Abstract
BACKGROUND—Endoscopic biliary manometry is useful in the assessment of patients with types II and III sphincter of Oddi dysfunction, but it is time consuming and invasive. AIM—To investigate the role of 99mTc-DISIDA scanning, with and without morphine provocation, as a non-invasive investigation in these patients compared with endoscopic biliary manometry. SUBJECTS AND METHODS—A total of 34 patients with a clinical diagnosis of type II (n=21) or III (n=13) sphincter of Oddi dysfunction were studied. Biliary scintigraphy with 100 MBq of 99mTc-DISIDA was carried out with and without morphine provocation (0.04 mg/kg intravenously) and time/activity curves were compared with the results of subsequent endoscopic biliary manometry. RESULTS—Eighteen (nine type II, nine type III) of the 34 (53%) patients had sphincter of Oddi basal pressures above the upper limit of normal (40 mm Hg). In the standard DISIDA scan without morphine, no significant differences were observed in time to maximal activity (Tmax) or percentage excretion at 45 or 60 minutes between those with normal and those with abnormal biliary manometry. However, following morphine provocation, median percentage excretion at 60 minutes was 4.9% in those with abnormal manometry and 28.2% in the normal manometry group (p=0.002). Using a cut off value of 15% excretion at 60 minutes, the sensitivity for detecting elevated sphincter of Oddi basal pressure by the morphine augmented DISIDA scan was 83% and specificity was 81%. Also, 14 of the 18 patients with abnormal manometry complained of biliary-type pain after morphine infusion compared with only two of 16 patients in the normal manometry group (p=0.001). CONCLUSIONS—99mTc-DISIDA with morphine provocation is a useful non-invasive investigation for types II and III sphincter of Oddi dysfunction to detect those with elevated sphincter basal pressures who may respond to endoscopic sphincterotomy. Keywords: sphincter of Oddi dysfunction; biliary manometry; 99mTc-DISIDA biliary scanning; radionuclide biliary imaging; biliary scintigraphy
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (126.1 KB).
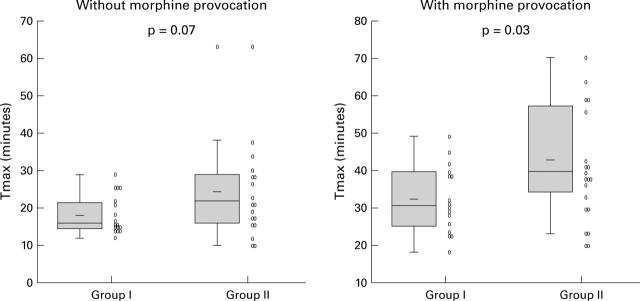
Figure 1 .
Time to maximal activity (Tmax) in patients with normal (group I) and elevated (>40 mm Hg) (group II) sphincter of Oddi basal pressure after 99mTc-DISIDA scanning, with and without morphine provocation. The shaded box indicates the interquartile range and the vertical line the upper and lower adjacent values (the upper or lower quartile ±1.5 times the interquartile range).
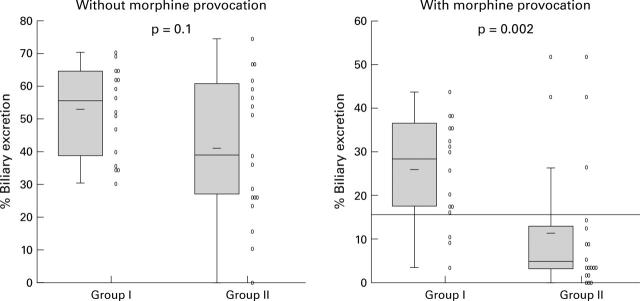
Figure 2 .
Percentage of maximal activity cleared from the biliary system at 60 minutes (E60) in patients with normal (group I) and elevated (>40 mm Hg) (group II) sphincter of Oddi basal pressure after 99mTc-DISIDA scanning, with and without morphine provocation. The shaded box indicates the interquartile range and the vertical line the upper and lower adjacent values (the upper or lower quartile ±1.5 times the interquartile range).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akita Y., Nimura Y., Yasui A. Percutaneous transhepatic manometry of sphincter of Oddi. Dig Dis Sci. 1991 Oct;36(10):1410–1417. doi: 10.1007/BF01296808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Meir S., Geenen J. E., Hogan W. J., Dodds W. J., Stewart E. T., Arndorfer R. C. Biliary and pancreatic duct pressures measured by ERCP manometry in patients with suspected papillary stenosis. Dig Dis Sci. 1979 Mar;24(3):209–213. doi: 10.1007/BF01308431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Meir S., Halpern Z., Bardan E., Gilat T. Frequency of papillary dysfunction among cholecystectomized patients. Hepatology. 1984 Mar-Apr;4(2):328–330. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botoman V. A., Kozarek R. A., Novell L. A., Patterson D. J., Ball T. J., Wechter D. G., Neal L. A. Long-term outcome after endoscopic sphincterotomy in patients with biliary colic and suspected sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Gastrointest Endosc. 1994 Mar-Apr;40(2 Pt 1):165–170. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(94)70160-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozkurt T., Orth K. H., Butsch B., Lux G. Long-term clinical outcome of post-cholecystectomy patients with biliary-type pain: results of manometry, non-invasive techniques and endoscopic sphincterotomy. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1996 Mar;8(3):245–249. doi: 10.1097/00042737-199603000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chessick K. C., Black S., Hoye S. J. Spasm and operative cholangiography. Arch Surg. 1975 Jan;110(1):53–57. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1975.01360070053009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coelho J. C., Wiederkehr J. C. Motility of Oddi's sphincter: recent developments and clinical applications. Am J Surg. 1996 Jul;172(1):48–51. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9610(97)89549-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedrick D. F., Tanner W. W., Bushkin F. L. Common bile duct pressure during enflurane anesthesia. Effects of morphine and subsequent naloxone. Arch Surg. 1980 Jul;115(7):820–822. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1980.01380070014003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullarton G. M., Allan A., Hilditch T., Murray W. R. Quantitative 99mTc-DISIDA scanning and endoscopic biliary manometry in sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Gut. 1988 Oct;29(10):1397–1401. