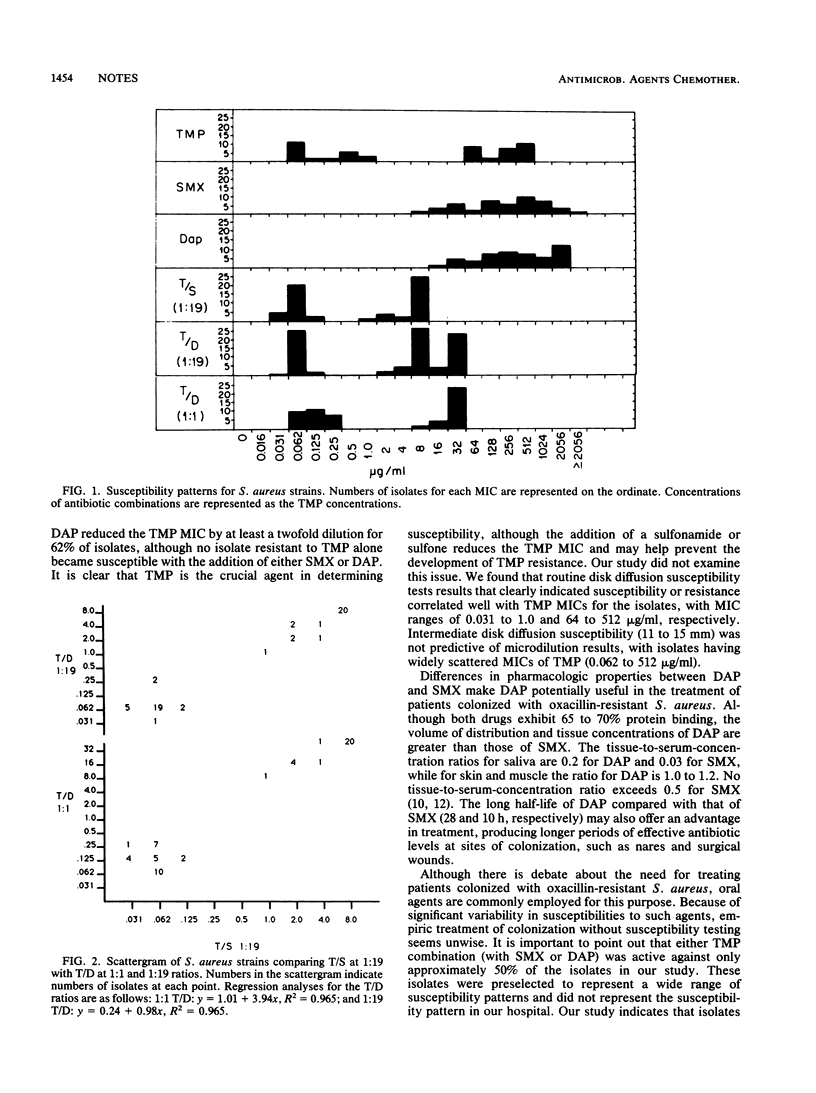
Abstract
The in vitro activity of trimethoprim plus dapsone against oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus was comparable to that of trimethoprim plus sulfamethoxazole. Because of its different pharmacologic properties, dapsone may be a useful agent in combination with trimethoprim for the treatment of patients colonized with oxacillin-resistant S. aureus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHATTERJEE K. R., PODDAR R. K. Preferential uptake of sulphone by affected skin tissue of leprosy patients as detected by a tracer method. Nature. 1956 Oct 13;178(4537):799–800. doi: 10.1038/178799b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGowin R. L. A review of therapeutic and hemolytic effects of dapsone. Arch Intern Med. 1967 Aug;120(2):242–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunberg E., Beskid G. Studies on the in vitro development of drug resistance of Proteeae to sulfonamides, trimethoprim and combinations of a sulfonamide and trimethoprim. Chemotherapy. 1977;23(5):309–313. doi: 10.1159/000222000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley R. W., Hightower A. W., Khabbaz R. F., Thornsberry C., Martone W. J., Allen J. R., Hughes J. M. The emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in United States hospitals. Possible role of the house staff-patient transfer circuit. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Sep;97(3):297–308. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-3-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormser G. P., Keusch G. T., Heel R. C. Co-trimoxazole (trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole): an updated review of its antibacterial activity and clinical efficacy. Drugs. 1982 Dec;24(6):459–518. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198224060-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


