Abstract
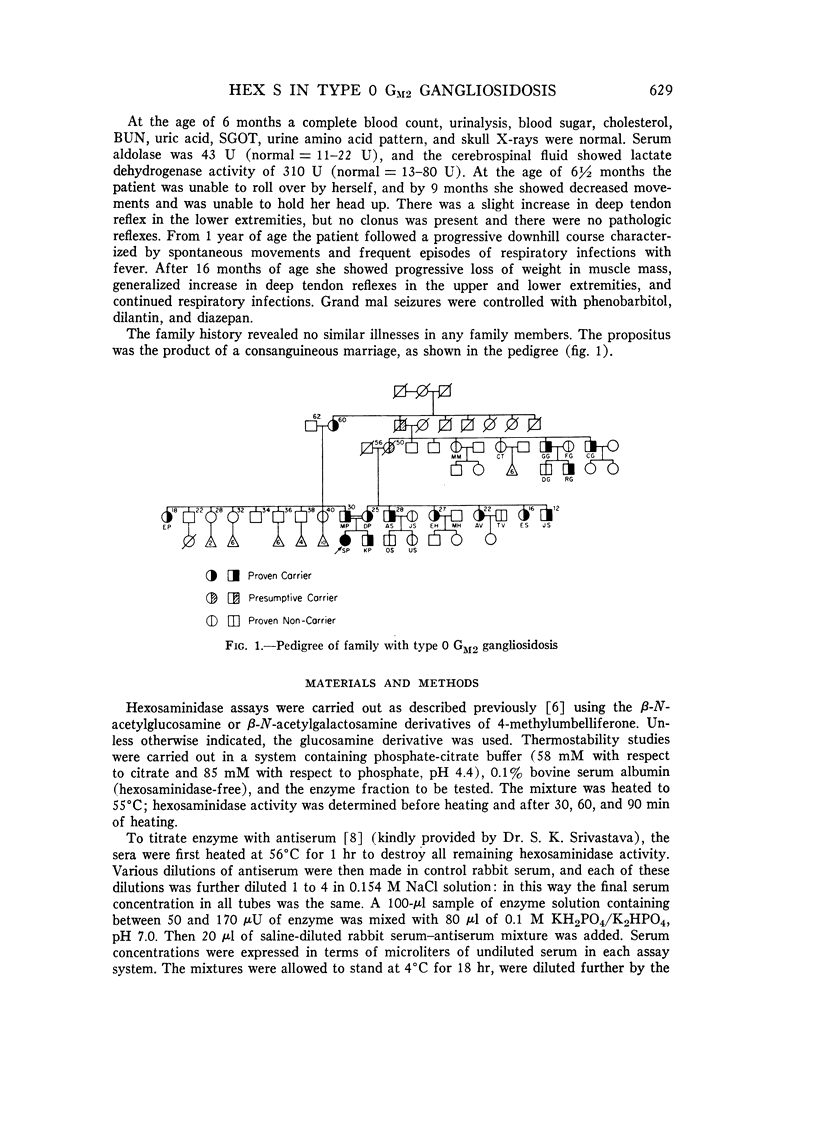
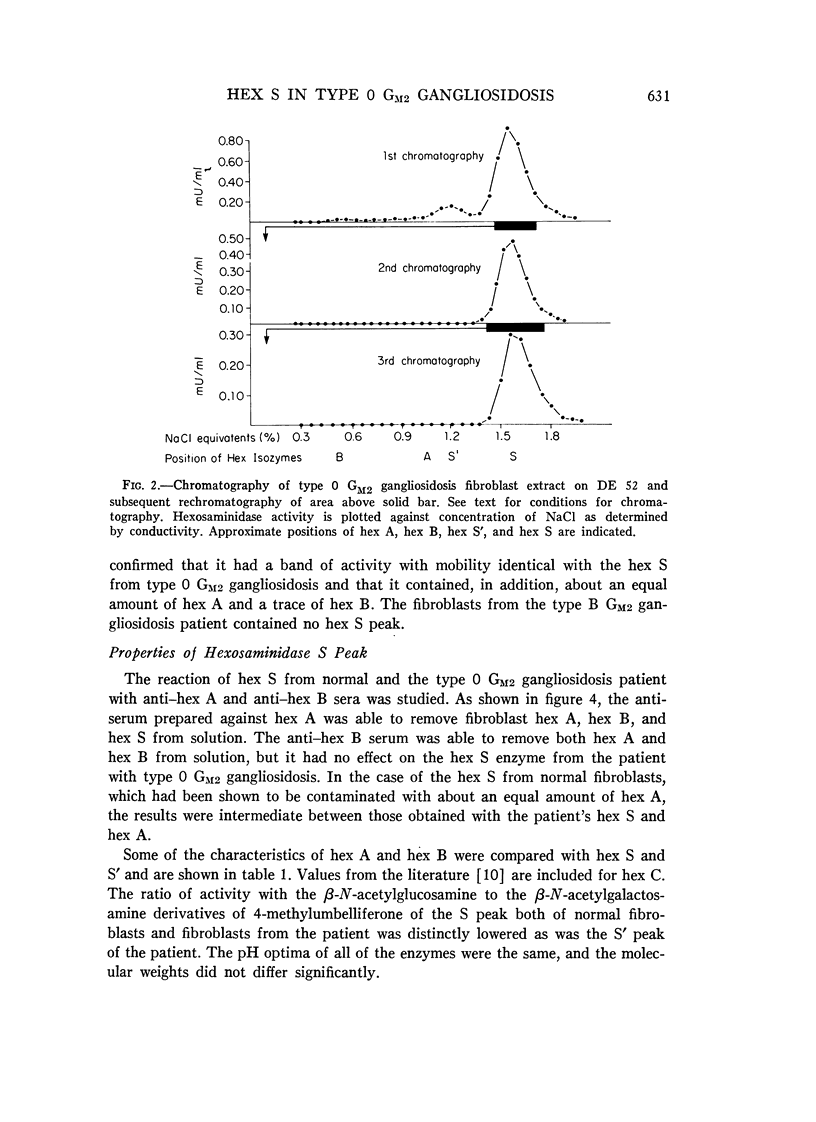
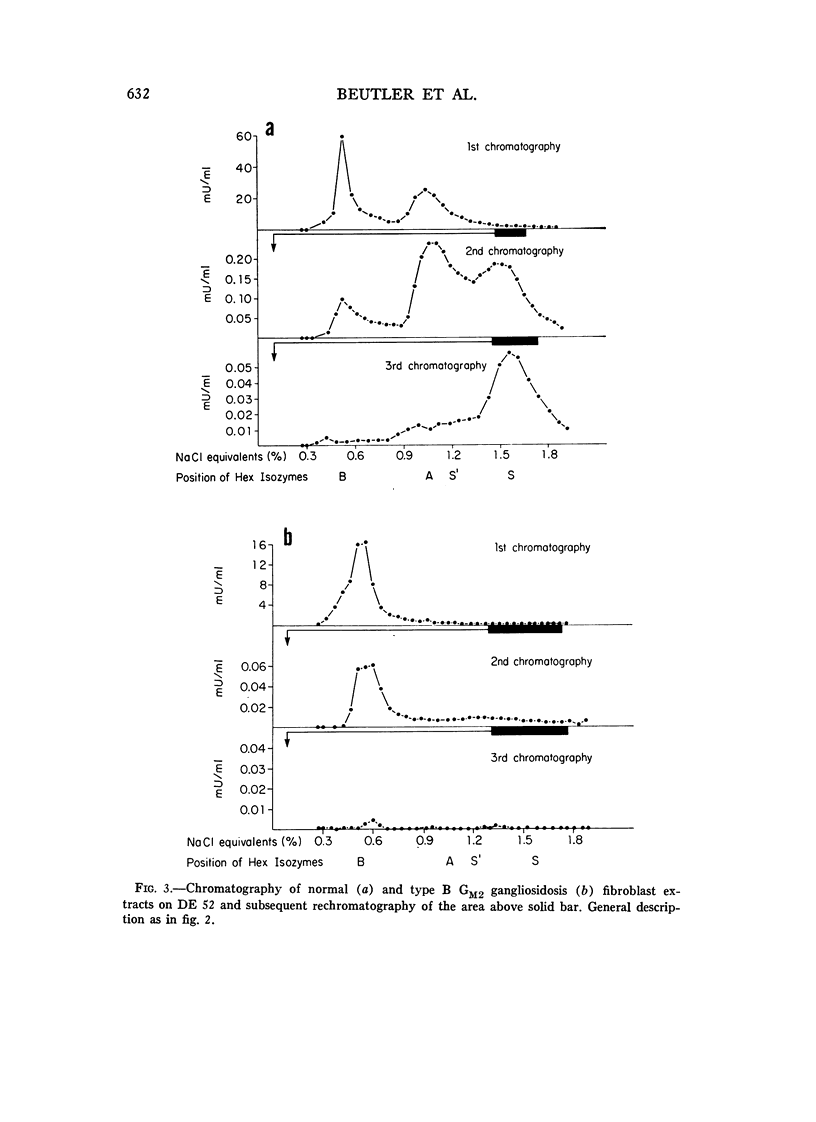
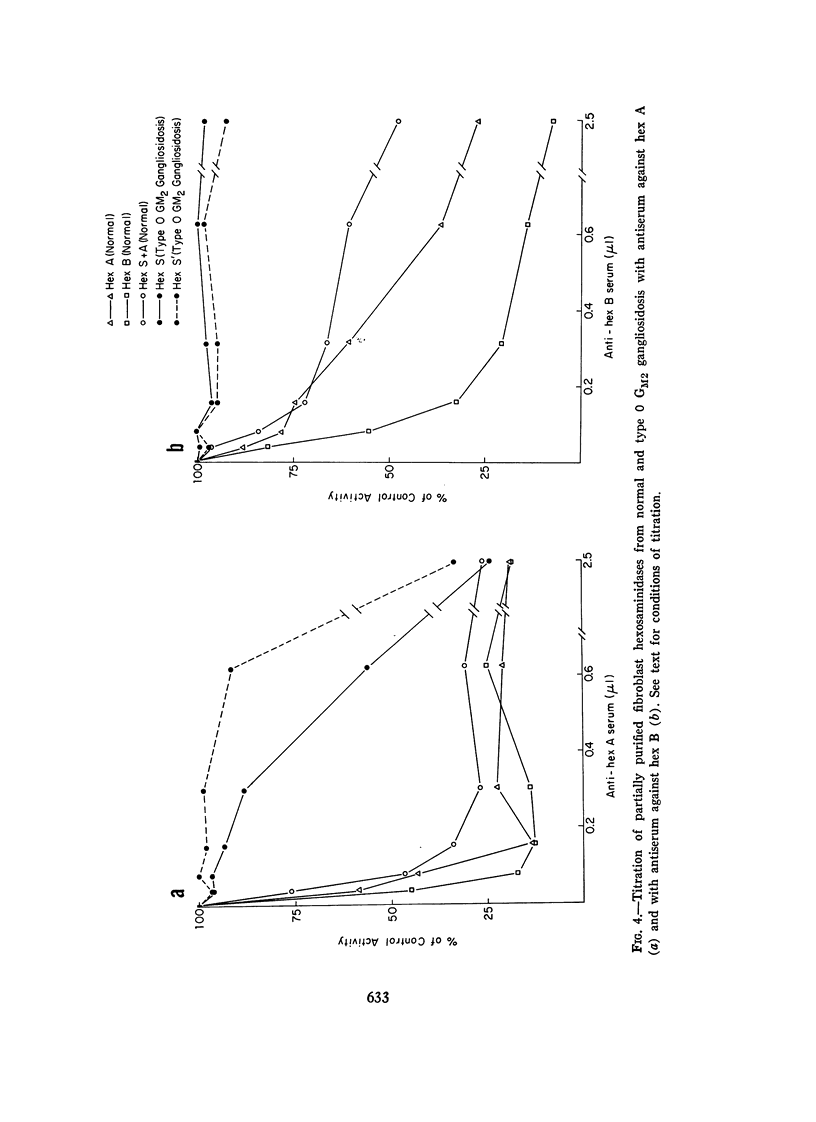
The residual enzyme of the fibroblasts of a child with homozygous type 0 GM2 gangliosidosis (Sandhoff-Jatzkewitz disease) has been found to correspond with a minor fraction of enzyme which can be isolated from normal fibroblasts by repeated chromatography. This enzyme is designated as hexosaminidase (hex) S. It reacts with antiserum prepared against homogeneous hex A but not with serum prepared against homogeneous hex B. These findings support our previously described model of the relationship between hex A and hex G: hex A has the structure (alpha beta)3, while hex B is (beta)6. Type B GM2 gangliosidosis (Tay-Sachs disease) is the alpha- mutation, while type 0 GM2 gangliosidosis (Sandhoff-Jatzkewitz disease) is the beta- mutation. In the absence of normal beta subunits there is increased polymerization of alpha subunits forming hex S, which probably has a structure of (alpha)6. A parallel between the thalassemias and GM2 gangliosidosis is evident: deficiency of one of the chains of which the protein is composed leads to an excess of polymers comprised of the other chains. In type B GM2 gangliosidosis, the excess of beta chanis leads to increased amounts of hex B beta)6; in type 0 GM2 gangliosidosis, the excess of alpha chains leads to formation of increased amounts of the alpha chain polymer, hex S.