Abstract
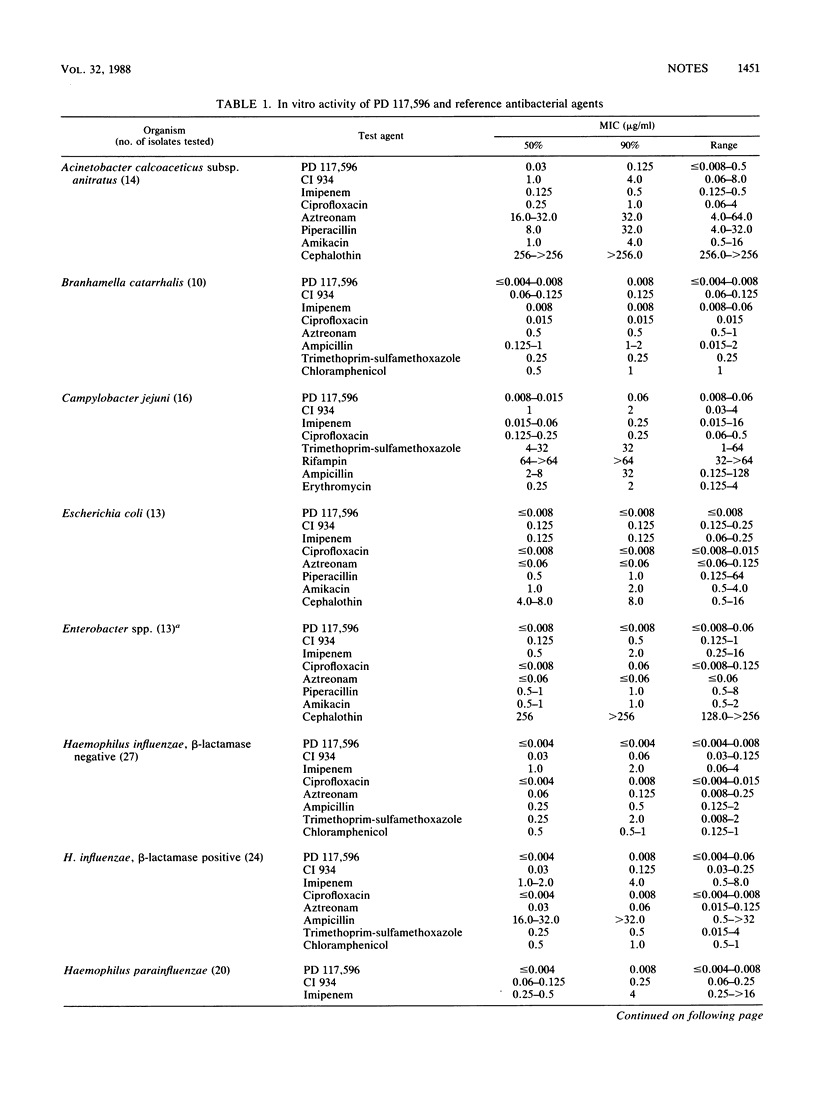
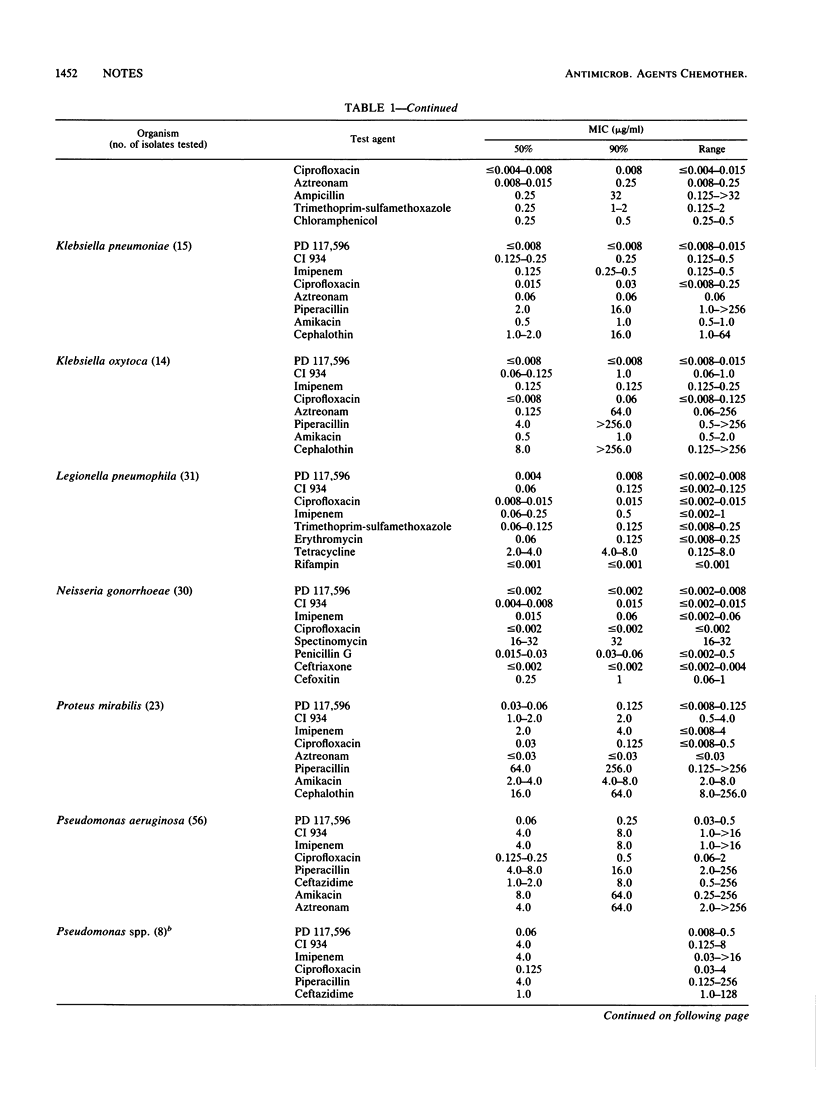
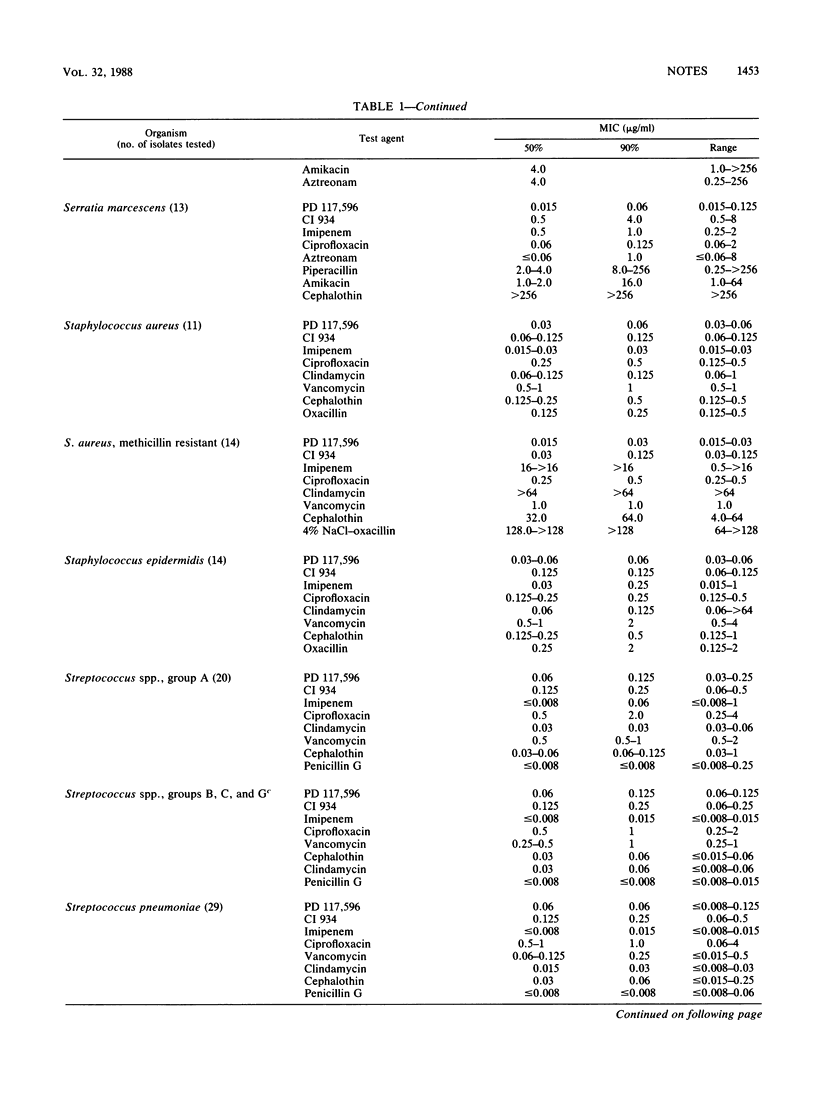
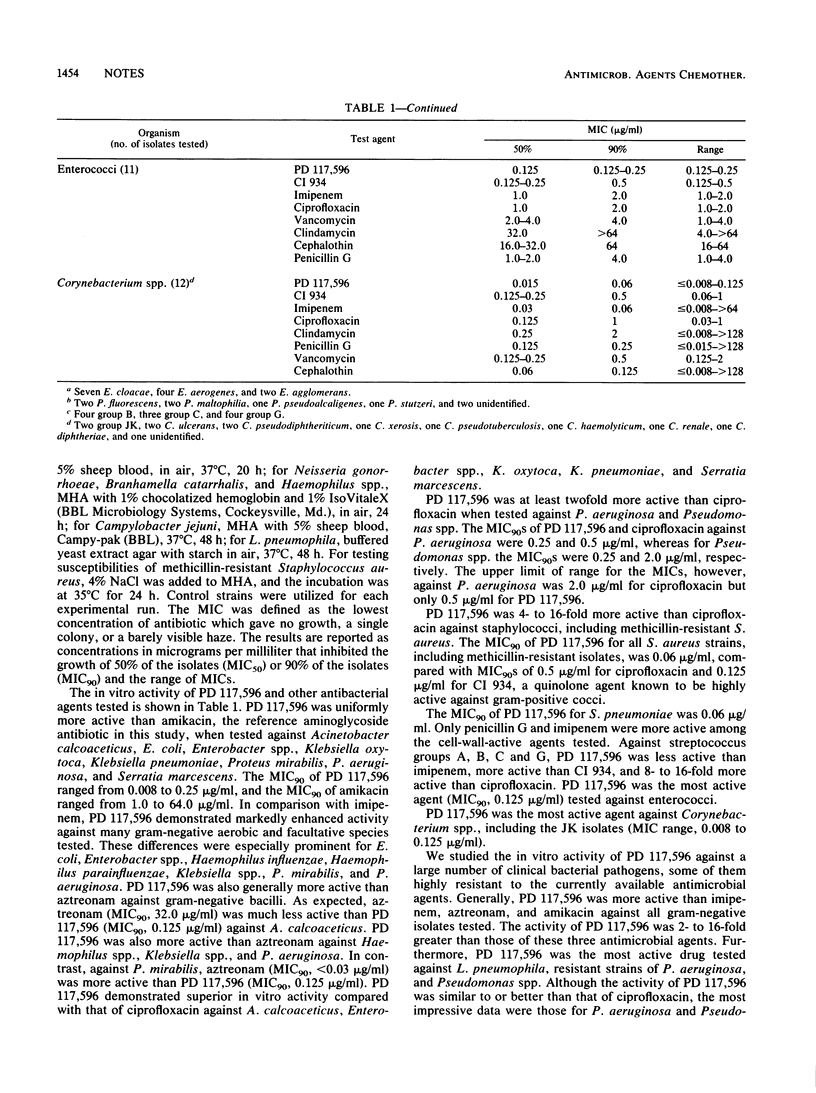
The in vitro activity of PD 117,596, a new fluoroquinolone antibiotic, was tested against 448 bacterial isolates (15 genera) by agar dilution (inoculum, 10(4) CFU per spot). The activity of PD 117,596 was compared with that of 15 antibiotics against 327 gram-negative strains and with that of 8 other antibiotics against 121 gram-positive strains. PD 117,596 demonstrated the best activity against Klebsiella spp., Enterobacter spp., Acinetobacter spp., Serratia marcescens, and Branhamella catarrhalis (MICs for 90% of the isolates [MIC90S], 0.008 to 0.25 microgram/ml). PD 117,596 (MIC90, 0.25 microgram/ml) was at least twofold more active than ciprofloxacin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas spp. PD 117,596 and ciprofloxacin were similar in activity against Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, Haemophilus influenzae, H. parainfluenzae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Legionella pneumophila, and Campylobacter jejuni (MIC90, 0.002 to 0.125 microgram/ml). PD 117,596 was more active than ciprofloxacin against streptococcal groups A, B, C, and G, S. pneumoniae, and enterococci (MIC90S, 0.06 to 0.125 microgram/ml). Against Staphylococcus aureus, including methicillin-resistant isolates, PD 117,596 (MIC90S, 0.03 to 0.06 microgram/ml) was 4- to 16-fold more active than ciprofloxacin and was most active against Corynebacterium spp. PD 117,596 appears to be the most active fluoroquinolone to date, with excellent activity against gram-positive bacteria and enhanced activity against gram-negative aerobic-facultative bacteria.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chin N. X., Neu H. C. Ciprofloxacin, a quinolone carboxylic acid compound active against aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):319–326. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. A., Griffin T. J., Bien P. A., Heifetz C. L., Domagala J. M. In vitro activity of CI-934, a quinolone carboxylic acid active against gram-positive and -negative bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Dec;28(6):766–772. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.6.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos G. M., Gardella A., Moellering R. C., Jr In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, a new carboxyquinoline antimicrobial agent. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):331–335. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S. The fluoroquinolones: pharmacology, clinical uses, and toxicities in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):716–721. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A., Shannon K., Phillips I. The in-vitro activities of enoxacin and ofloxacin compared with that of ciprofloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 May;15(5):551–558. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.5.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandell W., Neu H. C. In vitro activity of CI-934, a new quinolone, compared with that of other quinolones and other antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 May;29(5):852–857. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.5.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves D. S., Bywater M. J., Holt H. A., White L. O. In-vitro studies with ciprofloxacin, a new 4-quinolone compound. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Apr;13(4):333–346. doi: 10.1093/jac/13.4.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez J. P., Domagala J. M., Hagen S. E., Heifetz C. L., Hutt M. P., Nichols J. B., Trehan A. K. Quinolone antibacterial agents. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of 8-substituted quinoline-3-carboxylic acids and 1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acids. J Med Chem. 1988 May;31(5):983–991. doi: 10.1021/jm00400a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. P., Baltch A. L., Hammer M. C., Conroy J. V. In vitro activity of CI-934 and other antimicrobial agents against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Clin Ther. 1986;9(1):106–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


