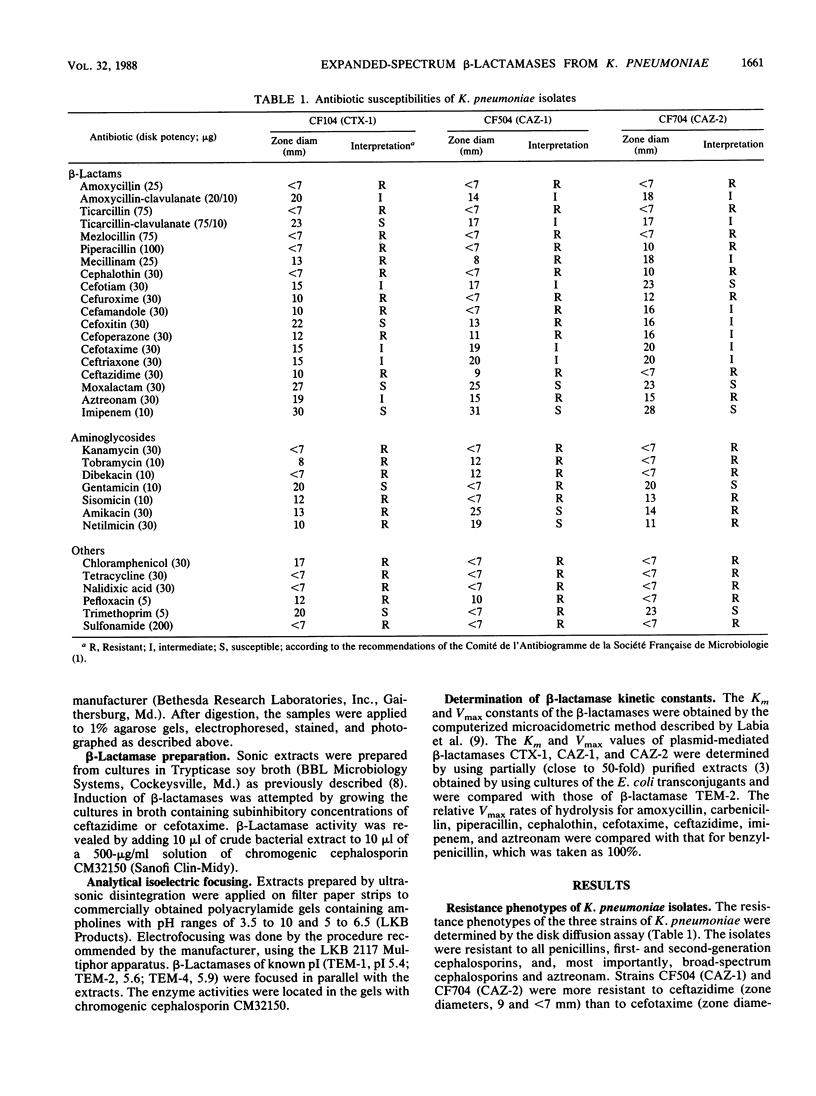
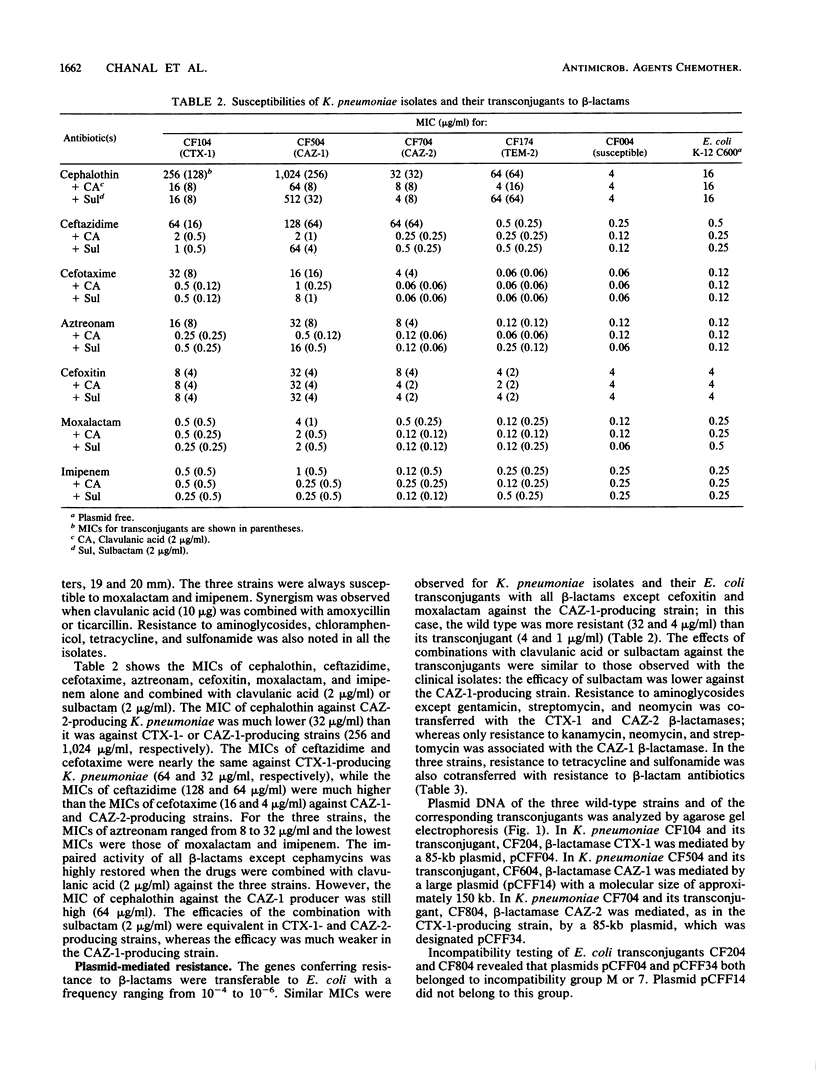
Abstract
Infections caused by strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae resistant to broad-spectrum cephalosporins have been observed recently in hospitals in Clermont-Ferrand, France. beta-Lactam resistance resulted primarily from the plasmid-mediated, expanded-spectrum CTX-1 beta-lactamase. Furthermore, since 1987 some K. pneumoniae isolates more resistant to ceftazidime than to other cephalosporins have been observed. This new resistance phenotype was the result of the production of ceftazidimase CAZ-1 and, more recently, CAZ-2. As in CTX-1-producing strains, resistance to beta-lactams resulting from CAZ-2 was associated with resistance to aminoglycosides except gentamicin, sulfonamide, and tetracycline and was transferable to Escherichia coli by conjugation. Agarose gel electrophoresis of plasmid DNA from wild-type strains and transconjugants indicated that CAZ-2 production was mediated by a plasmid of 85 kilobases highly related to plasmid pCFF04 coding for CTX-1 beta-lactamase. The isoelectric point, close to 6.0, of this novel enzyme differed from those of CTX-1 and CAZ-1. Like CAZ-1, the CAZ-2 enzyme efficiently hydrolyzed ceftazidime and aztreonam, but as with CTX-1, cefotaxime gave the maximal reaction rate. For each expanded-spectrum beta-lactamase, the activity of broad-spectrum cephalosporins was restored by clavulanic acid or sulbactam.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barthélémy M., Peduzzi J., Verchère-Beaur C., Ben Yaghlane H., Labia R. Purification and biochemical properties of Pitton's type 2 beta-lactamase (SHV-1). Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Jul-Aug;137B(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauernfeind A., Hörl G. Novel R-factor borne beta-lactamase of Escherichia coli confering resistance to cephalosporins. Infection. 1987 Jul-Aug;15(4):257–259. doi: 10.1007/BF01644127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabbert Y. A., Derlot E., Courvalin P. Etude du Centre National de Référence des Antibiotiques sur l'inoculum de l'antibiogramme. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1986 May;34(5):317–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabbert Y. A., Scavizzi M. R., Witchitz J. L., Gerbaud G. R., Bouanchaud D. H. Incompatibility groups and the classification of fi - resistance factors. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):666–675. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.666-675.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann L., Kitzis M. D., Billot-Klein D., Goldstein F., Tran Van Nhieu G., Lu T., Carlet J., Collatz E., Williamson R. Plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase (TEM-7) involved in resistance to ceftazidime and aztreonam. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):860–866. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R., Andrillon J., Le Goffic F. Computerized microacidimetric determination of beta lactamase Michaelis-Menten constants. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jun 15;33(1):42–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80154-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labia R. Comportement enzyme-substrat. Introduction de la notion de stabilité enzymatique dans le cas des beta lactamases. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1974 Jul 1;279(1):109–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesage D. D., Gerbaud G. R., Chabbert Y. A. Carte génétique et strucutre chez Escherichia coli K12 d'un plasmide de résistance isolé de Salmonella ordonez. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1975 May-Jun;126A(4):435–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit A., Sirot D. L., Chanal C. M., Sirot J. L., Labia R., Gerbaud G., Cluzel R. A. Novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae more resistant to ceftazidime than to other broad-spectrum cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):626–630. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirot D., Sirot J., Labia R., Morand A., Courvalin P., Darfeuille-Michaud A., Perroux R., Cluzel R. Transferable resistance to third-generation cephalosporins in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae: identification of CTX-1, a novel beta-lactamase. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Sep;20(3):323–334. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.3.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirot J., Chanal C., Petit A., Sirot D., Labia R., Gerbaud G. Klebsiella pneumoniae and other Enterobacteriaceae producing novel plasmid-mediated beta-lactamases markedly active against third-generation cephalosporins: epidemiologic studies. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):850–859. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirot J., Labia R., Thabaut A. Klebsiella pneumoniae strains more resistant to ceftazidime than to other third-generation cephalosporins. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Oct;20(4):611–612. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.4.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sougakoff W., Goussard S., Gerbaud G., Courvalin P. Plasmid-mediated resistance to third-generation cephalosporins caused by point mutations in TEM-type penicillinase genes. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):879–884. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer R. C., Wheat P. F., Winstanley T. G., Cox D. M., Plested S. J. Novel beta-lactamase in a clinical isolate of Klebsiella pneumoniae conferring unusual resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Dec;20(6):919–921. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.6.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]