Full text
PDF






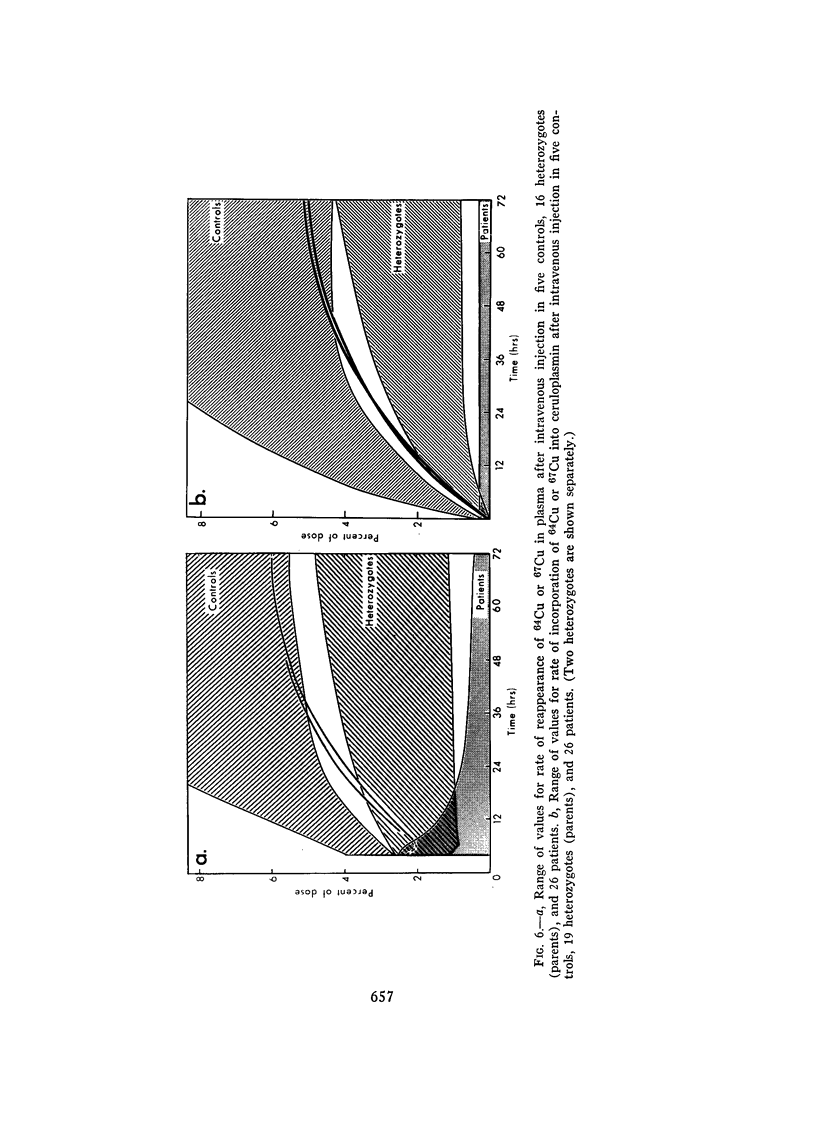
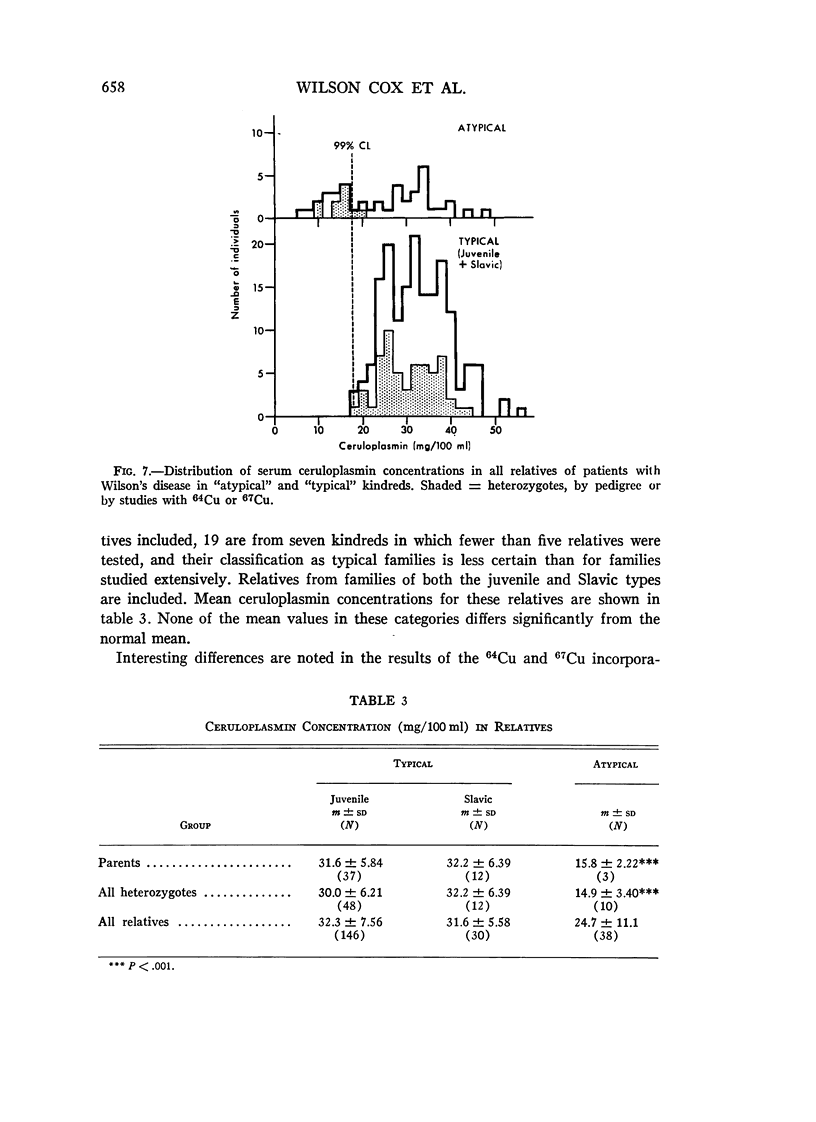








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEARN A. G. A genetical analysis of thirty families with Wilson's disease (hepatolenticular degeneration). Ann Hum Genet. 1960 Apr;24:33–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1959.tb01713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEARN A. G. Genetic and biochemical aspects of Wilson's disease. Am J Med. 1953 Oct;15(4):442–449. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(53)90134-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEARN A. G., KUNKEL H. G. Localization of Cu64 in serum fractions following oral administration: an alteration in Wilson's disease. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Jan;85(1):44–48. doi: 10.3181/00379727-85-20780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUSH J. A., MAHONEY J. P., MARKOWITZ H., GUBLER C. J., CARTWRIGHT G. E., WINTROBE M. M. Studies on copper metabolism. XIV. Radioactive copper studies in normal subjects and in patients with hepatolenticular degeneration. J Clin Invest. 1955 Dec;34(12):1766–1778. doi: 10.1172/JCI103232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers M. E., Hobbs C. B., Warren R. L. Raised serum copper and caeruloplasmin levels in subjects taking oral contraceptives. J Clin Pathol. 1966 Sep;19(5):498–500. doi: 10.1136/jcp.19.5.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. W. A screening test for Wilson's disease and its application to psychiatric patients. Can Med Assoc J. 1967 Jan 14;96(2):83–86. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. W. Factors influencing serum ceruloplasmin levels in normal individuals. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Dec;68(6):893–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cropp G. J. Changes in blood and plasma volumes during growth. J Pediatr. 1971 Feb;78(2):220–229. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans G. W., Myron D. R., Wiederanders R. E. Effect of protein synthesis inhibitors on plasma ceruloplasmin in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1969 Feb;216(2):340–342. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.2.340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregoriadis G., Sourkes T. L. Role of protein in removal of copper from the liver. Nature. 1968 Apr 20;218(5138):290–291. doi: 10.1038/218290a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman N. A., Gaumnitz B. M. Identification of an apoceruloplasmin-like substance in the plasma of copper-deficient rats. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 10;245(9):2350–2353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman N. A., Gaumnitz B. M. Studies on the rate of release and turnover of ceruloplasmin and apoceruloplasmin in rat plasma. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 10;245(9):2354–2358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISEN P., MORELL A. G. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL STUDIES ON CERULOPLASMIN. 3. A STABILIZING COPPER-COPPER INTERACTION IN CERULOPLASMIN. J Biol Chem. 1965 May;240:1974–1978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi A. J., Sherlock S., Scheuer P. J., Cumings J. N. Presymptomatic Wilson's disease. Lancet. 1967 Sep 16;2(7516):575–579. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90735-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. C., Mantel N. A simple method of estimating the segregation ratio under complete ascertainment. Am J Hum Genet. 1968 Jan;20(1):61–81. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS W. B., MILNE M. D., BELL M. The metabolic disorder in hepato-lenticular degeneration. Q J Med. 1952 Oct;21(84):425–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marceau N., Kruck T. P., McConnell D. B., Aspin N. The production of copper 67 from natural zinc using a linear acceleration. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1970 Nov;21(11):667–669. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(70)90121-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann P. Z., Silverberg M. Active copper transport in mammalian tissues--a possible role in Wilson's disease. Nature. 1966 Apr 23;210(5034):414–416. doi: 10.1038/210414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osaki S., Johnson D. A., Frieden E. The mobilization of iron from the perfused mammalian liver by a serum copper enzyme, ferroxidase I. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):3018–3023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn S. B., Walshe J. M. Studies with radioactive copper (64Cu and 67Cu) in relation to the natural history of Wilson's disease. Lancet. 1967 Feb 8;1(7486):346–350. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92893-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R., Shorthouse M., Walshe J. M. Studies on the toxicity of copper. II. The behaviour of microsomal membrane ATPase of the pigeon's brain tissue to copper and some other metallic substances. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1966 Dec 13;166(1004):285–294. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1966.0099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. N. Some aspects of metal incorporation into porphyrins. Enzymologia. 