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.10.1397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullarton G. M., Murray W. R. Evaluation of endoscopic sphincterotomy in sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Endoscopy. 1992 Mar;24(3):199–202. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1010462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geenen J. E., Hogan W. J., Dodds W. J., Toouli J., Venu R. P. The efficacy of endoscopic sphincterotomy after cholecystectomy in patients with sphincter-of-Oddi dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jan 12;320(2):82–87. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198901123200203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helm J. F., Venu R. P., Geenen J. E., Hogan W. J., Dodds W. J., Toouli J., Arndorfer R. C. Effects of morphine on the human sphincter of Oddi. Gut. 1988 Oct;29(10):1402–1407. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.10.1402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan W. J., Geenen J. E. Biliary dyskinesia. Endoscopy. 1988 Aug;20 (Suppl 1):179–183. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1018172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joehl R. J., Koch K. L., Nahrwold D. L. Opioid drugs cause bile duct obstruction during hepatobiliary scans. Am J Surg. 1984 Jan;147(1):134–138. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(84)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. G., Gregg J. A., Koroshetz A. M., Hill T. C., Clouse M. E. Sphincter of Oddi stenosis: diagnosis using hepatobiliary scintigraphy and endoscopic manometry. Radiology. 1985 Sep;156(3):793–796. doi: 10.1148/radiology.156.3.4023245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LoGiudice J. A., Geenen J. E., Hogan W. J., Dodds W. J. Efficacy of the morphine-prostigmin test for evaluating patients with suspected papillary stenosis. Dig Dis Sci. 1979 Jun;24(6):455–458. doi: 10.1007/BF01299827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meshkinpour H., Mollot M. Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction and unexplained abdominal pain: clinical and manometric study. Dig Dis Sci. 1992 Feb;37(2):257–261. doi: 10.1007/BF01308180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng N. J., Lai K. H., Tsay D. G., Liu R. S., Su K. L., Yeh S. H. Efficacy of quantitative cholescintigraphy in the diagnosis of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Nucl Med Commun. 1994 Nov;15(11):899–904. doi: 10.1097/00006231-199411000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts-Thomson I. C., Toouli J. Abnormal responses to morphine-neostigmine in patients with undefined biliary type pain. Gut. 1985 Dec;26(12):1367–1372. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.12.1367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolny P., Geenen J. E., Hogan W. J. Post-cholecystectomy patients with "objective signs" of partial bile outflow obstruction: clinical characteristics, sphincter of Oddi manometry findings, and results of therapy. Gastrointest Endosc. 1993 Nov-Dec;39(6):778–781. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(93)70264-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaffer E. A., Hershfield N. B., Logan K., Kloiber R. Cholescintigraphic detection of functional obstruction of the sphincter of Oddi. Effect of papillotomy. Gastroenterology. 1986 Mar;90(3):728–733. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)91130-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S., Troiano F. P., Hawes R. H., O'Connor K. W., Lehman G. A. Frequency of abnormal sphincter of Oddi manometry compared with the clinical suspicion of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Am J Gastroenterol. 1991 May;86(5):586–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sostre S., Kalloo A. N., Spiegler E. J., Camargo E. E., Wagner H. N., Jr A noninvasive test of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction in postcholecystectomy patients: the scintigraphic score. J Nucl Med. 1992 Jun;33(6):1216–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg W. M., Salvato R. F., Toskes P. P. The morphine-prostigmin provocative test--is it useful for making clinical decisions? Gastroenterology. 1980 Apr;78(4):728–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toouli J. Biliary motility disorders. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol. 1997 Dec;11(4):725–740. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3528(97)90018-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toouli J., Roberts-Thomson I. C., Dent J., Lee J. Manometric disorders in patients with suspected sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Gastroenterology. 1985 May;88(5 Pt 1):1243–1250. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80086-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viceconte G., Micheletti A. Endoscopic manometry of the sphincter of Oddi: its usefulness for the diagnosis and treatment of benign papillary stenosis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1995 Aug;30(8):797–803. doi: 10.3109/00365529509096330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrmann T., Wiemer K., Lembcke B., Caspary W. F., Jung M. Do patients with sphincter of Oddi dysfunction benefit from endoscopic sphincterotomy? A 5-year prospective trial. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1996 Mar;8(3):251–256. doi: 10.1097/00042737-199603000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]