Abstract
Background/Aims—Studies in animals suggest a physiological role for glucagon-like peptide-1-(7-36)-amide (GLP-1) in regulating satiety. The role of GLP-1 in regulating food intake in man has, however, not been investigated. Subjects—Sixteen healthy male subjects were examined in a double blind placebo controlled fashion. Methods—The effect of graded intravenous doses (0,0.375, 0.75, and 1.5 pmol/kg/min) of synthetic human GLP-1 on food intake and feelings of hunger and satiety was tested in healthy volunteers. Results—Graded GLP-1 infusions resulted in a dose dependent reduction in food intake (maximal inhibition 35%, p<0.001 v control) and a similar reduction in calorie intake (32%; p<0.001). Fluid ingestion was also reduced by GLP-1 (18% reduction, p<0.01). No overt side effects were produced by GLP-1, but subjects experienced less hunger and early fullness in the period before a meal during GLP-1 infusion at the highest dose (p<0.05). Conclusions—Intravenous infusions of GLP-1 decrease spontaneous food intake even at physiological plasma concentrations, implying an important role for GLP-1 in the regulation of the early satiety response in humans.
Keywords: glucagon-like peptide-1; satiety; food intake; hunger and fullness score
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (124.3 KB).
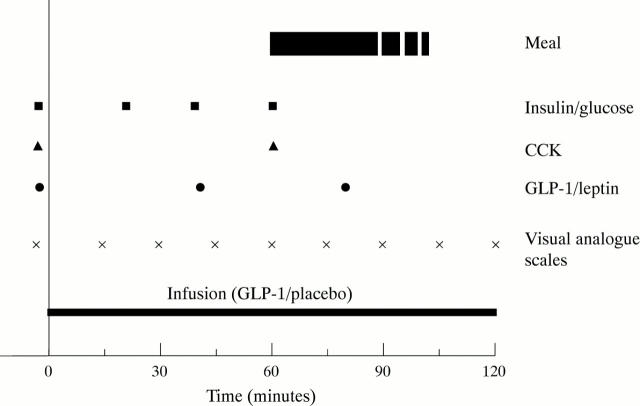
Figure 1 .
Daily time course of procedures.
Figure 2 .
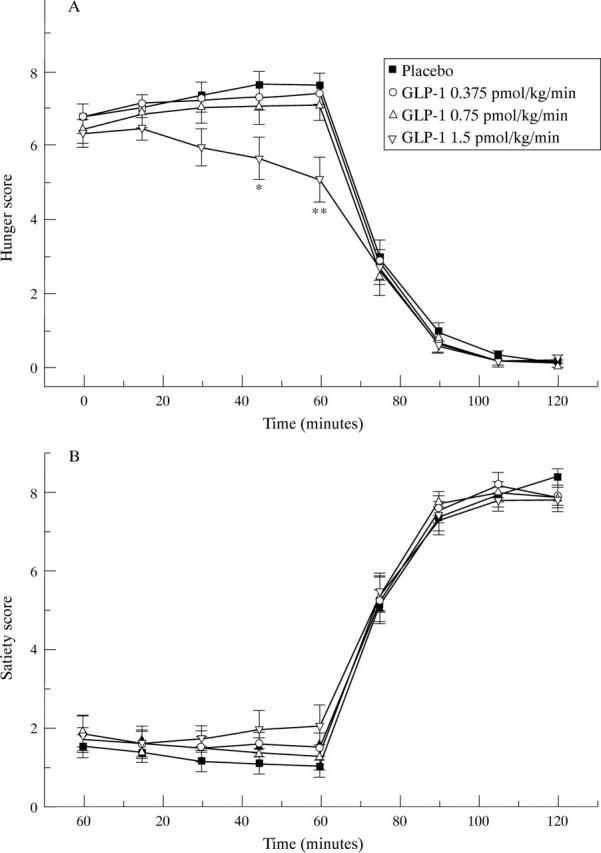
Subjective sensations of hunger (A) and fullness (B) experienced by healthy male subjects before and after food intake during intravenous infusion of 5% glucose (placebo) or one dose (0.375, 0.75, or 1.5 pmol/kg/min) of human glucagon-like peptide-1. Results are expressed as mean and SEM (n = 16). *p<0.05, **p<0.01 v control.
