Abstract
Background—The course of Crohn's disease is characterised by the occurrence of intestinal complications such as strictures, intra-abdominal fistulas, or abscesses. Standard diagnostic procedures may fail to show these complications, in particular fistulas. Aims—To test the value of transabdominal bowel sonography (TABS) for the detection of intestinal complications in Crohn's disease. Methods—TABS was prospectively performed in 213 patients with Crohn's disease in a university based inflammatory bowel disease referral centre. Thirty three underwent resective bowel surgery and were included in this study. The accuracy of TABS to detect strictures, intra-abdominal fistulas, or abscesses was compared with surgical and pathological findings. Results—TABS was able to identify strictures in 22/22 patients and to exclude it in 10/11 patients (100% sensitivity, 91% specificity). Fistulas were correctly identified in 20/23 patients and excluded in 9/10 patients (87% sensitivity, 90% specificity). Intra-abdominal abscesses were correctly detected in 9/9 patients and excluded in 22/24 patients (100% sensitivity, 92% specificity). Conclusions—In experienced hands TABS is an accurate method for the detection of intestinal complications in Crohn's disease. TABS is thus recommended as a primary investigative method for evaluation of severe Crohn's disease.
Keywords: Crohn's disease complications; fistula; stricture; abscess; bowel sonography
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (150.4 KB).
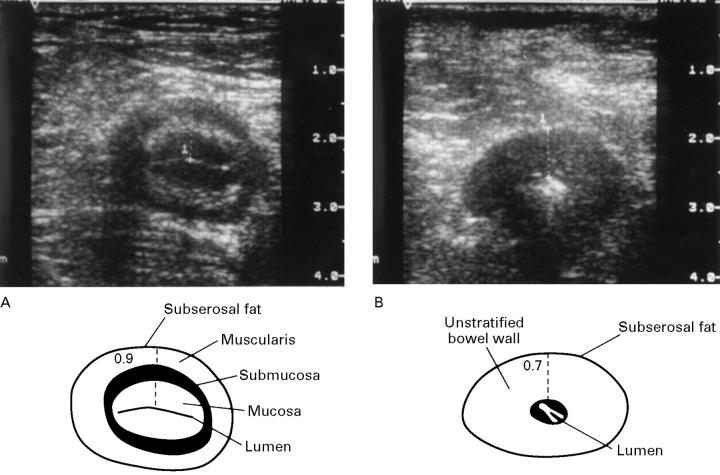
Figure 1 .
Transverse TABS section (using a 10-5 MHz array) through the terminal ileum of two patients, five years (A) and eight years (B) after ileocaecal resection. Both patients show significant bowel wall thickening, 0.9 cm (A) and 0.7 cm (B). In (A), note the four layers of a typical target lesion and the hyperechoic, linear shaped collapsed lumen of the gut. No significant luminal narrowing and no other complications are present. In (B), note the loss of stratification of the bowel wall echo pattern reflecting destruction of layers after long term inflammation. The central hyperechoic, point shaped lumen corresponds to a stricture.
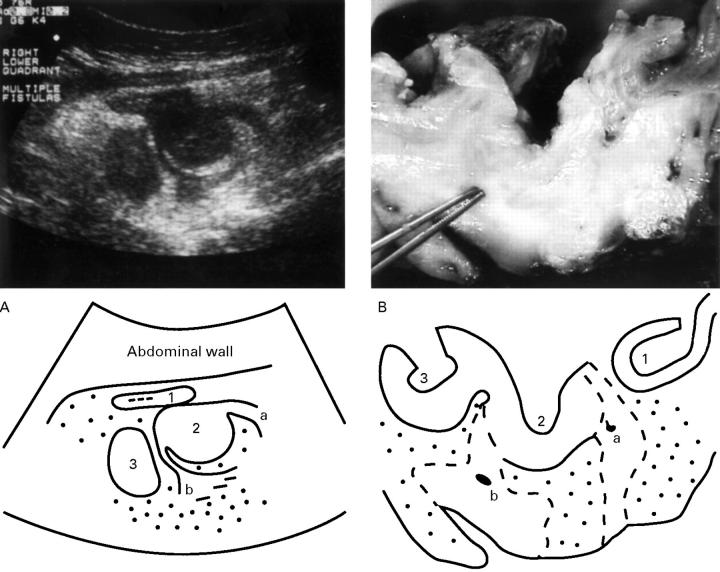
Figure 2 .
(A) Transverse TABS section (3.5 MHz array) through the right lower quadrant of a patient with Crohn's disease. Three adherent bowel loops of the terminal ileum (1, 2, 3, from oral to anal) are shown with hypoechoic peri-intestinal lesions (a, b) arising from loop 2 and hyperechoic wrapping mesentery (dotted area). Loop 1 is collapsed with only little thickening of the bowel wall (0.4 cm). Loops 2 and 3 show severe thickening of the bowel wall (1.2 cm and 1.0 cm), loss of bowel wall layering, and no detectable luminal hyperechoic content. These findings were regarded as high grade bowel obstruction of loops 2 and 3 with fistulas arising from loop 2. (B) Transverse section through the corresponding resection specimen after overnight fixation, longitudinal incision of the lumen, and unfolding of bowel loops (1, 2, 3, according to A) which resulted in rearrangement of loop 1. The forceps point into one of two fistulous tracts (a, b, according to A). Note perifistulous fibrotic tissue (broken lines) surrounded by fibrofatty proliferation of the mesentery (dotted area).
