Abstract
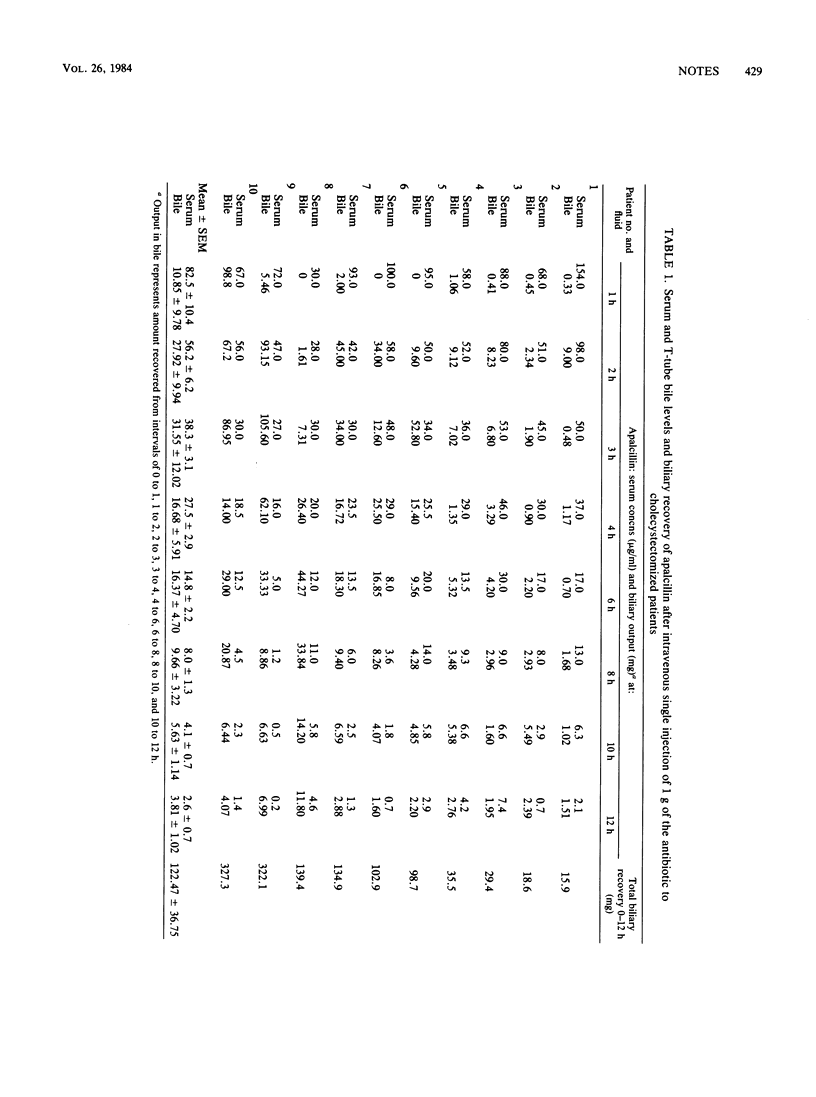
Apalcillin was administered intravenously as a single 1-g dose on day 8 after surgery to 10 cholecystectomized patients with T-tube drainage. A peak of 2,093 +/- standard error of the mean 859 micrograms/ml of bile was attained at 3 h after dosage. Biliary recovery over a 12-h period amounted to 12.2% of the dose. In 20 patients undergoing biliary surgery, apalcillin concentrations 1 h after a 1-g dose were 65.5 +/- 5.0, 3,680 +/- 551, and 2,552 +/- 627 micrograms/ml in serum, choledochal bile, and gallbladder bile, respectively.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodey G. P., Weaver S., Pan T. PC-904, a new semisynthetic penicillin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jan;13(1):14–18. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.1.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brogard J. M., Kopferschmitt J., Arnaud J. P., Dorner M., La Villaureix J. Biliary elimination of mezlocillin: an experimental and clinical study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Jul;18(1):69–76. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Labthavikul P. In vitro activity of apalcillin compared with that of other new penicillins and anti-Pseudomonas cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jun;21(6):906–911. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.6.906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUNDLE F. F., CASS M. H., ROBSON B., MIDDLETON M. Bile drainage after choledochostomy in man, with some observations on biliary fistula. Surgery. 1955 Jun;37(6):903–910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



