Abstract
Objective: To explore, using functional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), the functional organisation of phonological processing in young adults born very preterm.
Subjects: Six right handed male subjects with radiological evidence of thinning of the corpus callosum were selected from a cohort of very preterm subjects. Six normal right handed male volunteers acted as controls.
Method: Blood oxygenation level dependent contrast echoplanar images were acquired over five minutes at 1.5 T while subjects performed the tasks. During the ON condition, subjects were visually presented with pairs of non-words and asked to press a key when a pair of words rhymed (phonological processing). This task alternated with the OFF condition, which required subjects to make letter case judgments of visually presented pairs of consonant letter strings (orthographic processing). Generic brain activation maps were constructed from individual images by sinusoidal regression and non-parametric testing. Between group differences in the mean power of experimental response were identified on a voxel wise basis by analysis of variance.
Results: Compared with controls, the subjects with thinning of the corpus callosum showed significantly reduced power of response in the left hemisphere, including the peristriate cortex and the cerebellum, as well as in the right parietal association area. Significantly increased power of response was observed in the right precentral gyrus and the right supplementary motor area.
Conclusions: The data show evidence of increased frontal and decreased occipital activation in male subjects with neurodevelopmental thinning of the corpus callosum, which may be due to the operation of developmental compensatory mechanisms.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (632.8 KB).
Figure 1 .
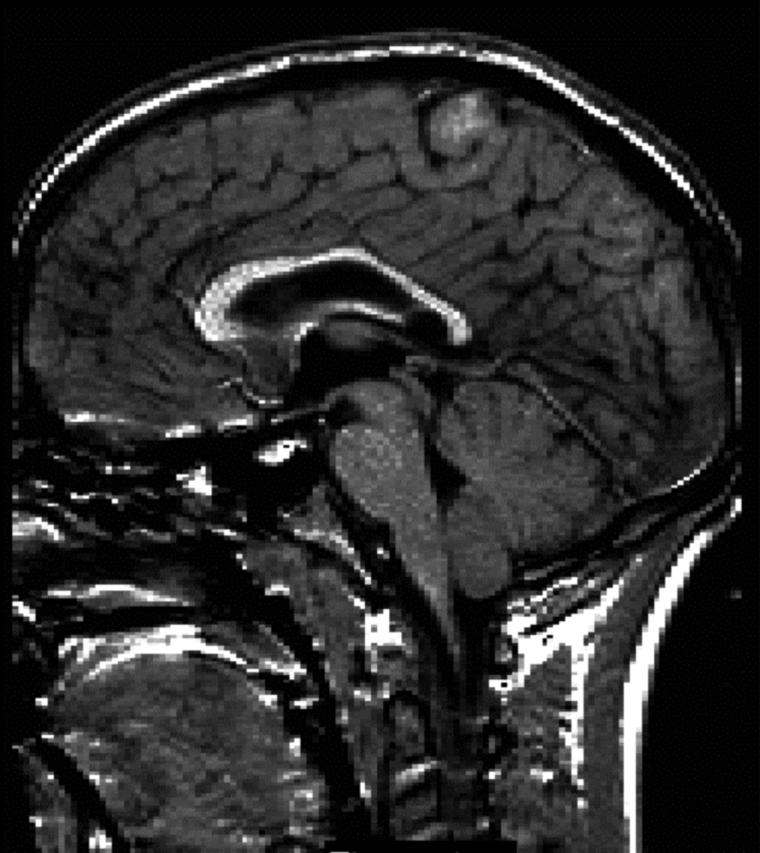
Image from a very preterm subject showing evidence of thinning of the corpus callosum.
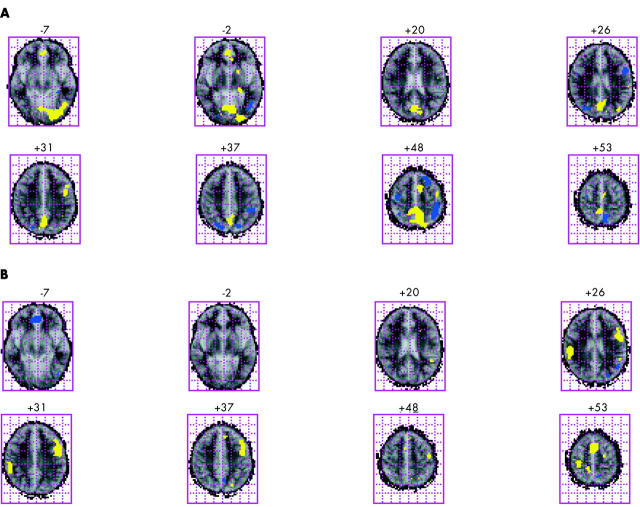
Figure 2 .
Brain activation in phase with non-word rhyming (shown in yellow) and case alternation judgment (shown in blue) of six controls (A) and six very preterm subjects with thinning of the corpus callosum (B). For each brain image, the left hemisphere is represented on the right of the image, and the right hemisphere is represented on the left.