1967 Jan 31;32(1):13–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SASS-KORTSAK A., CHERNIAK M., GEIGER D. W., SLATER R. J. Observations on ceruloplasmin in Wilson's disease. J Clin Invest. 1959 Oct;38:1672–1682. doi: 10.1172/JCI103945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEINBERG I. H., GITLIN D. Deficiency of ceruloplasmin in patients with hepatolenticular degeneration (Wilson's disease). Science. 1952 Oct 31;116(3018):484–485. doi: 10.1126/science.116.3018.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERNLIEB I., SCHEINBERG I. H. The diagnosis of Wilson's disease in asymptomatic patients. JAMA. 1963 Mar 2;183:747–750. doi: 10.1001/jama.1963.03700090067011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sass-Kortsak A. Copper metabolism. Adv Clin Chem. 1965;8:1–67. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2423(08)60412-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shokeir M. H., Shreffler D. C. Cytochrome oxidase deficiency in Wilson's disease: a suggested ceruloplasmin function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):867–872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soothill J. F., Blainey J. D., Neale F. C., Fischer-Williams M., Melnick S. C. A family study of the biochemical defects in Wilson's disease. J Clin Pathol. 1961 May;14(3):264–270. doi: 10.1136/jcp.14.3.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternlieb I., Scheinberg I. H. Prevention of Wilson's disease in asymptomatic patients. N Engl J Med. 1968 Feb 15;278(7):352–359. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196802152780702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternlier I., Morell A. G., Bauer C. D., Combes B., De Bobes-Sternberg S., Schein-Berg I. H. DETECTION OF THE HETEROZYGOUS CARRIER OF THE WILSON'S DISEASE GENE. J Clin Invest. 1961 Apr;40(4):707–715. doi: 10.1172/JCI104304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TU J. B. A GENETIC, BIOCHEMICAL AND CLINICAL STUDY OF WILSON'S DISEASE AMONG CHINESE IN TAIWAN. Zhonghua Min Guo Xiao Er Ke Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi. 1963 Apr-Jun;4:81–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauxe W. N., Goldstein N. P., Randall R. V., Gross J. B. Radiocopper studies in patients with Wilson's disease and their relatives. Am J Med. 1966 Sep;41(3):375–380. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walshe J. M. The physiology of copper in man and its relation to Wilson's disease. Brain. 1967 Mar;90(1):149–176. doi: 10.1093/brain/90.1.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