Figure 3 .
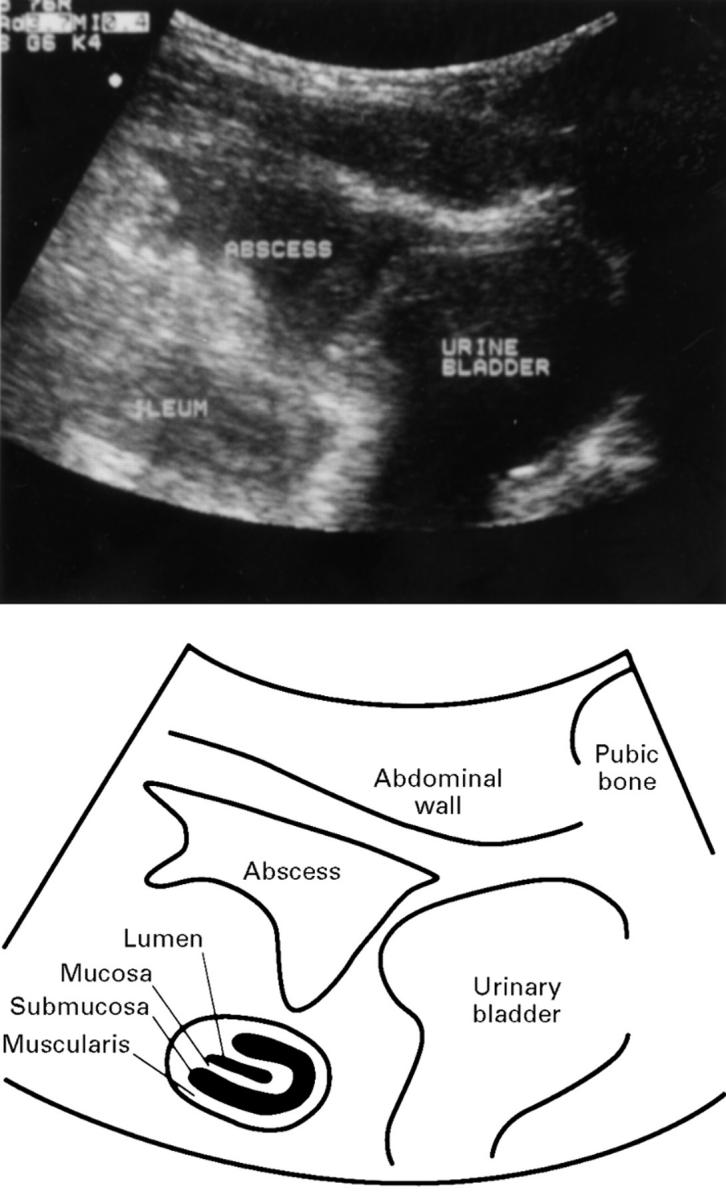
Sagittal TABS section through the mid lower abdomen of a patient with a two year history of uncomplicated Crohn's disease. A 4 cm hypoechoic peritoneal lesion (abscess) is present cranial to the urinary bladder. The adjacent ileum shows wall thickening (about 0.7 cm) with typical layering and a hyperechoic linear shaped central lumen without evidence of stricturing. The abscess originates from an ileal fistula (not visible on this section).
