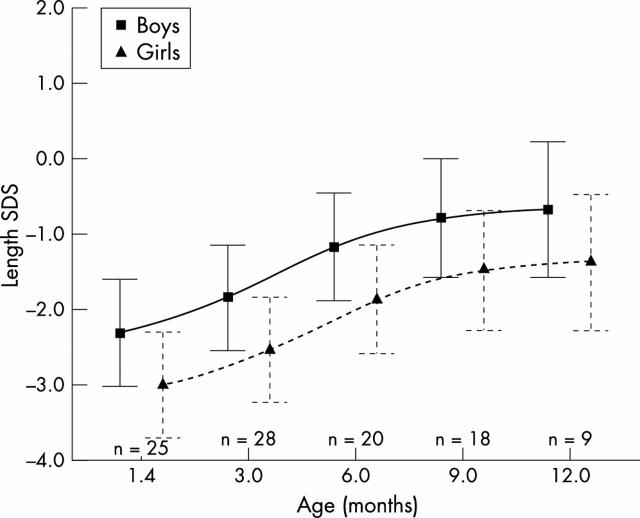
Results: In infants with BPD, the mean weight standard deviation scores (SD scores) 6 weeks after term were significantly lower (-1.44 and -2.68, boys and girls respectively) than in healthy term infants of the same age and did not improve during the first year. The mean length SD score was significantly lower in infants with BPD 6 weeks after term than in healthy term infants of the same age, and, although it improved significantly during the first year, the mean length SD score in girls with BPD was significantly below 0 12 months after term. In infants with BPD, the mean free fat mass (FFM) SD score and the mean total body fat (TBF) SD score at 6 weeks post-term age were significantly below 0. The mean FFM SD scores (-1.01 and -2.56, boys and girls respectively) and the mean TBF SD scores (-1.14 and -2.40, boys and girls respectively) 12 months after term were significantly lower than in healthy term infants of the same age.
Conclusions: Preterm infants with BPD have impaired growth, with a deficit in TBF and FFM already 6 weeks after term; FFM and TBF remain low compared with healthy term infants during the first year of life. Nutritional intervention studies in infants with BPD are needed to evaluate if nutrition is the major determinant of growth and body composition or if this pattern of growth in preterm infants with BPD is the result of disturbed endocrine control.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (160.9 KB).
Figure 1 .
Weight SD scores (SDS) in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia plotted against post-term age in the first year of life. The mean and the 25th and 75th centiles are shown.
Figure 2 .
Length SD scores (SDS) in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia plotted against post-term age in the first year of life. The mean and the 25th and 75th centiles are shown.
Figure 3 .
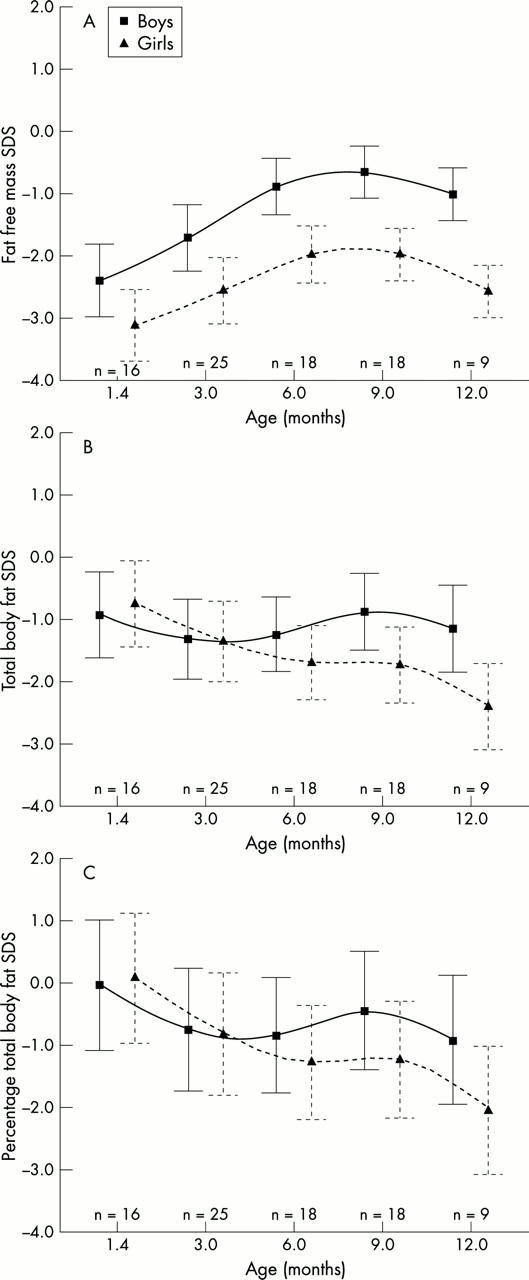
Fat free mass (A), total body fat (B), and % total body fat (C) in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia plotted against post-term age in the first year of life. The mean and the 25th and 75th centiles are shown.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker D. J., Winter P. D., Osmond C., Margetts B., Simmonds S. J. Weight in infancy and death from ischaemic heart disease. Lancet. 1989 Sep 9;2(8663):577–580. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90710-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunton J. A., Saigal S., Atkinson S. A. Growth and body composition in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia up to 3 months corrected age: a randomized trial of a high-energy nutrient-enriched formula fed after hospital discharge. J Pediatr. 1998 Sep;133(3):340–345. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(98)70266-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butte N. F., Wong W. W., Hopkinson J. M., Heinz C. J., Mehta N. R., Smith E. O. Energy requirements derived from total energy expenditure and energy deposition during the first 2 y of life. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000 Dec;72(6):1558–1569. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/72.6.1558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carver J. D., Wu P. Y., Hall R. T., Ziegler E. E., Sosa R., Jacobs J., Baggs G., Auestad N., Lloyd B. Growth of preterm infants fed nutrient-enriched or term formula after hospital discharge. Pediatrics. 2001 Apr;107(4):683–689. doi: 10.1542/peds.107.4.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. J., Embleton N. D., Griffin I. J., Wells J. C., McCormick K. P. Feeding preterm infants after hospital discharge: growth and development at 18 months of age. Pediatr Res. 2001 May;49(5):719–722. doi: 10.1203/00006450-200105000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. J., McCormick K., Griffin I. J., Embleton N., Faulkner K., Wells J. C., Rawlings D. C. Feeding preterm infants after hospital discharge: effect of diet on body composition. Pediatr Res. 1999 Oct;46(4):461–464. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199910000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. J., Rawlings D. J., McCormick K., Griffin I. J., Faulkner K., Wells J. C., Smith J. S., Robinson S. J. Body composition of preterm infants during infancy. