Abstract
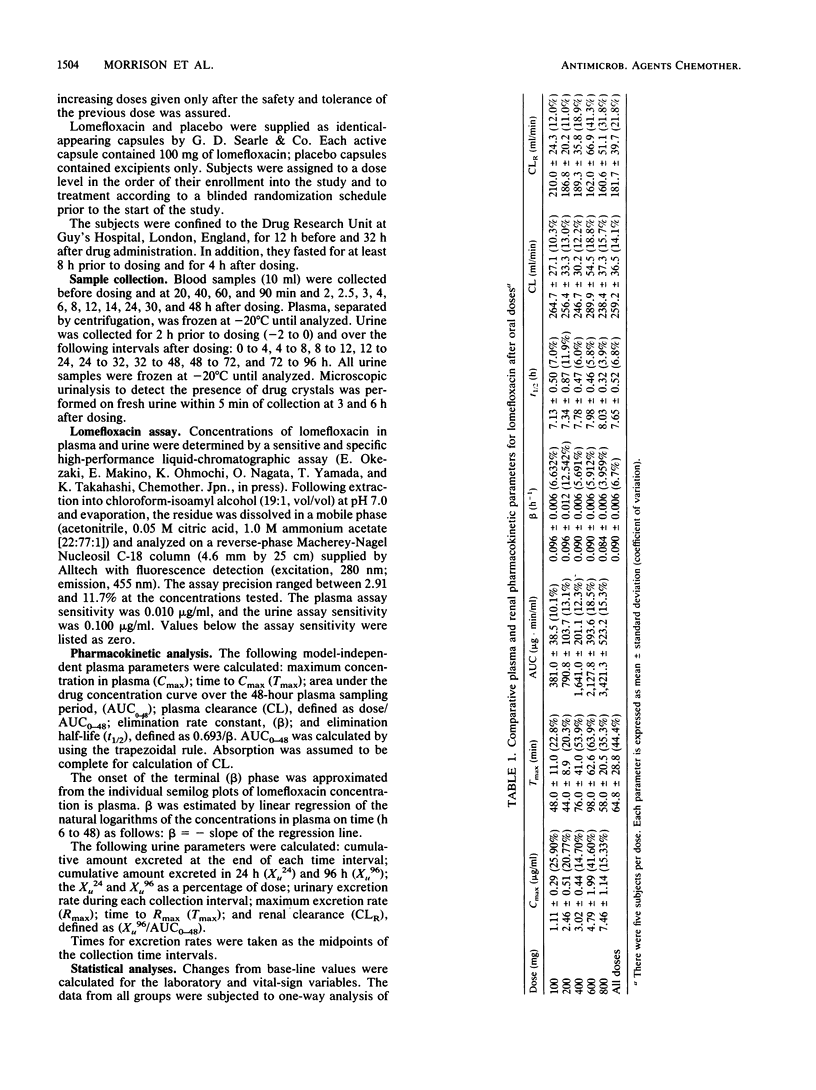
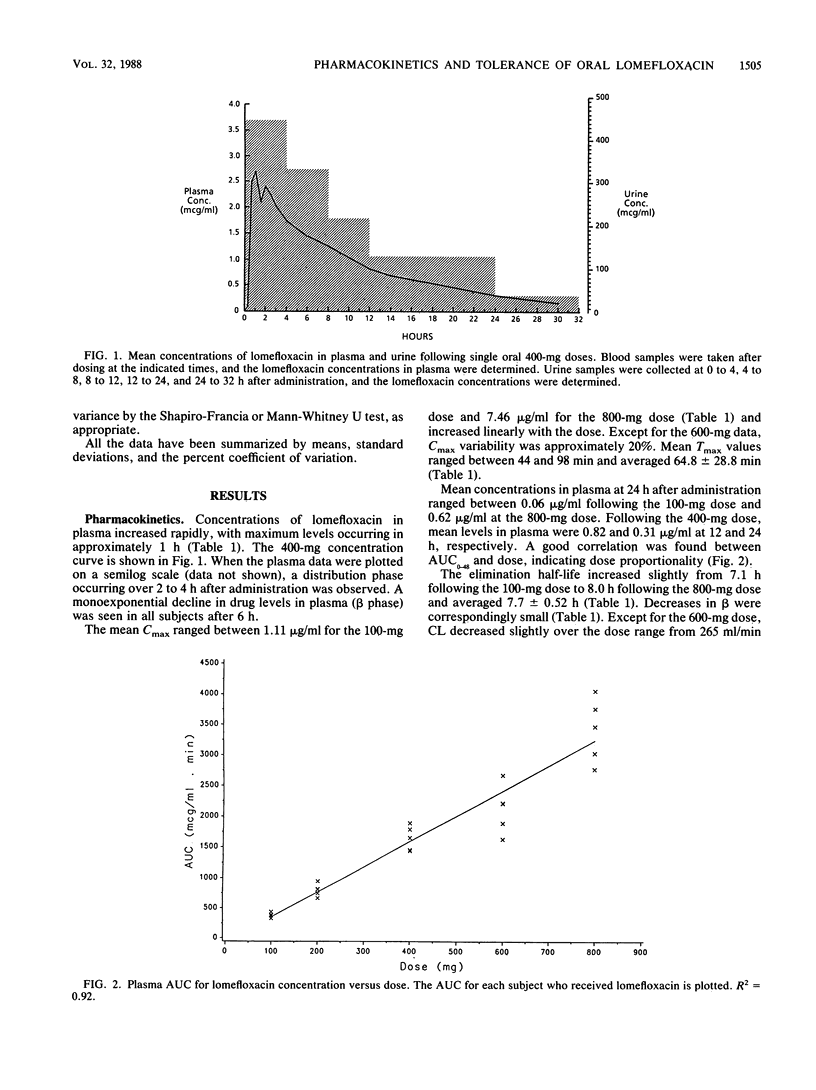
The pharmacokinetics of five dose levels of lomefloxacin (100, 200, 400, 600, and 800 mg) were examined in a single-dose, double-blind, placebo-controlled study involving 40 subjects. There were eight subjects in each group: five received active drug and three received placebo; each subject was given only one dose. All subjects completed the study, and lomefloxacin was well tolerated at all doses. No drug crystals were noted in the urine at 3 and 6 h after the dose. The mean maximum concentration in serum (Cmax) ranged from 1.11 to 7.46 micrograms/ml for the 100- to 800-mg doses, respectively, and the AUC increased proportionally with the dose. The mean time to Cmax (Tmax) values averaged 64.8 +/- 28.8 min. The elimination half-life and plasma clearance averaged 7.7 +/- 0.52 h and 259 +/- 37 ml/min, respectively. Mean concentrations in urine were highest during the first 4 h after the dose and ranged from 104 to 713 micrograms/ml following the 100- and 800-mg doses, respectively. Concentrations above 20 micrograms/ml in urine were observed in most subjects over 24 h at the three lower doses and averaged over 120 micrograms/ml during the 12- to 24-h interval at the 400-mg dose, thus supporting once-per-day dosing. Excretion rates from urine and the cumulative amount excreted increased in a dose-related fashion. Renal clearance decreased moderately at the higher doses. Thus, lomefloxacin was well tolerated, and dose proportionality was demonstrated by most pharmacokinetic parameters. The 400-mg dose produced concentrations in plasma and urine above the MIC for susceptible pathogens.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hirose T., Okezaki E., Kato H., Ito Y., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro and in vivo activity of NY-198, a new difluorinated quinolone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jun;31(6):854–859. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.6.854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lode H., Höffken G., Olschewski P., Sievers B., Kirch A., Borner K., Koeppe P. Pharmacokinetics of ofloxacin after parenteral and oral administration. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1338–1342. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson B. N., Boppana V. K., Vlasses P. H., Rotmensch H. H., Ferguson R. K. Norfloxacin disposition after sequentially increasing oral doses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Feb;23(2):284–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.2.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglione T. A., Raffalovich A. C., Poynor W. J., Espinel-Ingroff A., Kerkering T. M. Pharmacokinetics and tolerance of ciprofloxacin after sequential increasing oral doses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jan;29(1):62–66. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorsteinsson S. B., Bergan T., Oddsdottir S., Rohwedder R., Holm R. Crystalluria and ciprofloxacin, influence of urinary pH and hydration. Chemotherapy. 1986;32(5):408–417. doi: 10.1159/000238444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijnands W. J., Vree T. B., Baars A. M., van Herwaarden C. L. Steady-state kinetics of the quinolone derivatives ofloxacin, enoxacin, ciprofloxacin and pefloxacin during maintenance treatment with theophylline. Drugs. 1987;34 (Suppl 1):159–169. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198700341-00034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Lockley R., Webberly M., Adhami Z. N. The pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of enoxacin and norfloxacin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Sep;14 (Suppl 100):75–81. doi: 10.1093/jac/14.suppl_c.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf R., Eberl R., Dunky A., Mertz N., Chang T., Goulet J. R., Latts J. The clinical pharmacokinetics and tolerance of enoxacin in healthy volunteers. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984 Sep;14 (Suppl 100):63–69. doi: 10.1093/jac/14.suppl_c.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


