Abstract
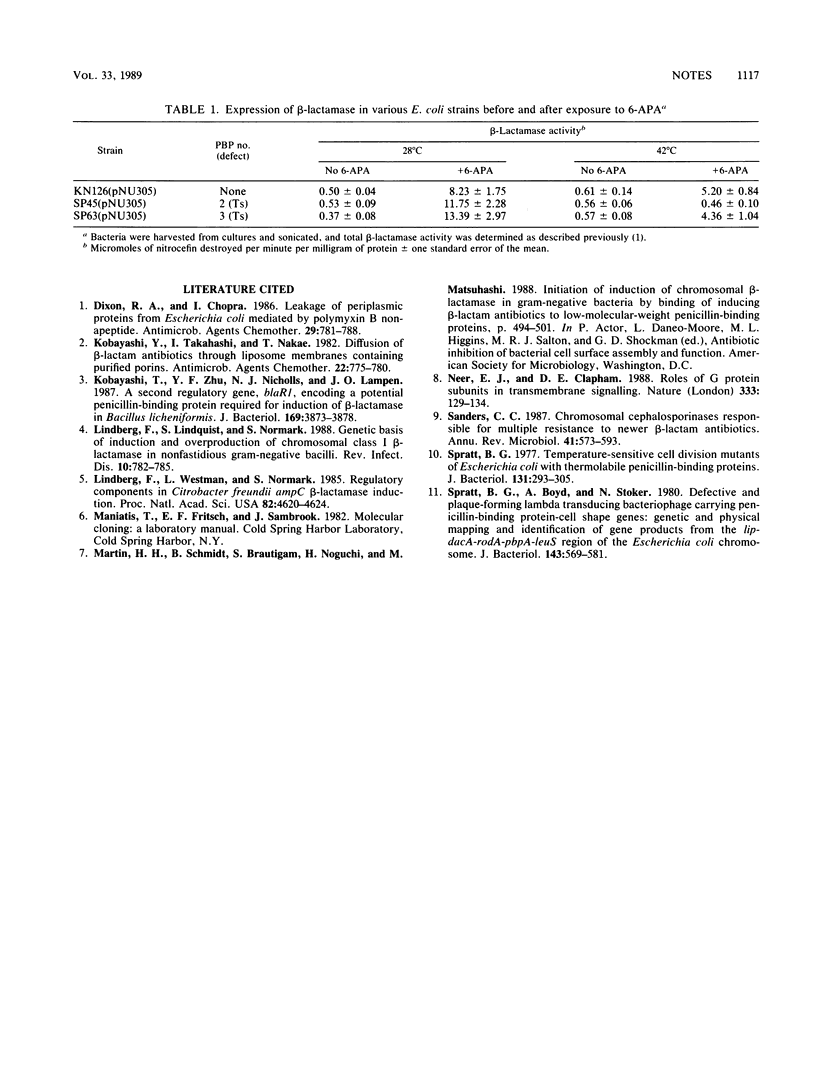
Involvement of Escherichia coli penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) in induction of the cloned ampC Citrobacter freundii beta-lactamase by 6-aminopenicillanic acid was investigated. The enzyme was not inducible at 42 degrees C in a mutant thermosensitive for expression of PBP 2. The results imply that PBP 2 is involved in the process leading to induction of ampC.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dixon R. A., Chopra I. Leakage of periplasmic proteins from Escherichia coli mediated by polymyxin B nonapeptide. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 May;29(5):781–788. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.5.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi T., Zhu Y. F., Nicholls N. J., Lampen J. O. A second regulatory gene, blaR1, encoding a potential penicillin-binding protein required for induction of beta-lactamase in Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):3873–3878. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.3873-3878.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Takahashi I., Nakae T. Diffusion of beta-lactam antibiotics through liposome membranes containing purified porins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Nov;22(5):775–780. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.5.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Lindquist S., Normark S. Genetic basis of induction and overproduction of chromosomal class I beta-lactamase in nonfastidious gram-negative bacilli. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10(4):782–785. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.4.782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Westman L., Normark S. Regulatory components in Citrobacter freundii ampC beta-lactamase induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4620–4624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Clapham D. E. Roles of G protein subunits in transmembrane signalling. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):129–134. doi: 10.1038/333129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C. Chromosomal cephalosporinases responsible for multiple resistance to newer beta-lactam antibiotics. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:573–593. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.003041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G., Boyd A., Stoker N. Defective and plaque-forming lambda transducing bacteriophage carrying penicillin-binding protein-cell shape genes: genetic and physical mapping and identification of gene products from the lip-dacA-rodA-pbpA-leuS region of the Escherichia coli chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):569–581. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.569-581.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Temperature-sensitive cell division mutants of Escherichia coli with thermolabile penicillin-binding proteins. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):293–305. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.293-305.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


