Abstract
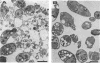
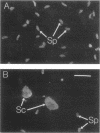
An in situ enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was developed to measure in vitro development of Eimeria tenella. The assay used a polyclonal, anti-merozoite serum produced by immunization with culture-derived, chromatographically purified merozoites. Although this antiserum cross-reacted with sporozoite-infected cultures (by indirect immunofluorescence and in situ enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay), it clearly distinguished the increase in antigen synthesized throughout intracellular growth. The assay can be used for high-throughput, anticoccidial drug screening, for which it gives quantitative results that are comparable to the published radiometric [( 3H]uracil incorporation) endpoint.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- André P. M., Narbonne C. H., Donnio P. Y., Ruffault A., Fauconnier B. Evaluation of herpes simplex virus susceptibility to acyclovir using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Ann Inst Pasteur Virol. 1988 Apr-Jun;139(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2617(88)80016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz F. E., Levin M. J. Use of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay performed directly on fixed infected cell monolayers for evaluating drugs against varicella-zoster virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Aug;28(2):207–210. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson P. L. Adaptation of enzyme-linked immunoassay for detection of avian and murine antibodies to Eimeria. Avian Dis. 1984 Oct-Dec;28(4):1115–1119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danforth H. D., McAndrew S. J. Hybridoma antibody characterization of stage-specific and stage-cross-reactive antigens of Eimeria tenella. J Parasitol. 1987 Oct;73(5):985–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Titto E. H., Araujo F. G. Enzyme immunoassay in cell monolayers for evaluation of in vitro activity of chemotherapeutic agents against Trypanosoma cruzi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Sep;39(3):274–281. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.39.274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derouin F., Chastang C. Enzyme immunoassay to assess effect of antimicrobial agents on Toxoplasma gondii in tissue culture. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Mar;32(3):303–307. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.3.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feit C., Bartal A. H., Tauber G., Dymbort G., Hirshaut Y. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the detection of monoclonal antibodies recognizing surface antigens expressed on viable cells. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Mar 25;58(3):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90358-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert J. M., Bhanushali J. K., McDougald L. R. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for coccidiosis in chickens: correlation of antibody levels with prior exposure to coccidia in the laboratory and in the field. Avian Dis. 1988 Oct-Dec;32(4):688–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingdale M. R., Kilejian A. Purification of Plasmodium lophurae exoerythrocytic merozoites by an ion exchange column. J Protozool. 1979 Nov;26(4):616–619. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1979.tb04207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J. O., Pai C. H. In situ enzyme immunoassay for antiviral susceptibility testing of respiratory syncytial virus. Am J Clin Pathol. 1989 Mar;91(3):323–326. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/91.3.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilejian A. A unique histidine-rich polypeptide from the malaria parasite, Plasmodium lophurae. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4650–4655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merli A., Canessa A., Melioli G. Enzyme immunoassay for evaluation of Toxoplasma gondii growth in tissue culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):88–91. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.88-91.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirabelli C. K., Bartus H., Bartus J. O., Johnson R., Mong S. M., Sung C. P., Crooke S. T. Application of a tissue culture microtiter test for the detection of cytotoxic agents from natural products. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1985 Jun;38(6):758–766. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.38.758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilheden E., Jeansson S., Vahlne A. Typing of herpes simplex virus by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;17(4):677–680. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.4.677-680.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onaga H., Saeki H., Hoshi S., Ueda S. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for serodiagnosis of coccidiosis in chickens: use of a single serum dilution. Avian Dis. 1986 Oct-Dec;30(4):658–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton W. H. Eimeria tenella: cultivation of the asexual stages in cultured animal cells. Science. 1965 Nov 5;150(3697):767–769. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3697.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner M. R., Antoniou D., Griffin J., Schlossman S. F., Lazarus H. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the detection of monoclonal antibodies to cell surface antigens on viable cells. J Immunol Methods. 1982;48(1):23–31. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90206-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabalais G. P., Levin M. J., Berkowitz F. E. Rapid herpes simplex virus susceptibility testing using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay performed in situ on fixed virus-infected monolayers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jun;31(6):946–948. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.6.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. E., Mockett A. P. Antibodies to coccidia: detection by the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Parasite Immunol. 1983 Sep;5(5):479–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1983.tb00762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saatara Oz H., Markham R. J., Bemrick W. J., Stromberg B. E. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and indirect haemagglutination techniques for measurement of antibody responses to Eimeria tenella in experimentally infected chickens. J Parasitol. 1984 Dec;70(6):859–863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmatz D. M., Crane M. S., Murray P. K. Eimeria tenella: parasite-specific incorporation of 3H-uracil as a quantitative measure of intracellular development. J Protozool. 1986 Feb;33(1):109–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1986.tb05568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmatz D. M., Crane M. S., Murray P. K. Purification of Eimeria sporozoites by DE-52 anion exchange chromatography. J Protozool. 1984 Feb;31(1):181–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1984.tb04314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strout R. G., Quellette C. A. Eimeria tenella: screening of chemotherapeutic compounds in cell cultures. Exp Parasitol. 1973 Jun;33(3):477–485. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(73)90115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]