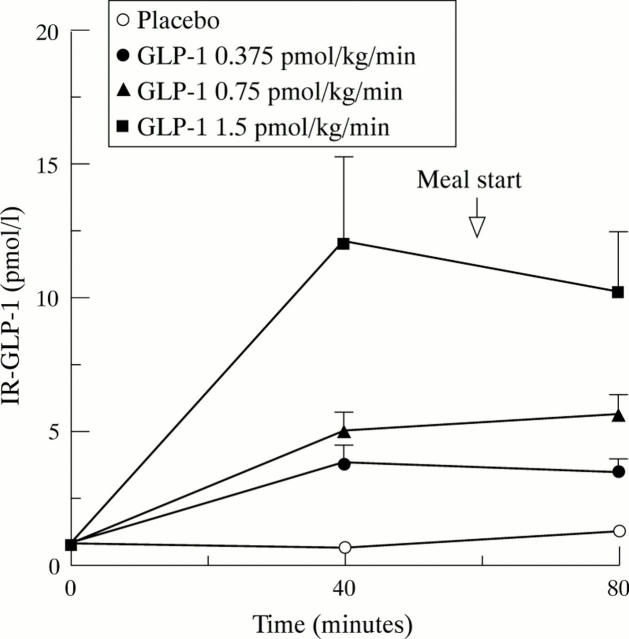
Figure 3 .
Immunoreactive glucagon-like peptide-1 (IR-GLP-1) measured in the plasma (pmol/l) in response to graded doses of intravenous GLP-1 or placebo in the preprandial period. Data are expressed as mean and SEM.
Figure 4 .
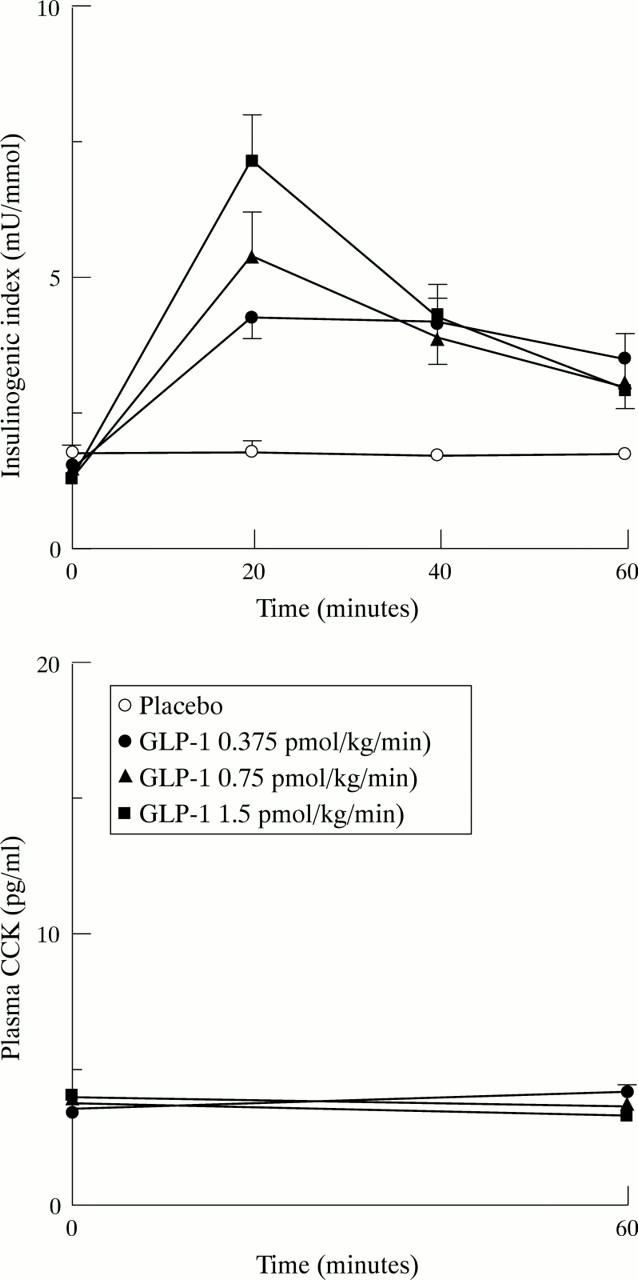
Insulinogenic index (insulin/glucose) and plasma cholecystokinin (CCK) levels (pmol/l) in response to graded doses of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) or placebo in the premeal period. Data are expressed as mean and SEM.
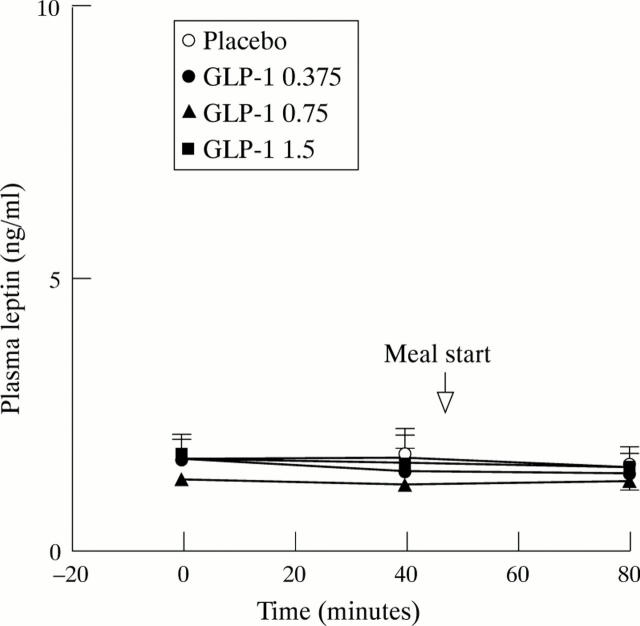
Figure 5 .
