Abstract
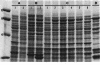
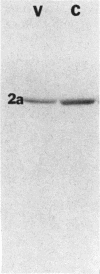
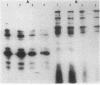
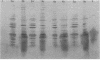
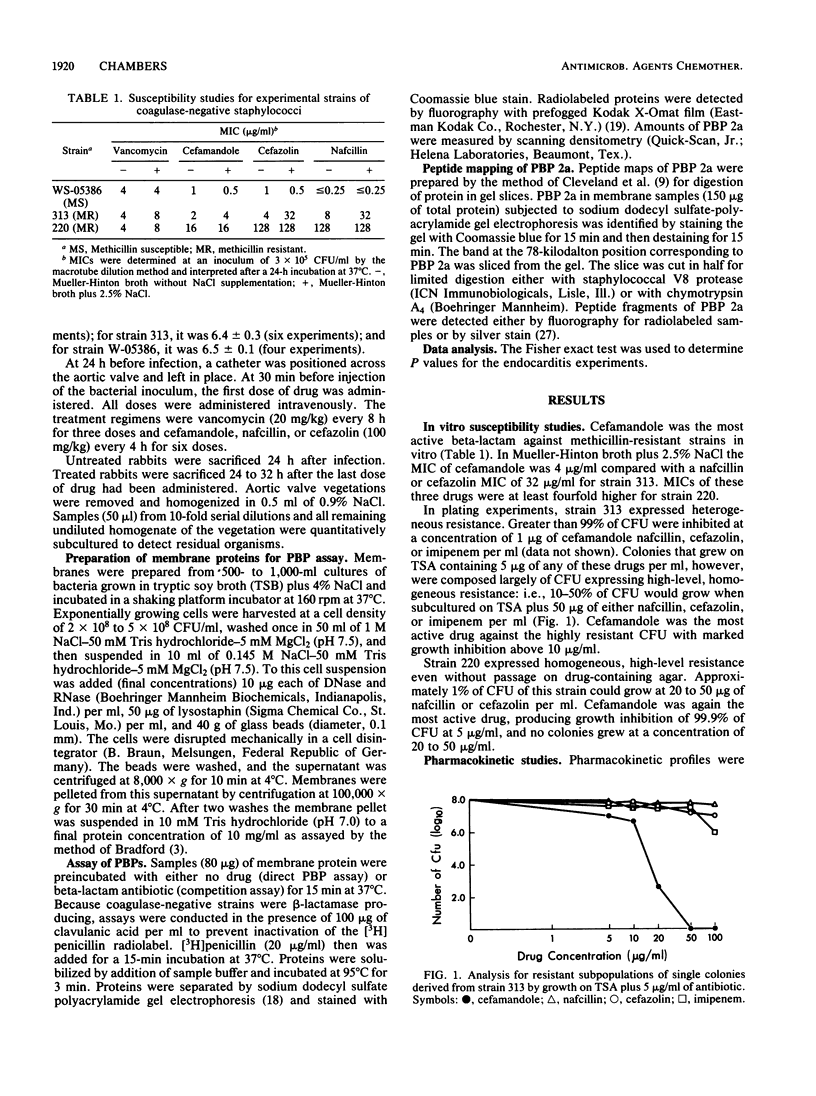
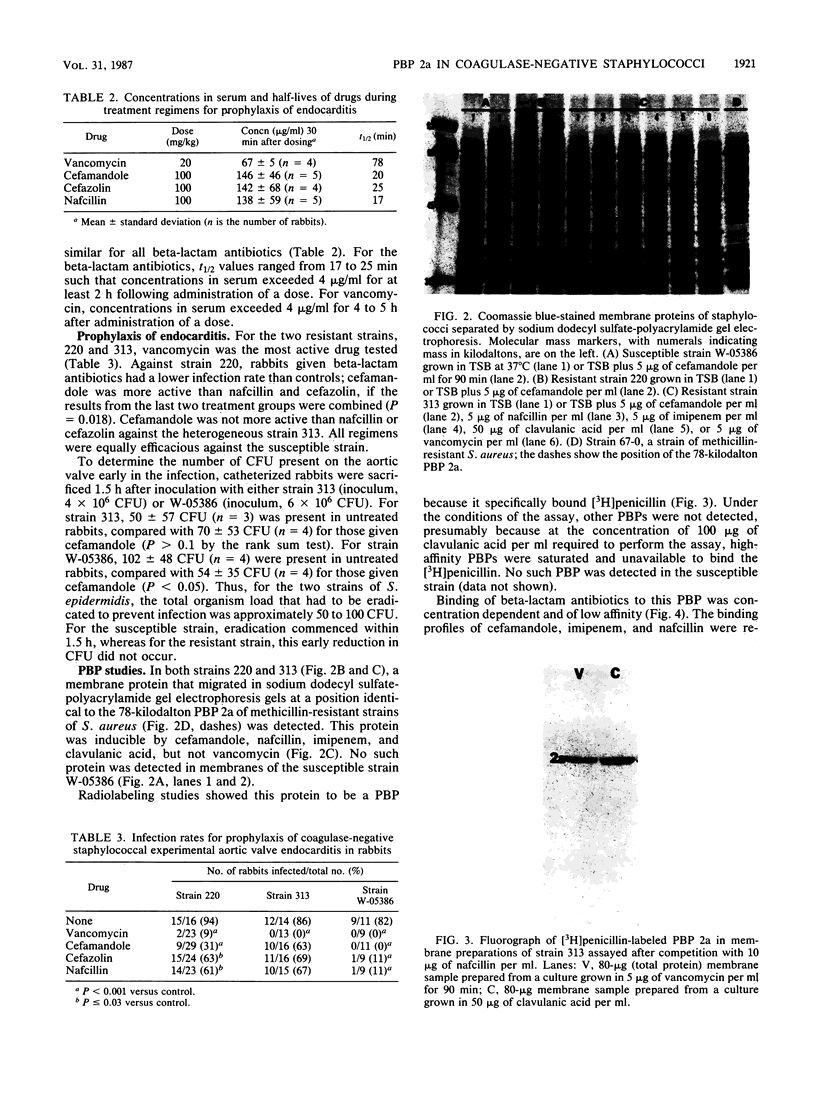
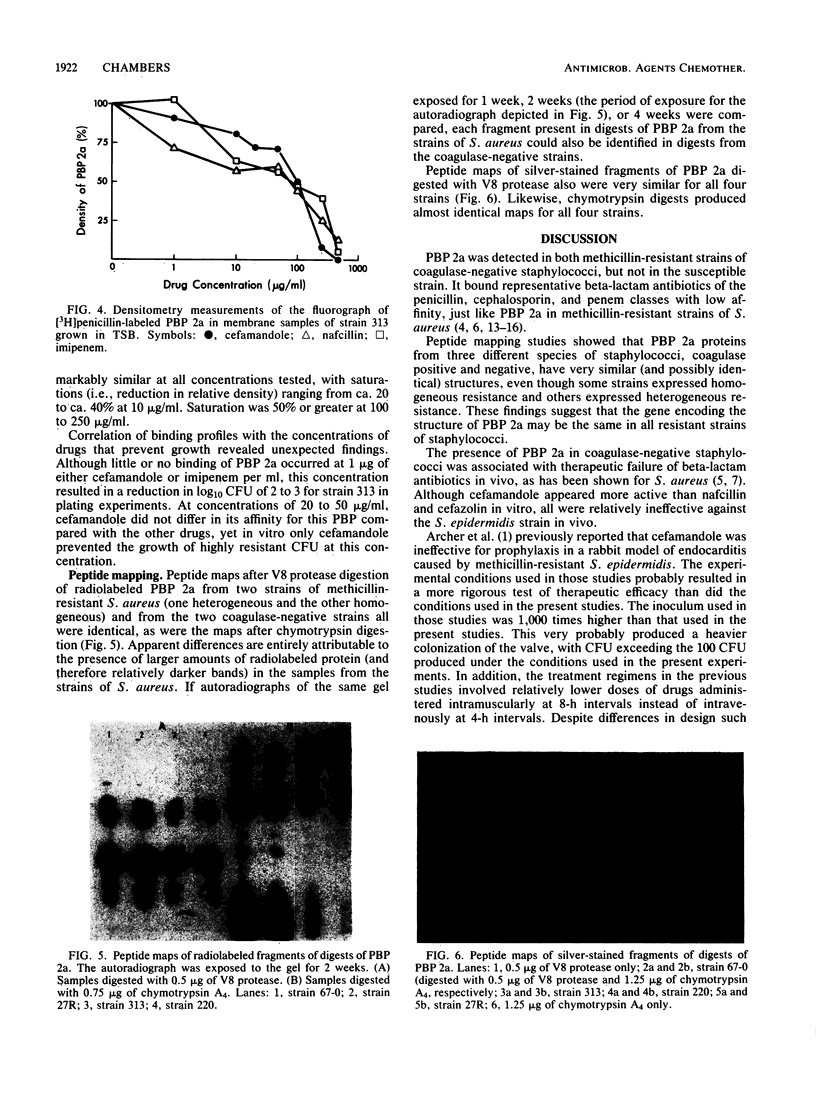
Strains of coagulase-negative staphylococci were tested for in vivo resistance in a rabbit model of prophylaxis of endocarditis. Regimens of nafcillin, cefazolin, cefamandole, and vancomycin were compared for efficacy in the prevention of infection caused by two methicillin-resistant strains and a susceptible strain. For the two resistant strains, vancomycin was the most effective drug tested. All regimens were effective against the susceptible strain. The two strains for which prophylaxis with beta-lactam antibiotics failed produced a beta-lactam antibiotic-inducible penicillin-binding protein (PBP) that comigrated in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels with the low-affinity PBP 2a that is associated with methicillin resistance in strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Like PBP 2a, this PBP had low binding affinity for beta-lactam antibiotics. Peptide maps after either V8 protease or chymotrypsin digestion of radiolabeled PBP 2a or silver-stained preparations were virtually identical to one another and to maps of PBP 2a from a heterogeneous and a homogeneous strain of S. aureus. Methicillin resistance in coagulase-negative staphylococci and therapeutic failure with beta-lactam antibiotics in vivo is associated with production of PBP 2a, which appears to be highly conserved structurally among different species of staphylococci.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer G. L., Vazquez G. J., Johnston J. L. Antibiotic prophylaxis of experimental endocarditis due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Nov;142(5):725–731. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.5.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddour L. M., Christensen G. D., Hester M. G., Bisno A. L. Production of experimental endocarditis by coagulase-negative staphylococci: variability in species virulence. J Infect Dis. 1984 Nov;150(5):721–727. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.5.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. F., Reynolds P. E. Intrinsic resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in Staphylococcus aureus. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 29;122(2):275–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80455-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers H. F., Hackbarth C. J., Drake T. A., Rusnak M. G., Sande M. A. Endocarditis due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in rabbits: expression of resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in vivo and in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jun;149(6):894–903. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.6.894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers H. F., Hartman B. J., Tomasz A. Increased amounts of a novel penicillin-binding protein in a strain of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus exposed to nafcillin. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):325–331. doi: 10.1172/JCI111965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers H. F., Miller M. H. Emergence of resistance to cephalothin and gentamicin during combination therapy for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis in rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):581–585. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Parisi J. T., Bisno A. L., Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Characterization of clinically significant strains of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):258–269. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.258-269.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng R. H., Wang C., Person A., Kiehn T. E., Armstrong D. Species identification of coagulase-negative staphylococcal isolates from blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Mar;15(3):439–442. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.3.439-442.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frongillo R. F., Bianchi P., Moretti A., Pasticci M. B., Ripa S., Pauluzzi S. Cross-resistance between methicillin and cephalosporins for staphylococci: a general assumption not true for cefamandole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 May;25(5):666–668. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.5.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frongillo R. F., Donati L., Federico G., Martino P., Moroni M., Ortona L., Palumbo M., Pasticci B. M., Pizzigallo E., Privitera G. Clinical comparative study on the activity of cefamandole in the treatment of serious staphylococcal infections caused by methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 May;29(5):789–796. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.5.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopapadakou N. H., Liu F. Y. Binding of beta-lactam antibiotics to penicillin-binding proteins of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus faecalis: relation to antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):834–836. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman B. J., Tomasz A. Expression of methicillin resistance in heterogeneous strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):85–92. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman B. J., Tomasz A. Low-affinity penicillin-binding protein associated with beta-lactam resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):513–516. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.513-516.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laverdiere M., Peterson P., Verhoef J., Williams D. N., Sabath L. D. In vitro activity of cephalosporins against methicillin-resistant, coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Infect Dis. 1978 Mar;137(3):245–250. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.3.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman B. B., Freedman L. R. Experimental endocarditis. II. Staphylococcal infection of the aortic valve following placement of a polyethylene catheter in the left side of the heart. Yale J Biol Med. 1971 Oct;44(2):206–213. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabath L. D., Wallace S. J. The problems of drug-resistant pathogenic bacteria. Factors influencing methicillin resistance in staphylococci. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 11;182:258–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb30662.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornsberry C., McDougal L. K. Successful use of broth microdilution in susceptibility tests for methicillin-resistant (heteroresistant) staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Nov;18(5):1084–1091. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.5.1084-1091.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ubukata K., Yamashita N., Konno M. Occurrence of a beta-lactam-inducible penicillin-binding protein in methicillin-resistant staphylococci. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):851–857. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]