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1999 May;80(3):F188–F191. doi: 10.1136/fn.80.3.f188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson S., Schrayer A., Wielunsky E., Krikler R., Lilos P., Reisner S. H. Energy intake, growth, and development in ventilated very-low-birth-weight infants with and without bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Dis Child. 1990 May;144(5):553–559. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1990.02150290047025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenkranz R. A., Younes N., Lemons J. A., Fanaroff A. A., Donovan E. F., Wright L. L., Katsikiotis V., Tyson J. E., Oh W., Shankaran S. Longitudinal growth of hospitalized very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics. 1999 Aug;104(2 Pt 1):280–289. doi: 10.1542/peds.104.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson J. G., Forsén T., Tuomilehto J., Winter P. D., Osmond C., Barker D. J. Catch-up growth in childhood and death from coronary heart disease: longitudinal study. BMJ. 1999 Feb 13;318(7181):427–431. doi: 10.1136/bmj.318.7181.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorotto M. L., Cochran W. J., Klish W. J. Fat-free mass and total body water of infants estimated from total body electrical conductivity measurements. Pediatr Res. 1987 Oct;22(4):417–421. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198710000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiorotto M. L., de Bruin N. C., Brans Y. W., Degenhart H. J., Visser H. K. Total body electrical conductivity measurements: an evaluation of current instrumentation for infants. Pediatr Res. 1995 Jan;37(1):94–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomon S. J., Haschke F., Ziegler E. E., Nelson S. E. Body composition of reference children from birth to age 10 years. Am J Clin Nutr. 1982 May;35(5 Suppl):1169–1175. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/35.5.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg M., Kurzner S. I., Bautista D. B., Keens T. G. Clinically unsuspected hypoxia during sleep and feeding in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics. 1988 May;81(5):635–642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzner S. I., Garg M., Bautista D. B., Bader D., Merritt R. J., Warburton D., Keens T. G. Growth failure in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia: nutrition and elevated resting metabolic expenditure. Pediatrics. 1988 Mar;81(3):379–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapillonne A., Braillon P., Claris O., Chatelain P. G., Delmas P. D., Salle B. L. Body composition in appropriate and in small for gestational age infants. Acta Paediatr. 1997 Feb;86(2):196–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1997.tb08868.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas A., Bishop N. J., King F. J., Cole T. J. Randomised trial of nutrition for preterm infants after discharge. Arch Dis Child. 1992 Mar;67(3):324–327. doi: 10.1136/adc.67.3.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas A., Fewtrell M. S., Morley R., Singhal A., Abbott R. A., Isaacs E., Stephenson T., MacFadyen U. M., Clements H. Randomized trial of nutrient-enriched formula versus standard formula for postdischarge preterm infants. Pediatrics. 2001 Sep;108(3):703–711. doi: 10.1542/peds.108.3.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markestad T., Fitzhardinge P. M. Growth and development in children recovering from bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr. 1981 Apr;98(4):597–602. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80774-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northway W. H., Jr, Rosan R. C., Porter D. Y. Pulmonary disease following respirator therapy of hyaline-membrane disease. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. N Engl J Med. 1967 Feb 16;276(7):357–368. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196702162760701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmond C., Barker D. J., Winter P. D., Fall C. H., Simmonds S. J. Early growth and death from cardiovascular disease in women. BMJ. 1993 Dec 11;307(6918):1519–1524. doi: 10.1136/bmj.307.6918.1519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman J. M., Volpe J. J. Movement disorder of premature infants with severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia: a new syndrome. Pediatrics. 1989 Aug;84(2):215–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigo J., Nyamugabo K., Picaud J. C., Gerard P., Pieltain C., De Curtis M. Reference values of body composition obtained by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in preterm and term neonates. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1998 Aug;27(2):184–190. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199808000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson C. M., Etches P. C., Goldson E., Kyle J. M. Eight-year school performance, neurodevelopmental, and growth outcome of neonates with bronchopulmonary dysplasia: a comparative study. Pediatrics. 1992 Mar;89(3):365–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sindel B. D., Maisels M. J., Ballantine T. V. Gastroesophageal reflux to the proximal esophagus in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Dis Child. 1989 Sep;143(9):1103–1106. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1989.02150210139034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer L., Martin R. J., Hawkins S. W., Benson-Szekely L. J., Yamashita T. S., Carlo W. A. Oxygen desaturation complicates feeding in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia after discharge. Pediatrics. 1992 Sep;90(3):380–384. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usher R., McLean F. Intrauterine growth of live-born Caucasian infants at sea level: standards obtained from measurements in 7 dimensions of infants born between 25 and 44 weeks of gestation. J Pediatr. 1969 Jun;74(6):901–910. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkataraman P. S., Ahluwalia B. W. Total bone mineral content and body composition by x-ray densitometry in newborns. Pediatrics. 1992 Nov;90(5):767–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vohr B. R., Bell E. F., Oh W. Infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Growth pattern and neurologic and developmental outcome. Am J Dis Child. 1982 May;136(5):443–447. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1982.03970410061015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIDDOWSON E. M., MCCANCE R. A. THE EFFECT OF FINITE PERIODS OF UNDERNUTRITION AT DIFFERENT AGES ON THE COMPOSITION AND SUBSEQUENT DEVELOPMENT OF THE RAT. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1963 Oct 22;158:329–342. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1963.0051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein M. R., Oh W. Oxygen consumption in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr. 1981 Dec;99(6):958–961. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh T. F., McClenan D. A., Ajayi O. A., Pildes R. S. Metabolic rate and energy balance in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr. 1989 Mar;114(3):448–451. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(89)80569-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruin N. C., Westerterp K. R., Degenhart H. J., Visser H. K. Measurement of fat-free mass in infants. Pediatr Res. 1995 Sep;38(3):411–417. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199509000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruin N. C., van Velthoven K. A., Stijnen T., Juttmann R. E., Degenhart H. J., Visser H. K. Quantitative assessment of infant body fat by anthropometry and total-body electrical conductivity. Am J Clin Nutr. 1995 Feb;61(2):279–286. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/61.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruin N. C., van Velthoven K. A., de Ridder M., Stijnen T., Juttmann R. E., Degenhart H. J., Visser H. K. Standards for total body fat and fat-free mass in infants. Arch Dis Child. 1996 May;74(5):386–399. doi: 10.1136/adc.74.5.386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meer K., Westerterp K. R., Houwen R. H., Brouwers H. A., Berger R., Okken A. Total energy expenditure in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia is associated with respiratory status. Eur J Pediatr. 1997 Apr;156(4):299–304. doi: 10.1007/s004310050605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deRegnier R. A., Guilbert T. W., Mills M. M., Georgieff M. K. Growth failure and altered body composition are established by one month of age in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Nutr. 1996 Jan;126(1):168–175. doi: 10.1093/jn/126.1.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Goudoever J. B., Sulkers E. J., Lafeber H. N., Sauer P. J. Short-term growth and substrate use in very-low-birth-weight infants fed formulas with different energy contents. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000 Mar;71(3):816–821. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/71.3.816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]