Leptin concentrations(ng/ml) measured in plasma in response to graded doses of intravenous glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) or placebo. Data are expressed as mean and SEM.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bado A., Rodriguez M., Lewin M. J., Martinez J., Dubrasquet M. Cholecystokinin suppresses food intake in cats: structure-activity characterization. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1988 Oct;31(2):297–303. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(88)90349-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne M. M., Göke B. Human studies with glucagon-like-peptide-1: potential of the gut hormone for clinical use. Diabet Med. 1996 Oct;13(10):854–860. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9136(199610)13:10<854::AID-DIA262>3.0.CO;2-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campfield L. A., Smith F. J., Guisez Y., Devos R., Burn P. Recombinant mouse OB protein: evidence for a peripheral signal linking adiposity and central neural networks. Science. 1995 Jul 28;269(5223):546–549. doi: 10.1126/science.7624778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drewe J., Gadient A., Rovati L. C., Beglinger C. Role of circulating cholecystokinin in control of fat-induced inhibition of food intake in humans. Gastroenterology. 1992 May;102(5):1654–1659. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91726-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint A., Raben A., Astrup A., Holst J. J. Glucagon-like peptide 1 promotes satiety and suppresses energy intake in humans. J Clin Invest. 1998 Feb 1;101(3):515–520. doi: 10.1172/JCI990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J., Smith G. P. Satiety: the roles of peptides from the stomach and the intestine. Fed Proc. 1986 Apr;45(5):1391–1395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J., Smith G. P. The actions of bombesin-like peptides on food intake. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;547:210–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb23889.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J., Young R. C., Smith G. P. Cholecystokinin decreases food intake in rats. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1973 Sep;84(3):488–495. doi: 10.1037/h0034870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutniak M. K., Larsson H., Heiber S. J., Juneskans O. T., Holst J. J., Ahrén B. Potential therapeutic levels of glucagon-like peptide I achieved in humans by a buccal tablet. Diabetes Care. 1996 Aug;19(8):843–848. doi: 10.2337/diacare.19.8.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutniak M., Orskov C., Holst J. J., Ahrén B., Efendic S. Antidiabetogenic effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 (7-36)amide in normal subjects and patients with diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1992 May 14;326(20):1316–1322. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199205143262003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutzwiller J. P., Drewe J., Hildebrand P., Rossi L., Lauper J. Z., Beglinger C. Effect of intravenous human gastrin-releasing peptide on food intake in humans. Gastroenterology. 1994 May;106(5):1168–1173. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göke R., Larsen P. J., Mikkelsen J. D., Sheikh S. P. Distribution of GLP-1 binding sites in the rat brain: evidence that exendin-4 is a ligand of brain GLP-1 binding sites. Eur J Neurosci. 1995 Nov 1;7(11):2294–2300. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1995.tb00650.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halaas J. L., Gajiwala K. S., Maffei M., Cohen S. L., Chait B. T., Rabinowitz D., Lallone R. L., Burley S. K., Friedman J. M. Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. Science. 1995 Jul 28;269(5223):543–546. doi: 10.1126/science.7624777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimura E., Shimizu F., Nishino T., Imagawa K., Tateishi K., Hamaoka T. Production of rabbit antibody specific for amino-terminal residues of cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK-8) by selective suppression of cross-reactive antibody response. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 30;55(3):375–387. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann C., Göke R., Richter G., Fehmann H. C., Arnold R., Göke B. Glucagon-like peptide-1 and glucose-dependent insulin-releasing polypeptide plasma levels in response to nutrients. Digestion. 1995;56(2):117–126. doi: 10.1159/000201231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörsch D., Göke R., Eissele R., Michel B., Göke B. Reciprocal cellular distribution of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) immunoreactivity and GLP-1 receptor mRNA in pancreatic islets of rat. Pancreas. 1997 Apr;14(3):290–294. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199704000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin S. L., Han V. K., Simmons J. G., Towle A. C., Lauder J. M., Lund P. K. Distribution of glucagonlike peptide I (GLP-I), glucagon, and glicentin in the rat brain: an immunocytochemical study. J Comp Neurol. 1988 May 22;271(4):519–532. doi: 10.1002/cne.902710405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissileff H. R., Pi-Sunyer F. X., Thornton J., Smith G. P. C-terminal octapeptide of cholecystokinin decreases food intake in man. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981 Feb;34(2):154–160. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/34.2.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieverse R. J., Jansen J. B., Masclee A. M., Lamers C. B. Satiety effects of cholecystokinin in humans. Gastroenterology. 1994 Jun;106(6):1451–1454. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90397-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nauck M. A., Heimesaat M. M., Orskov C., Holst J. J., Ebert R., Creutzfeldt W. Preserved incretin activity of glucagon-like peptide 1 [7-36 amide] but not of synthetic human gastric inhibitory polypeptide in patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):301–307. doi: 10.1172/JCI116186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelleymounter M. A., Cullen M. J., Baker M. B., Hecht R., Winters D., Boone T., Collins F. Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in ob/ob mice. Science. 1995 Jul 28;269(5223):540–543. doi: 10.1126/science.7624776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raybould H. E., Gayton R. J., Dockray G. J. Mechanisms of action of peripherally administered cholecystokinin octapeptide on brain stem neurons in the rat. J Neurosci. 1988 Aug;8(8):3018–3024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-08-03018.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salazar I., Vaillant C. Glucagon-like immunoreactivity in hypothalamic neurons of the rat. Cell Tissue Res. 1990 Aug;261(2):355–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00318677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirra J., Katschinski M., Weidmann C., Schäfer T., Wank U., Arnold R., Göke B. Gastric emptying and release of incretin hormones after glucose ingestion in humans. J Clin Invest. 1996 Jan 1;97(1):92–103. doi: 10.1172/JCI118411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirra J., Kuwert P., Wank U., Leicht P., Arnold R., Göke B., Katschinski M. Differential effects of subcutaneous GLP-1 on gastric emptying, antroduodenal motility, and pancreatic function in men. Proc Assoc Am Physicians. 1997 Jan;109(1):84–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidtler J., Dehne K., Allescher H. D., Schusdziarra V., Classen M., Holst J. J., Polack A., Schepp W. Rat parietal cell receptors for GLP-1-(7-36) amide: northern blot, cross-linking, and radioligand binding. Am J Physiol. 1994 Sep;267(3 Pt 1):G423–G432. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1994.267.3.G423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrocchi L. A., Brown T. J., MaClusky N., Brubaker P. L., Auerbach A. B., Joyner A. L., Drucker D. J. Glucose intolerance but normal satiety in mice with a null mutation in the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor gene. Nat Med. 1996 Nov;2(11):1254–1258. doi: 10.1038/nm1196-1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalev A., Vosmeer S., Keller U. Absence of short-term effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 and of hyperglycemia on plasma leptin levels in man. Metabolism. 1997 Jul;46(7):723–725. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(97)90112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver A. J., Flood J. F., Song A. M., Morley J. E. Evidence for a physiological role for CCK in the regulation of food intake in mice. Am J Physiol. 1989 Mar;256(3 Pt 2):R646–R652. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1989.256.3.R646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. F., Wilding J. P., Edwards C. M., Khan F. A., Ghatei M. A., Bloom S. R. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1): a trial of treatment in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Eur J Clin Invest. 1997 Jun;27(6):533–536. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2362.1997.1490691.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turton M. D., O'Shea D., Gunn I., Beak S. A., Edwards C. M., Meeran K., Choi S. J., Taylor G. M., Heath M. M., Lambert P. D. A role for glucagon-like peptide-1 in the central regulation of feeding. Nature. 1996 Jan 4;379(6560):69–72. doi: 10.1038/379069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uttenthal L. O., Blázquez E. Characterization of high-affinity receptors for truncated glucagon-like peptide-1 in rat gastric glands. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 12;262(1):139–141. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80173-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valverde I., Mérida E., Delgado E., Trapote M. A., Villanueva-Peñacarrillo M. L. Presence and characterization of glucagon-like peptide-1(7-36) amide receptors in solubilized membranes of rat adipose tissue. Endocrinology. 1993 Jan;132(1):75–79. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.1.8380388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch I. M., Sepple C. P., Read N. W. Comparisons of the effects on satiety and eating behaviour of infusion of lipid into the different regions of the small intestine. Gut. 1988 Mar;29(3):306–311. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.3.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch I., Saunders K., Read N. W. Effect of ileal and intravenous infusions of fat emulsions on feeding and satiety in human volunteers. Gastroenterology. 1985 Dec;89(6):1293–1297. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90645-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller A., Smith G. P., Gibbs J. Endogenous cholecystokinin reduces feeding in young rats. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1589–1591. doi: 10.1126/science.2321020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettergren A., Wøjdemann M., Meisner S., Stadil F., Holst J. J. The inhibitory effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) 7-36 amide on gastric acid secretion in humans depends on an intact vagal innervation. Gut. 1997 May;40(5):597–601. doi: 10.1136/gut.40.5.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]