Abstract
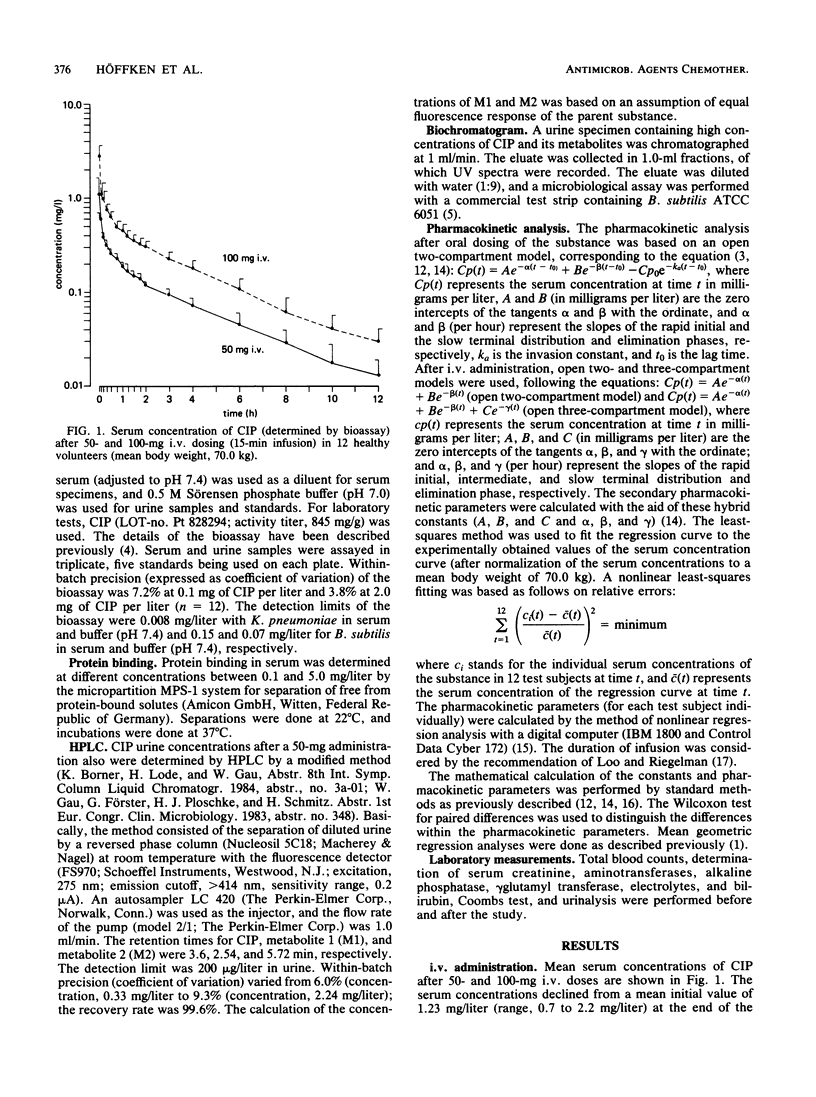
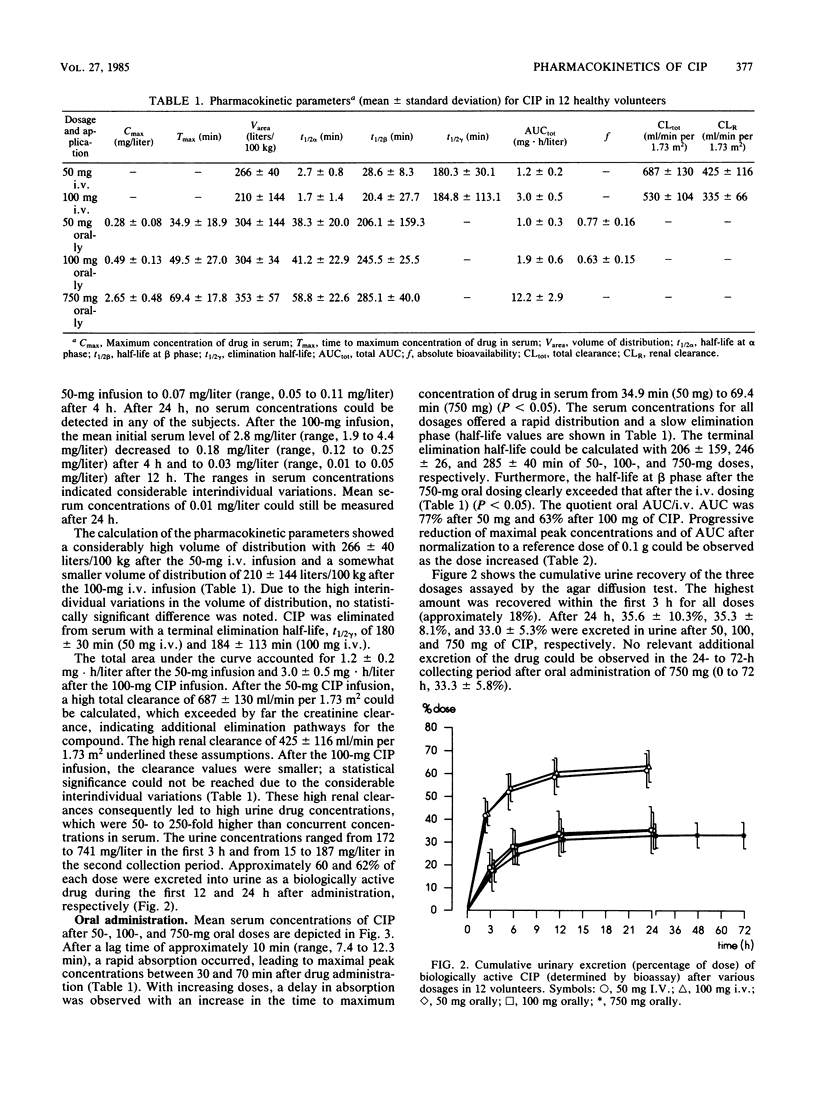
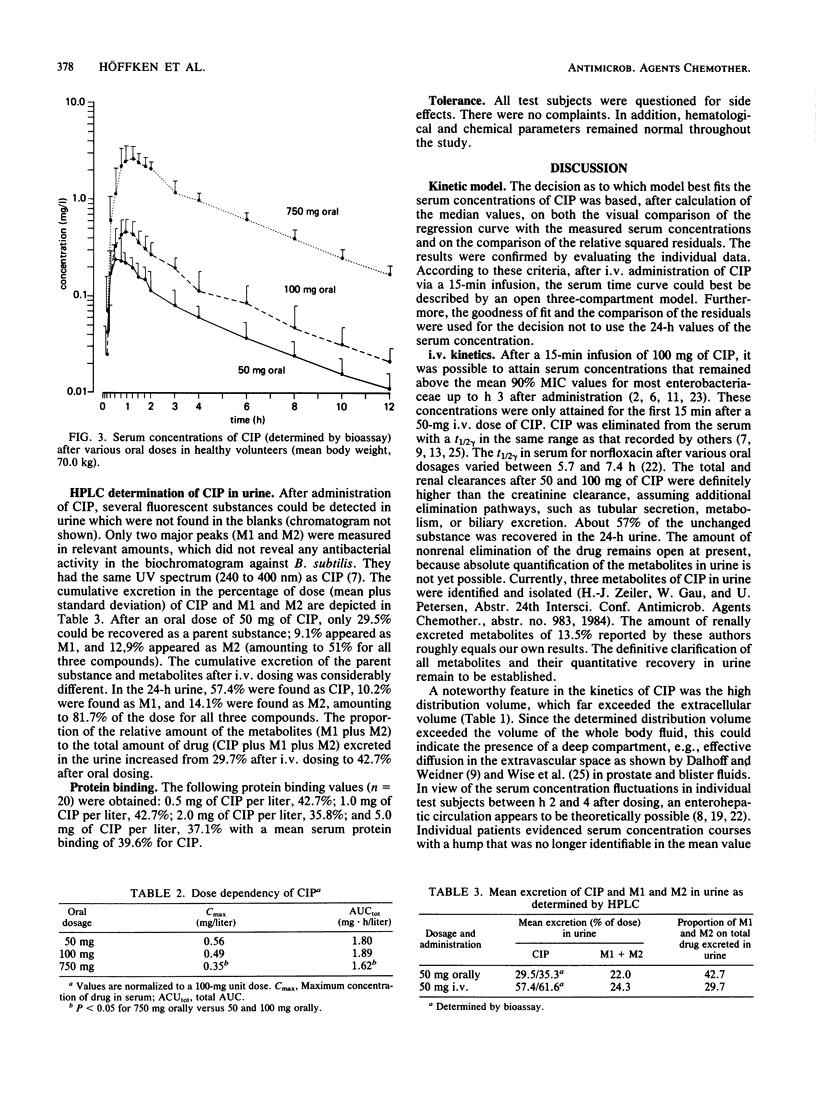
In 12 fasting volunteers, the pharmacokinetics of ciprofloxacin (Bay o 9867; 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluor-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinoline carbonic acid) were determined after the administration of 50, 100, and 750 mg orally as well as 50 and 100 mg intravenously over 15 min. Serum and urine concentrations were detected with a bioassay. In addition, urine concentrations after a 50-mg dosing were measured by high-pressure liquid chromatography. The serum course of ciprofloxacin could best be described by an open three-compartment model. High volumes of distribution (exceeding 200 liters/100 kg) suggested effective diffusions in the extravascular space. The terminal half-life of ciprofloxacin ranged between 3 and 4 h. High total and renal clearances suggested additional elimination pathways, such as tubular secretion, metabolism, or biliary excretion. After oral administration, absorption was sufficient, and the absolute bioavailability varied between 0.77 and 0.63. Maximal serum concentrations were attained 0.5 to 1 h after dosing; the higher dosage tended towards a delay in absorption. The proportion of the relative amount of metabolites to the total amount of drug excreted in urine increased from 29.7% after intravenous administration to 42.7% after oral dosing, indicating a first-pass effect of the liver. Ciprofloxacin concentrations with a bioassay were 3 to 27% higher than with high-pressure liquid chromatography, which may indicate the presence of biologically active metabolites. No side effects were recorded.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Averdunk R., Borner K. Korrelation der Thromboplastinzeiten bei Dicumarol-behandelten Patienten unter Verwendung verschiedener Thrombokinase-Präparate. Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem. 1970 May;8(3):263–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauernfeind A., Petermüller C. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and nalidixic acid. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;2(2):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF02001575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benet L. Z. Effect of route of administration and distribution on drug action. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1978 Dec;6(6):559–585. doi: 10.1007/BF01062110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. V., Brodie J. L., Benner E. J., Kirby W. M. Simplified, accurate method for antibiotic assay of clinical specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):170–177. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.170-177.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borner K., Lode H., Elvers A. Determination of apalcillin and its metabolites in human body fluids by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Dec;22(6):949–953. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.6.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin N. X., Neu H. C. Ciprofloxacin, a quinolone carboxylic acid compound active against aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):319–326. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crump B., Wise R., Dent J. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Nov;24(5):784–786. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.5.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlström B. E., Paalzow L. K. Pharmacokinetic interpretation of the enterohepatic recirculation and first-pass elimination of morphine in the rat. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1978 Dec;6(6):505–519. doi: 10.1007/BF01062106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalhoff A., Weidner W. Diffusion of ciprofloxacin into prostatic fluid. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;3(4):360–362. doi: 10.1007/BF01977495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliopoulos G. M., Gardella A., Moellering R. C., Jr In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, a new carboxyquinoline antimicrobial agent. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):331–335. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman L. J., Fliegelman R. M., Trenholme G. M., Kaplan R. L. Comparative in vitro activity of ciprofloxacin against Campylobacter spp. and other bacterial enteric pathogens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):504–506. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt D. J., Koch-Weser J. Clinical pharmacokinetics (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975 Nov 6;293(19):964–970. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197511062931905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höffler D., Dalhoff A., Gau W., Beermann D., Michl A. Dose- and sex-independent disposition of ciprofloxacin. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;3(4):363–366. doi: 10.1007/BF01977496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kienel G. Vergleich der Pharmakokinetik von Epicillin und Ampicillin. Arzneimittelforschung. 1976;26(5):781–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppe P., Hamann C. A program for non-linear regression analysis to be used on desk-top computers. Comput Programs Biomed. 1980 Dec;12(2-3):121–128. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(80)90058-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lode H., Stahlmann R., Koeppe P. Comparative pharmacokinetics of cephalexin, cefaclor, cefadroxil, and CGP 9000. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jul;16(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo J. C., Riegelman S. Assessment of pharmacokinetic constants from postinfusion blood curves obtained after I.V. infusion. J Pharm Sci. 1970 Jan;59(1):53–55. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600590107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson B. N., Boppana V. K., Vlasses P. H., Rotmensch H. H., Ferguson R. K. Norfloxacin disposition after sequentially increasing oral doses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Feb;23(2):284–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.2.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse F. L., Ballard F., Skinn J. Estimating the fraction reabsorbed in drugs undergoing enterohepatic circulation. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1982 Aug;10(4):455–461. doi: 10.1007/BF01065175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Caekenberghe D. L., Pattyn S. R. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin compared with those of other new fluorinated piperazinyl-substituted quinoline derivatives. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):518–521. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingender W., Graefe K. H., Gau W., Förster D., Beermann D., Schacht P. Pharmacokinetics of ciprofloxacin after oral and intravenous administration in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;3(4):355–359. doi: 10.1007/BF01977494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Lockley R. M., Webberly M., Dent J. Pharmacokinetics of intravenously administered ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):208–210. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


