Abstract
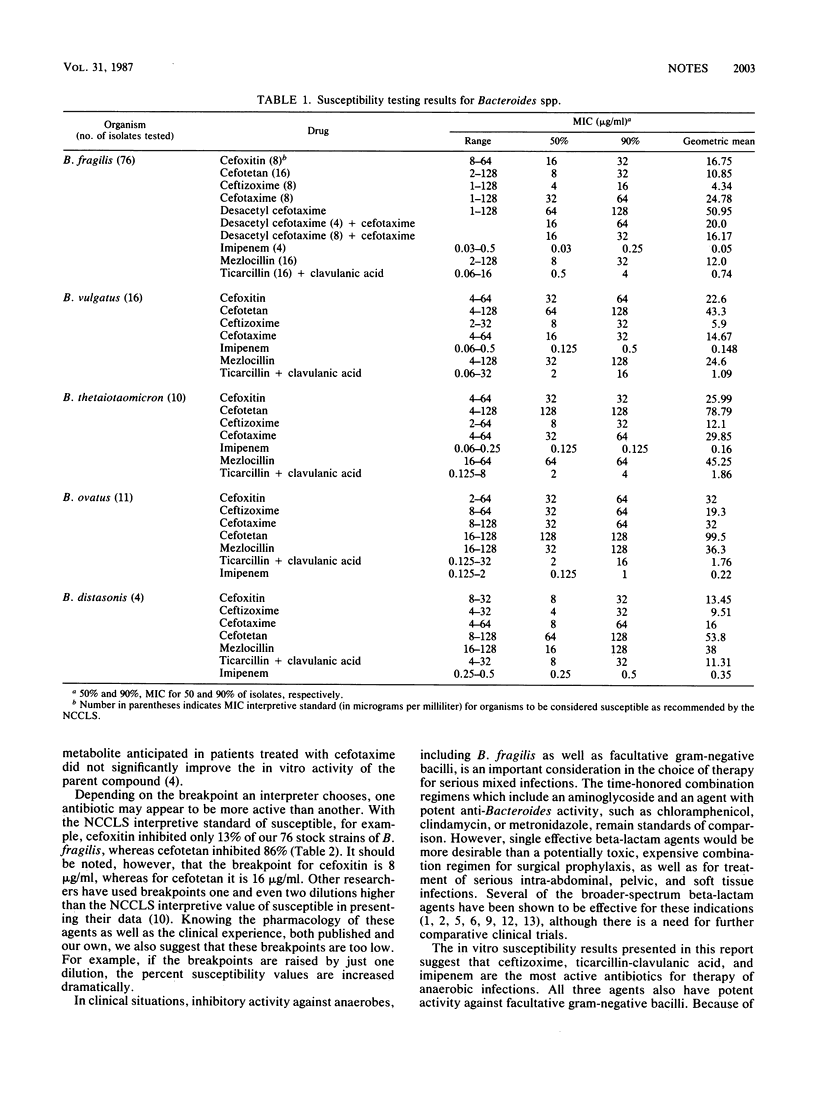
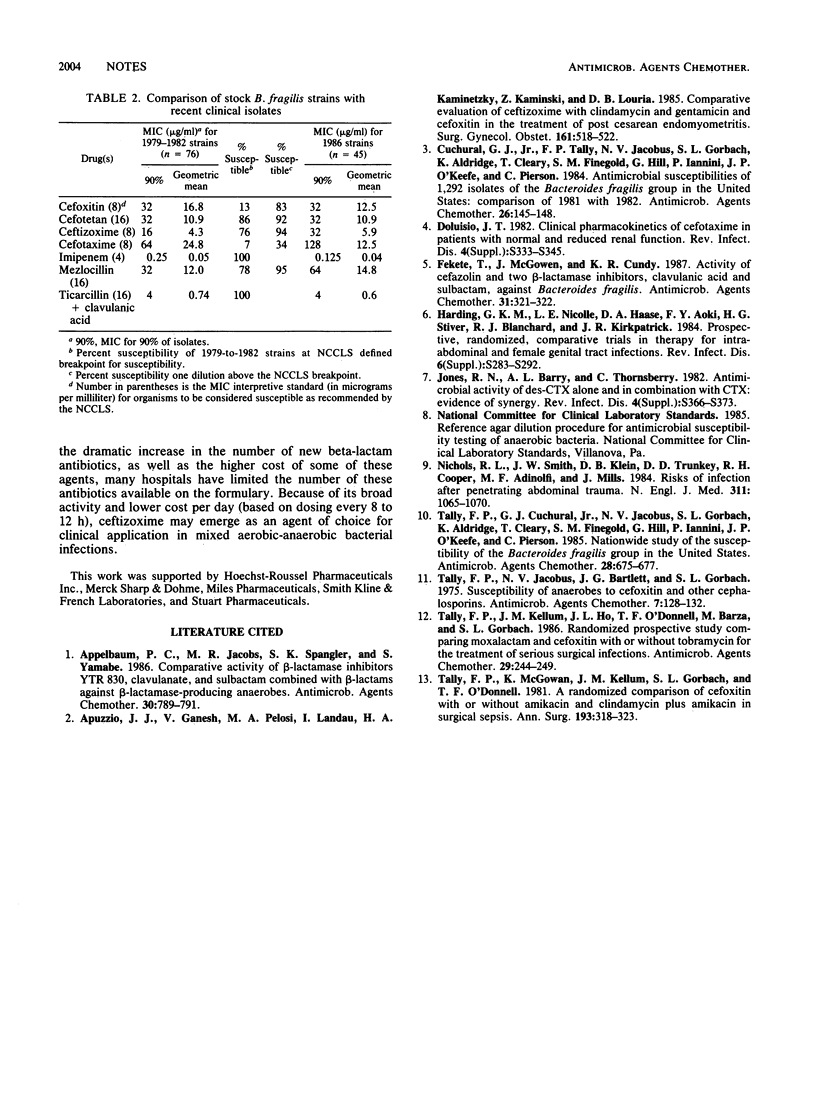
The in vitro activities of beta-lactam antibiotics against Bacteroides fragilis and B. fragilis group isolates are presented. Clinical isolates from 1986 were compared with strains from 1979 to 1982. Imipenem, ticarcillin-clavulanic acid, and ceftizoxime were the most active agents. Cefotetan was equivalent to cefoxitin against B. fragilis but less active against B. fragilis group isolates. Enhancement of cefotaxime by its desacetyl metabolite was minimal.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appelbaum P. C., Jacobs M. R., Spangler S. K., Yamabe S. Comparative activity of beta-lactamase inhibitors YTR 830, clavulanate, and sulbactam combined with beta-lactams against beta-lactamase-producing anaerobes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):789–791. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apuzzio J. J., Ganesh V., Pelosi M. A., Landau I., Kaminetzky H. A., Kaminski Z., Louria D. B. Comparative clinical evaluation of ceftizoxime with clindamycin and gentamicin and cefoxitin in the treatment of postcesarean endomyometritis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1985 Dec;161(6):518–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuchural G. J., Jr, Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Gorbach S. L., Aldridge K., Cleary T., Finegold S. M., Hill G., Iannini P., O'Keefe J. P. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of 1,292 isolates of the Bacteroides fragilis group in the United States: comparison of 1981 with 1982. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):145–148. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doluisio J. T. Clinical pharmacokinetics of cefotaxime in patients with normal and reduced renal function. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Sep-Oct;4 (Suppl):S333–S345. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.supplement_2.s333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fekete T., McGowen J., Cundy K. R. Activity of cefazolin and two beta-lactamase inhibitors, clavulanic acid and sulbactam, against Bacteroides fragilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):321–322. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harding G. K., Nicolle L. E., Haase D. A., Aoki F. Y., Stiver H. G., Blanchard R. J., Kirkpatrick J. R. Prospective, randomized, comparative trials in the therapy for intraabdominal and female genital tract infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Mar-Apr;6 (Suppl 1):S283–S292. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.supplement_1.s283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Barry A. L., Thornsberry C. Antimicrobial activity of desacetylcefotaxime alone and in combination with cefotaxime: evidence of synergy. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Sep-Oct;4 (Suppl):S366–S373. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.supplement_2.s366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols R. L., Smith J. W., Klein D. B., Trunkey D. D., Cooper R. H., Adinolfi M. F., Mills J. Risk of infection after penetrating abdominal trauma. N Engl J Med. 1984 Oct 25;311(17):1065–1070. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198410253111701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Cuchural G. J., Jr, Jacobus N. V., Gorbach S. L., Aldridge K., Cleary T., Finegold S. M., Hill G., Iannini P., O'Keefe J. P. Nationwide study of the susceptibility of the Bacteroides fragilis group in the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):675–677. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Jacobus N. V., Bartlett J. G., Gorbach S. L. Susceptibility of anaerobes to cefoxitin and other cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Feb;7(2):128–132. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.2.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., Kellum J. M., Ho J. L., O'Donnell T. F., Barza M., Gorbach S. L. Randomized prospective study comparing moxalactam and cefoxitin with or without tobramycin for the treatment of serious surgical infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Feb;29(2):244–249. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.2.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tally F. P., McGowan K., Kellum J. M., Gorbach S. L., O'Donnell T. F. A randomized comparison of cefoxitin with or without amikacin and clindamycin plus amikacin in surgical sepsis. Ann Surg. 1981 Mar;193(3):318–323. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198103000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


