Abstract
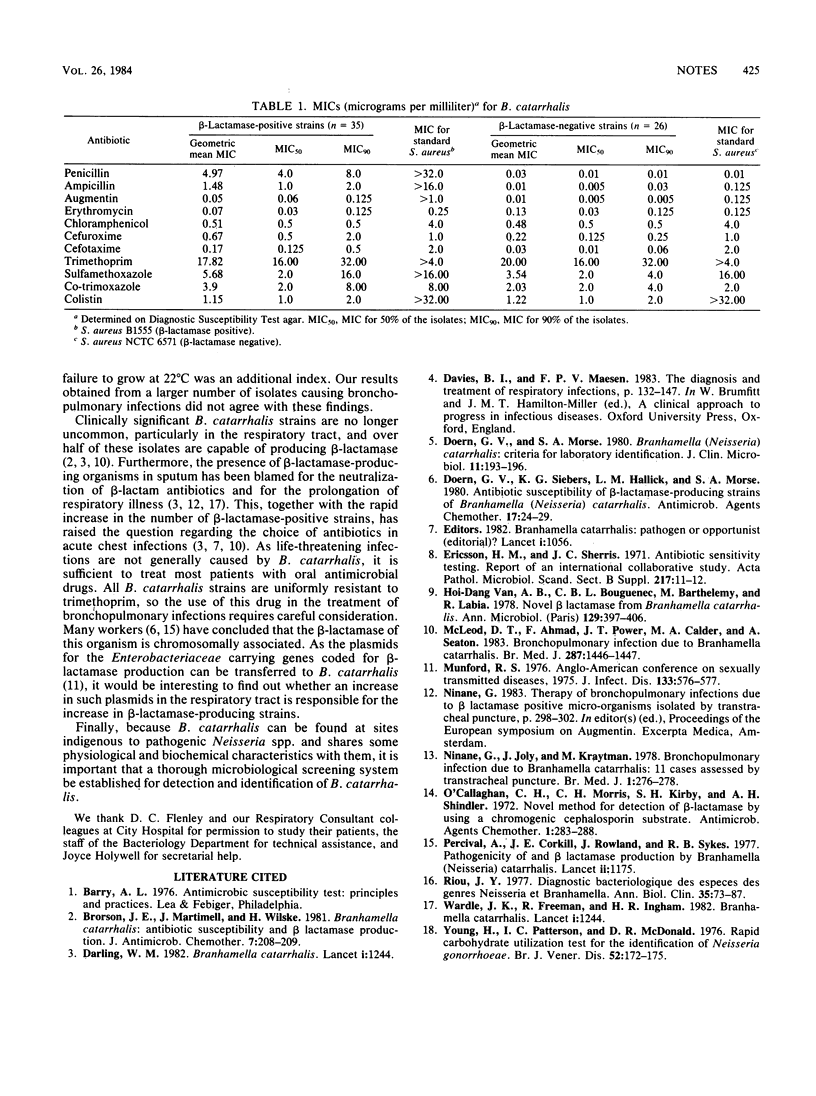
Fifty-four clinical isolates of Branhamella catarrhalis from patients with bronchopulmonary infections were studied. The MICs for 50 and 90% of the isolates and the geometric mean MICs were determined for 11 antimicrobial agents. All the strains were resistant to trimethoprim but were susceptible to clavulanate-potentiated amoxicillin (Augmentin; Beecham Research Laboratories, London), chloramphenicol, co-trimoxazole, erythromycin, cefotaxime, and cefuroxime. Beta-lactamase-negative strains were uniformly susceptible to penicillin and ampicillin.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Branhamella catarrhalis. Lancet. 1982 May 29;1(8283):1244–1245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branhamella catarrhalis. Lancet. 1982 May 29;1(8283):1244–1245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brorson J. E., Martinell J., Wilske H. Branhamella catarrhalis: antibiotic susceptibility and beta-lactamase production. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Feb;7(2):208–209. doi: 10.1093/jac/7.2.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doern G. V., Morse S. A. Branhamella (Neisseria) catarrhalis: criteria for laboratory identification. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Feb;11(2):193–195. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.2.193-195.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doern G. V., Siebers K. G., Hallick L. M., Morse S. A. Antibiotic susceptibility of beta-lactamase-producing strains of Branhamella (Neisseria) catarrhalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jan;17(1):24–29. doi: 10.1128/aac.17.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson H. M., Sherris J. C. Antibiotic sensitivity testing. Report of an international collaborative study. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;217(Suppl):1+–1+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoi-Dang A. B., Brive-Le Bouguenec C., Barthelemy M., Labia R. Novel beta-lactamase from Branhamella catarrhalis. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1978 Oct;129 B(3):397–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod D. T., Ahmad F., Power J. T., Calder M. A., Seaton A. Bronchopulmonary infection due to Branhamella catarrhalis. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Nov 12;287(6403):1446–1447. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6403.1446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munford R. S. Anglo-American Conference on Sexually Transmitted Diseases. J Infect Dis. 1976 May;133(5):576–577. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.5.576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninane G., Joly J., Kraytman M. Bronchopulmonary infection due to Branhamella catarrhalis: 11 cases assessed by transtracheal puncture. Br Med J. 1978 Feb 4;1(6108):276–278. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6108.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival A., Corkill J. E., Rowlands J., Sykes R. B. Pathogenicity of and beta-lactamase production by Branhamella (Neisseria) catarrhalis. Lancet. 1977 Dec 3;2(8049):1175–1175. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91562-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riou J. Y., Guibourdenche M. Diagnostic bactériologique des espèces des genres Neisseria et Branhamella. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1977;35(2):73–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H., Paterson I. C., McDonald D. R. Rapid carbohydrate utilization test for the identification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Br J Vener Dis. 1976 Jun;52(3):172–175. doi: 10.1136/sti.52.3.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