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein C. N., Boult I. F., Greenberg H. M., van der Putten W., Duffy G., Grahame G. R. A prospective randomized comparison between small bowel enteroclysis and small bowel follow-through in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1997 Aug;113(2):390–398. doi: 10.1053/gast.1997.v113.pm9247455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybulsky I. J., Tam P. Intra-abdominal abscesses in Crohn's disease. Am Surg. 1990 Nov;56(11):678–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer R. G., Hawk W. A., Turnbull R. B., Jr Indications for surgery in Crohn's disease: analysis of 500 cases. Gastroenterology. 1976 Aug;71(2):245–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer R. G., Whelan G., Fazio V. W. Long-term follow-up of patients with Crohn's disease. Relationship between the clinical pattern and prognosis. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jun;88(6):1818–1825. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman E. K., Wolf E. J., Jones B., Bayless T. M., Siegelman S. S. CT evaluation of Crohn's disease: effect on patient management. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987 Mar;148(3):537–540. doi: 10.2214/ajr.148.3.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasche C., Schober E., Turetschek K. Small bowel barium studies in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1998 Jun;114(6):1349–1349. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(98)70454-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg H. I., Gore R. M., Margulis A. R., Moss A. A., Baker E. L. Computed tomography in the evaluation of Crohn disease. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1983 Feb;140(2):277–282. doi: 10.2214/ajr.140.2.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gore R. M., Marn C. S., Kirby D. F., Vogelzang R. L., Neiman H. L. CT findings in ulcerative, granulomatous, and indeterminate colitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984 Aug;143(2):279–284. doi: 10.2214/ajr.143.2.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggett P. J., Moore N. R., Shearman J. D., Travis S. P., Jewell D. P., Mortensen N. J. Pelvic and perineal complications of Crohn's disease: assessment using magnetic resonance imaging. Gut. 1995 Mar;36(3):407–410. doi: 10.1136/gut.36.3.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey R. F., Bradshaw J. M. A simple index of Crohn's-disease activity. Lancet. 1980 Mar 8;1(8167):514–514. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92767-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hata J., Haruma K., Suenaga K., Yoshihara M., Yamamoto G., Tanaka S., Shimamoto T., Sumii K., Kajiyama G. Ultrasonographic assessment of inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992 Apr;87(4):443–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S., Samuel E. Grey scale ultrasound in Crohn's disease. Gut. 1979 Jul;20(7):590–595. doi: 10.1136/gut.20.7.590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaftori J. K., Pery M., Kleinhaus U. Ultrasonography in Crohn's disease. Gastrointest Radiol. 1984;9(2):137–142. doi: 10.1007/BF01887820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. K., Preshaw R. M. Origin of fistulas in Crohn's disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1989 Apr;11(2):193–196. doi: 10.1097/00004836-198904000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. K., Siu T. O. The strictures, sinuses, and fissures of Crohn's disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1986 Oct;8(5):594–598. doi: 10.1097/00004836-198610000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. K., Sutherland L. R. The chronological sequence in the pathology of Crohn's disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1988 Feb;10(1):28–33. doi: 10.1097/00004836-198802000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettritz U., Isaacs K., Warshauer D. M., Semelka R. C. Crohn's disease. Pilot study comparing MRI of the abdomen with clinical evaluation. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1995 Oct;21(3):249–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmey M. B., Wang K. Y., Haggitt R. C., Mack L. A., Silverstein F. E. Diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease with ultrasound. An in vitro study. Invest Radiol. 1990 Oct;25(10):1085–1090. doi: 10.1097/00004424-199010000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolkman J. J., Falke T. H., Roos J. C., Van Dijk D. H., Bannink I. M., Den Hollander W., Cuesta M. A., Peña A. S., Meuwissen S. G. Computed tomography and granulocyte scintigraphy in active inflammatory bowel disease. Comparison with endoscopy and operative findings. Dig Dis Sci. 1996 Apr;41(4):641–650. doi: 10.1007/BF02213118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limberg B. Diagnosis of acute ulcerative colitis and colonic Crohn's disease by colonic sonography. J Clin Ultrasound. 1989 Jan;17(1):25–31. doi: 10.1002/jcu.1870170106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maconi G., Bollani S., Bianchi Porro G. Ultrasonographic detection of intestinal complications in Crohn's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 1996 Aug;41(8):1643–1648. doi: 10.1007/BF02087914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maconi G., Parente F., Bollani S., Cesana B., Bianchi Porro G. Abdominal ultrasound in the assessment of extent and activity of Crohn's disease: clinical significance and implication of bowel wall thickening. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996 Aug;91(8):1604–1609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen S. M., Thomsen H. S., Munkholm P., Schlichting P., Davidsen B. Magnetic resonance imaging of Crohn disease: early recognition of treatment response and relapse. Abdom Imaging. 1997 Mar-Apr;22(2):164–166. doi: 10.1007/s002619900163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orel S. G., Rubesin S. E., Jones B., Fishman E. K., Bayless T. M., Siegelman S. S. Computed tomography vs barium studies in the acutely symptomatic patient with Crohn disease. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1987 Nov-Dec;11(6):1009–1016. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198711000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro M. B., Greenstein A. J., Yamazaki Y., Aufses A. H., Jr Intra-abdominal abscess in regional enteritis. Ann Surg. 1991 Jan;213(1):32–36. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199101000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneekloth G., Terrier F., Fuchs W. A. Computed tomography of intraperitoneal abscesses. Gastrointest Radiol. 1982;7(1):35–41. doi: 10.1007/BF01887603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan M. B., Nicholson D. A., Martin D. F. Transabdominal ultrasonography as the primary investigation in patients with suspected Crohn's disease or recurrence: a prospective study. Clin Radiol. 1993 Dec;48(6):402–404. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(05)81109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalej M., Makowiec F., Weinlich M., Jenss H., Laniado M., Starlinger M. Kernspintomographie bei perianalem Morbus Crohn. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1993 Dec 10;118(49):1791–1796. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1059515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Erckenbrecht J., Peter P., Niederau C. Detection of Crohn's disease by ultrasound. Gastroenterology. 1982 Aug;83(2):430–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler J. G., Slack N. F., Duncan A., Whitehead P. J., Russell G., Harvey R. F. The diagnosis of intra-abdominal abscesses in patients with severe Crohn's disease. Q J Med. 1992 Feb;82(298):159–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worlicek H., Lutz H., Heyder N., Matek W. Ultrasound findings in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis: a prospective study. J Clin Ultrasound. 1987 Mar-Apr;15(3):153–163. doi: 10.1002/jcu.1870150302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]