Abstract
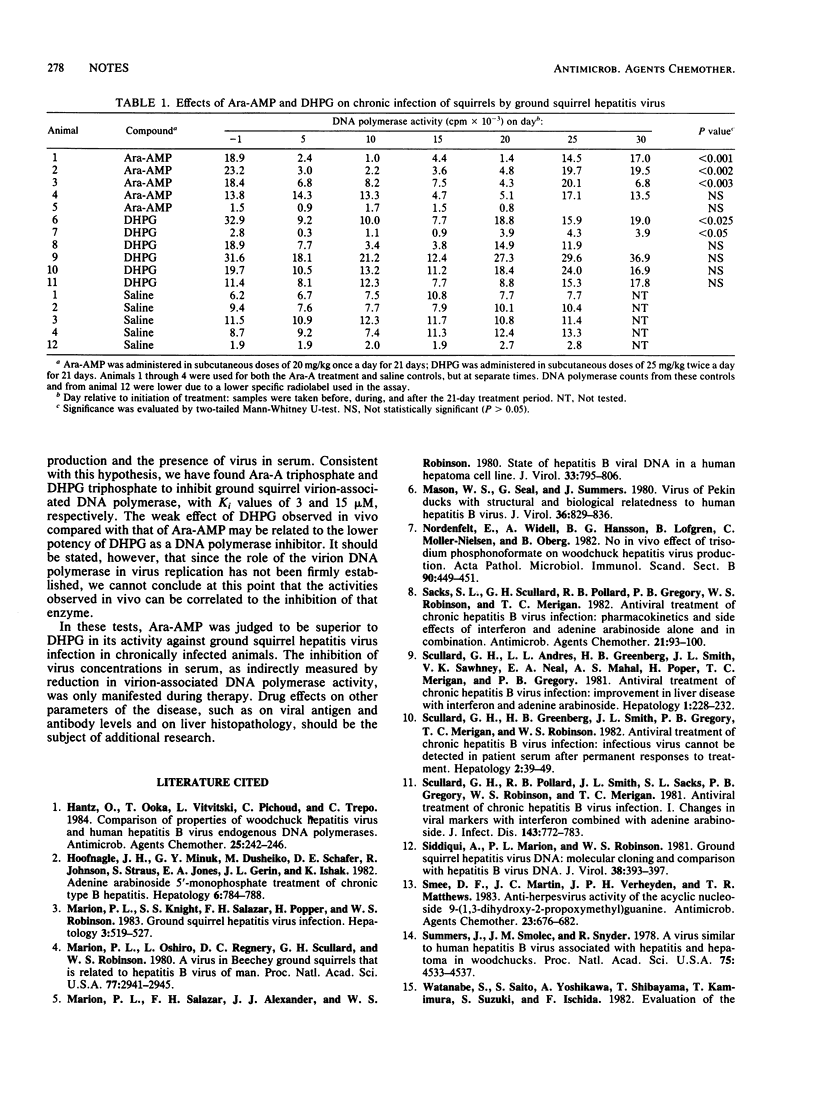
Treatment of chronic ground squirrel hepatitis virus infection with arabinosyladenine monophosphate at 20 mg/kg per day for 3 weeks caused marked decreases in serum virion-associated DNA polymerase concentrations in three of five squirrels. Statistically significant but less dramatic decreases in enzymatic activity were noted in two of six squirrels treated with 50 mg of 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine per kg per day. After therapy, DNA polymerase activities rose to pretreatment levels.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hantz O., Ooka T., Vitvitski L., Pichoud C., Trepo C. Comparison of properties of woodchuck hepatitis virus and human hepatitis B virus endogenous DNA polymerases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Feb;25(2):242–246. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.2.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H., Minuk G. Y., Dusheiko G. M., Schafer D. F., Johnson R., Straus S., Jones E. A., Gerin J. L., Ishak K. Adenine arabinoside 5'-monophosphate treatment of chronic type B hepatitis. Hepatology. 1982 Nov-Dec;2(6):784–788. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion P. L., Knight S. S., Salazar F. H., Popper H., Robinson W. S. Ground squirrel hepatitis virus infection. Hepatology. 1983 Jul-Aug;3(4):519–527. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion P. L., Oshiro L. S., Regnery D. C., Scullard G. H., Robinson W. S. A virus in Beechey ground squirrels that is related to hepatitis B virus of humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2941–2945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion P. L., Salazar F. H., Alexander J. J., Robinson W. S. State of hepatitis B viral DNA in a human hepatoma cell line. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):795–806. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.795-806.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. S., Seal G., Summers J. Virus of Pekin ducks with structural and biological relatedness to human hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):829–836. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.829-836.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordenfelt E., Widell A., Hansson B. G., Löfgren B., Möller-Nielsen C., Oberg B. No in vivo effect of trisodium phosphonoformate on woodchuck hepatitis virus production. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1982 Dec;90(6):449–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1982.tb00145.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks S. L., Scullard G. H., Pollard R. B., Gregory P. B., Robinson W. S., Merigan T. C. Antiviral treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: pharmacokinetics and side effects of interferon and adenine arabinoside alone and in combination. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):93–100. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scullard G. H., Andres L. L., Greenberg H. B., Smith J. L., Sawhney V. K., Neal E. A., Mahal A. S., Popper H., Merigan T. C., Robinson W. S. Antiviral treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: improvement in liver disease with interferon and adenine arabinoside. Hepatology. 1981 May-Jun;1(3):228–232. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scullard G. H., Greenberg H. B., Smith J. L., Gregory P. B., Merigan T. C., Robinson W. S. Antiviral treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: infectious virus cannot be detected in patient serum after permanent responses to treatment. Hepatology. 1982 Jan-Feb;2(1):39–49. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840020107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scullard G. H., Pollard R. B., Smith J. L., Sacks S. L., Gregory P. B., Robinson W. S., Merigan T. C. Antiviral treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. I. Changes in viral markers with interferon combined with adenine arabinoside. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jun;143(6):772–783. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.6.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Marion P. L., Robinson W. S. Ground squirrel hepatitis virus DNA: molecular cloning and comparison with hepatitis B virus DNA. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):393–397. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.393-397.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smee D. F., Martin J. C., Verheyden J. P., Matthews T. R. Anti-herpesvirus activity of the acyclic nucleoside 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 May;23(5):676–682. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.5.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Smolec J. M., Snyder R. A virus similar to human hepatitis B virus associated with hepatitis and hepatoma in woodchucks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4533–4537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller I. V., Bassendine M. F., Craxi A., Fowler M. J., Monjardino J., Thomas H. C., Sherlock S. Successful treatment of HBs and HBeAg positive chronic liver disease: prolonged inhibition of viral replication by highly soluble adenine arabinoside 5'-monophosphate (ARA-AMP). Gut. 1982 Sep;23(9):717–723. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.9.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller I. V., Carreno V., Fowler M. J., Monjardino J., Makinen D., Varghese Z., Sweny P., Thomas H. C., Sherlock S. Acyclovir in hepatitis B antigen-positive chronic liver disease: inhibition of viral replication and transient renal impairment with iv bolus administration. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Mar;11(3):223–231. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.3.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



