Abstract
A phenazine antibiotic (mp, 243 to 244 degrees C), isolated in a yield of 134 micrograms/ml from cultures of Pseudomonas fluorescens 2-79 (NRRL B-15132), was indistinguishable in all of its measured physicochemical (melting point, UV and infrared spectra, and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry data) and biological properties from synthetic phenazine-1-carboxylic acid. Gurusiddaiah et al. (S. Gurusiddaiah, D. M. Weller, A. Sarkar, and R. J. Cook, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 29:488-495, 1986) attributed a dimeric phenazine structure to an antibiotic with demonstrably similar properties obtained from the same bacterial strain. Direct comparison of the physicochemical properties of the authentic antibiotic obtained from D. M. Weller with synthetic phenazine-1-carboxylic acid and with the natural product from the present study established that all three samples were indistinguishable within the experimental error of each method. No evidence to support the existence of a biologically active dimeric species was obtained. Phenazine-1-carboxylic acid has a pKa of 4.24 +/- 0.01 (25 degrees C; I = 0.09), and its carboxylate anion shows no detectable antimicrobial activity compared with the active uncharged carboxylic acid species. These data suggest that phenazine-1-carboxylic acid is probably not an effective biological control agent for phytopathogens in environments with a pH greater than 7.
Full text
PDF
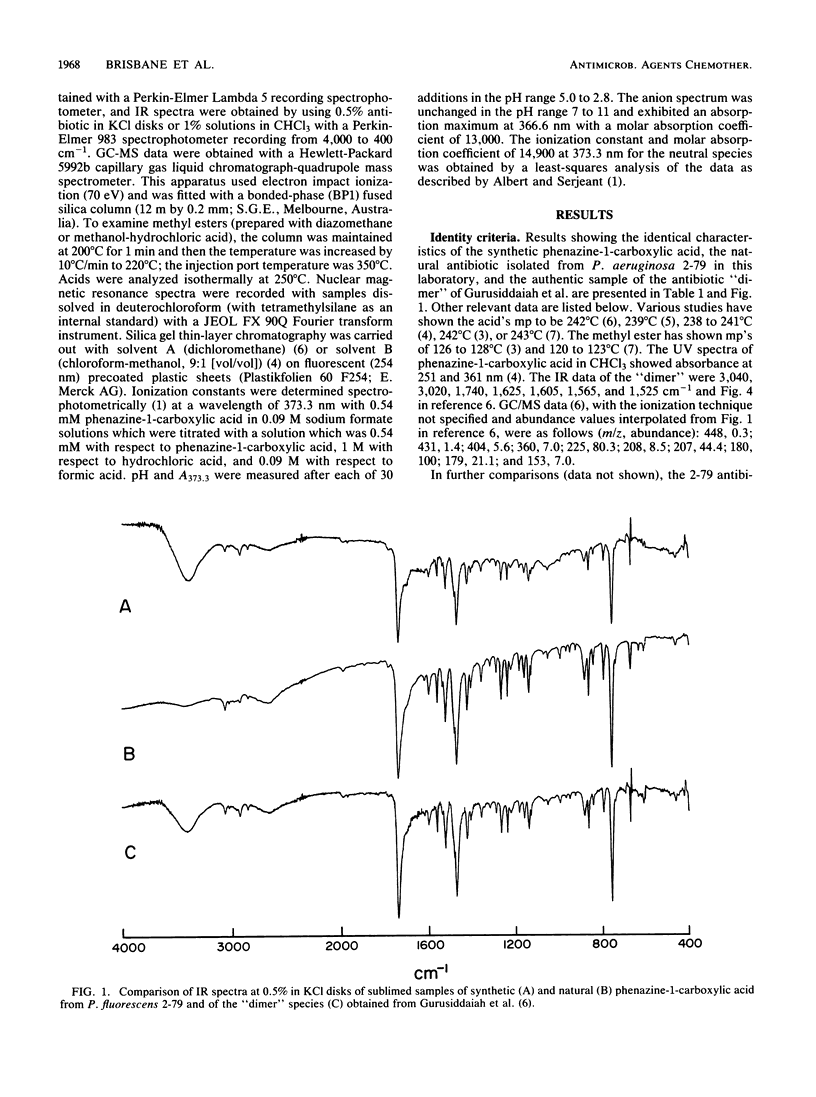
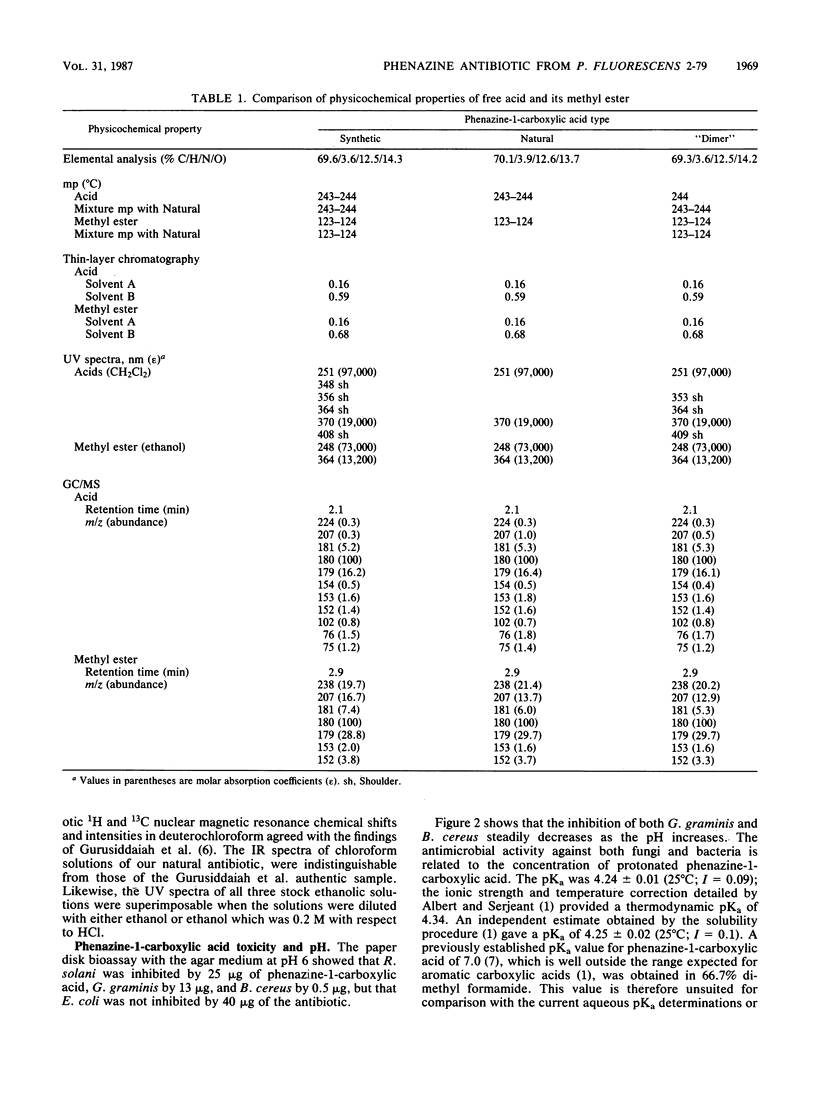


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang P. C., Blackwood A. C. Simultaneous production of three phenazine pigments by Pseudomonas aeruginosa Mac 436. Can J Microbiol. 1969 May;15(5):439–444. doi: 10.1139/m69-077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurusiddaiah S., Weller D. M., Sarkar A., Cook R. J. Characterization of an antibiotic produced by a strain of Pseudomonas fluorescens inhibitory to Gaeumannomyces graminis var. tritici and Pythium spp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):488–495. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson C. W., Martin W. J. Microwave oven for melting laboratory media. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Apr;7(4):401–402. doi: 10.1128/jcm.7.4.401-402.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]