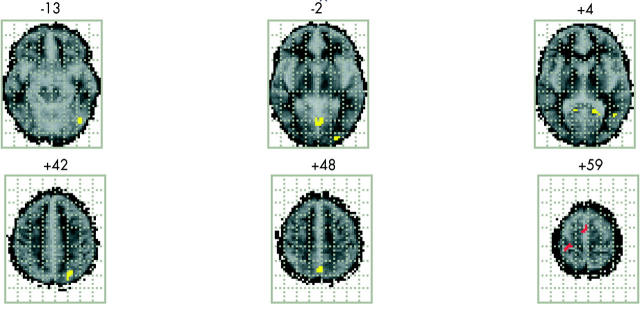
Figure 3 .
Brain activation pattern showing the regional differences between the two groups (six very preterm subjects and six controls) after analysis of covariance. Regions shown in yellow are those that show significantly more activation in the control group. Regions shown in red are those that show significantly more activation for the very preterm subjects with evidence of thinning of the corpus callosum.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allin M., Matsumoto H., Santhouse A. M., Nosarti C., AlAsady M. H., Stewart A. L., Rifkin L., Murray R. M. Cognitive and motor function and the size of the cerebellum in adolescents born very pre-term. Brain. 2001 Jan;124(Pt 1):60–66. doi: 10.1093/brain/124.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briscoe J., Gathercole S. E., Marlow N. Short-term memory and language outcomes after extreme prematurity at birth. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 1998 Jun;41(3):654–666. doi: 10.1044/jslhr.4103.654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. B., Bendersky M., Chapman T. The early utterances of preterm infants. Br J Disord Commun. 1986 Dec;21(3):307–319. doi: 10.3109/13682828609019844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullmore E., Brammer M., Williams S. C., Rabe-Hesketh S., Janot N., David A., Mellers J., Howard R., Sham P. Statistical methods of estimation and inference for functional MR image analysis. Magn Reson Med. 1996 Feb;35(2):261–277. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910350219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee M. W., O'Craven K. M., Bergida R., Rosen B. R., Savoy R. L. Auditory and visual word processing studied with fMRI. Hum Brain Mapp. 1999;7(1):15–28. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0193(1999)7:1<15::AID-HBM2>3.0.CO;2-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L., Dehaene S., Naccache L., Lehéricy S., Dehaene-Lambertz G., Hénaff M. A., Michel F. The visual word form area: spatial and temporal characterization of an initial stage of reading in normal subjects and posterior split-brain patients. Brain. 2000 Feb;123(Pt 2):291–307. doi: 10.1093/brain/123.2.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. W., Abernethy L. J. Cranial magnetic resonance imaging and school performance in very low birth weight infants in adolescence. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1999 Sep;81(2):F116–F121. doi: 10.1136/fn.81.2.f116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Démonet J. F., Chollet F., Ramsay S., Cardebat D., Nespoulous J. L., Wise R., Rascol A., Frackowiak R. The anatomy of phonological and semantic processing in normal subjects. Brain. 1992 Dec;115(Pt 6):1753–1768. doi: 10.1093/brain/115.6.1753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eken P., de Vries L. S., van der Graaf Y., Meiners L. C., van Nieuwenhuizen O. Haemorrhagic-ischaemic lesions of the neonatal brain: correlation between cerebral visual impairment, neurodevelopmental outcome and MRI in infancy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1995 Jan;37(1):41–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1995.tb11931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross S. J., Mettelman B. B., Dye T. D., Slagle T. A. Impact of family structure and stability on academic outcome in preterm children at 10 years of age. J Pediatr. 2001 Feb;138(2):169–175. doi: 10.1067/mpd.2001.111945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson L., Ek U., Fernell E., Flodmark O., Broberger U. Visual impairment in preterm children with periventricular leukomalacia--visual, cognitive and neuropaediatric characteristics related to cerebral imaging. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1996 Aug;38(8):724–735. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1996.tb12142.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Largo R. H., Molinari L., Comenale Pinto L., Weber M., Duc G. Language development of term and preterm children during the first five years of life. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1986 Jun;28(3):333–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1986.tb03882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas A., Morley R., Cole T. J., Gore S. M., Lucas P. J., Crowle P., Pearse R., Boon A. J., Powell R. Early diet in preterm babies and developmental status at 18 months. Lancet. 1990 Jun 23;335(8704):1477–1481. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93026-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride-Chang Catherine, Kail Robert V. Cross-cultural similarities in the predictors of reading acquisition. Child Dev. 2002 Sep-Oct;73(5):1392–1407. doi: 10.1111/1467-8624.00479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses P., Courchesne E., Stiles J., Trauner D., Egaas B., Edwards E. Regional size reduction in the human corpus callosum following pre- and perinatal brain injury. Cereb Cortex. 2000 Dec;10(12):1200–1210. doi: 10.1093/cercor/10.12.1200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nosarti Chiara, Al-Asady Mazin H. S., Frangou Sophia, Stewart Ann L., Rifkin Larry, Murray Robin M. Adolescents who were born very preterm have decreased brain volumes. Brain. 2002 Jul;125(Pt 7):1616–1623. doi: 10.1093/brain/awf157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa S., Lee T. M., Nayak A. S., Glynn P. Oxygenation-sensitive contrast in magnetic resonance image of rodent brain at high magnetic fields. Magn Reson Med. 1990 Apr;14(1):68–78. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910140108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulesu E., Connelly A., Frith C. D., Friston K. J., Heather J., Myers R., Gadian D. G., Frackowiak R. S. Functional MR imaging correlations with positron emission tomography. Initial experience using a cognitive activation paradigm on verbal working memory. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 1995 May;5(2):207–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulesu E., Frith C. D., Frackowiak R. S. The neural correlates of the verbal component of working memory. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):342–345. doi: 10.1038/362342a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen S. E., Fox P. T., Snyder A. Z., Raichle M. E. Activation of extrastriate and frontal cortical areas by visual words and word-like stimuli. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1041–1044. doi: 10.1126/science.2396097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson B. S., Vohr B., Staib L. H., Cannistraci C. J., Dolberg A., Schneider K. C., Katz K. H., Westerveld M., Sparrow S., Anderson A. W. Regional brain volume abnormalities and long-term cognitive outcome in preterm infants. JAMA. 2000 Oct 18;284(15):1939–1947. doi: 10.1001/jama.284.15.1939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. J., Wise R. J., Warburton E. A., Moore C. J., Howard D., Patterson K., Frackowiak R. S., Friston K. J. Hearing and saying. The functional neuro-anatomy of auditory word processing. Brain. 1996 Jun;119(Pt 3):919–931. doi: 10.1093/brain/119.3.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh K. R., Shaywitz B. A., Shaywitz S. E., Constable R. T., Skudlarski P., Fulbright R. K., Bronen R. A., Shankweiler D. P., Katz L., Fletcher J. M. Cerebral organization of component processes in reading. Brain. 1996 Aug;119(Pt 4):1221–1238. doi: 10.1093/brain/119.4.1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickards A. L., Ford G. W., Kitchen W. H., Doyle L. W., Lissenden J. V., Keith C. G. Extremely-low-birthweight infants: neurological, psychological, growth and health status beyond five years of age. Med J Aust. 1987 Nov 16;147(10):476–481. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1987.tb133638.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubia Katya. The dynamic approach to neurodevelopmental psychiatric disorders: use of fMRI combined with neuropsychology to elucidate the dynamics of psychiatric disorders, exemplified in ADHD and schizophrenia. Behav Brain Res. 2002 Mar 10;130(1-2):47–56. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(01)00437-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushe T. M., Rifkin L., Stewart A. L., Townsend J. P., Roth S. C., Wyatt J. S., Murray R. M. Neuropsychological outcome at adolescence of very preterm birth and its relation to brain structure. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2001 Apr;43(4):226–233. doi: 10.1017/s0012162201000433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sergent J., Zuck E., Lévesque M., MacDonald B. Positron emission tomography study of letter and object processing: empirical findings and methodological considerations. Cereb Cortex. 1992 Jan-Feb;2(1):68–80. doi: 10.1093/cercor/2.1.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A. L., Rifkin L., Amess P. N., Kirkbride V., Townsend J. P., Miller D. H., Lewis S. W., Kingsley D. P., Moseley I. F., Foster O. Brain structure and neurocognitive and behavioural function in adolescents who were born very preterm. Lancet. 1999 May 15;353(9165):1653–1657. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(98)07130-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart A., Hope P. L., Hamilton P., Costello A. M., Baudin J., Bradford B., Amiel-Tison C., Reynolds E. O. Prediction in very preterm infants of satisfactory neurodevelopmental progress at 12 months. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1988 Feb;30(1):53–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1988.tb04726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temple C. M., Ilsley J. Phonemic discrimination in callosal agenesis. Cortex. 1993 Jun;29(2):341–348. doi: 10.1016/s0010-9452(13)80187-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temple C. M., Jeeves M. A., Vilarroya O. O. Reading in callosal agenesis. Brain Lang. 1990 Aug;39(2):235–253. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(90)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temple C. M., Jeeves M. A., Vilarroya O. Ten pen men: rhyming skills in two children with callosal agenesis. Brain Lang. 1989 Nov;37(4):548–564. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(89)90111-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolke D., Meyer R. Cognitive status, language attainment, and prereading skills of 6-year-old very preterm children and their peers: the Bavarian Longitudinal Study. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1999 Feb;41(2):94–109. doi: 10.1017/s0012162299000201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatorre R. J., Evans A. C., Meyer E., Gjedde A. Lateralization of phonetic and pitch discrimination in speech processing. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):846–849. doi: 10.1126/science.1589767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]