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler E., Guinto E., Kuhl W. Variability of -galactosidase A and B in different tissues of man. Am J Hum Genet. 1973 Jan;25(1):42–46. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braidman I., Carroll M., Dance N., Robinson D., Poenaru L., Weber A., Dreyfus J. C., Overdijk B., Hooghwinkel G. J. Characterisation of human N-acetyl-beta-hexosaminidase C. FEBS Lett. 1974 May 1;41(2):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81206-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmody P. J., Rattazzi M. C. Conversion of human hexosaminidase A to hexosaminidase "B" by crude Vibrio cholerae neuraminidase preparations: merthiolate is the active factor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 5;371(1):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90160-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M., Robinson D. Immunological identity of human liver hexosaminidases. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(3):17P–17P. doi: 10.1042/bj1260017pa. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M., Robinson D. Immunological properties of N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase of normal human liver and of GM2-gangliosidosis liver. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;131(1):91–96. doi: 10.1042/bj1310091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohwein Y. Z., Gatt S. Isolation of beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase, beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase, and beta-N-acetylgalactosaminidase from calf brain. Biochemistry. 1967 Sep;6(9):2775–2782. doi: 10.1021/bi00861a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert F., Kucherlapati R., Creagan R. P., Murnane M. J., Darlington G. J., Ruddle F. H. Tay-Sachs' and Sandhoff's diseases: the assignment of genes for hexosaminidase A and B to individual human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):263–267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grzeschik K. H., Grzeschik A. M., Banhof S., Romeo G., Siniscalco M., van Someren H., Meera Khan P., Westerveld A., Bootsma D. X-linkage of human -galactosidase. Nat New Biol. 1972 Nov 8;240(97):48–50. doi: 10.1038/newbio240048a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikonne J. U., Rattazzi M. C., Desnick R. J. Characterization of Hex S, the major residual beta hexosaminidase activity in type O Gm2 gangliosidosis (Sandhoff-Jatzkewitz disease). Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Sep;27(5):639–650. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalley P. A., Rattazzi M. C., Shows T. B. Human beta-D-N-acetylhexosaminidases A and B: expression and linkage relationships in somatic cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1569–1573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada S., O'Brien J. S. Tay-Sachs disease: generalized absence of a beta-D-N-acetylhexosaminidase component. Science. 1969 Aug 15;165(3894):698–700. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3894.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenaru L., Dreyfus J. C. Electrophoretic study of hexosaminidases. Hexosaminidase C. Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Feb 12;43(3):439–442. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90486-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D., Stirling J. L. N-Acetyl-beta-glucosaminidases in human spleen. Biochem J. 1968 Apr;107(3):321–327. doi: 10.1042/bj1070321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhoff K., Harzer K., Wässle W., Jatzkewitz H. Enzyme alterations and lipid storage in three variants of Tay-Sachs disease. J Neurochem. 1971 Dec;18(12):2469–2489. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb00204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava S. K., Awasthi Y. C., Yoshida A., Beutler E. Studies on human beta-D-N-acetylhexosaminidases. I. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2043–2048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava S. K., Beutler E. Antibody against purified human hexosaminidase B cross-reacting with human hexosaminidase A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 26;47(4):753–759. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90556-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava S. K., Beutler E. Studies on human beta-D-N-acetylhexosaminidases. 3. Biochemical genetics of Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff's diseases. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2054–2057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava S. K., Yoshida A., Awasthi Y. C., Beutler E. Studies on human beta-D-N-acetylhexosaminidases. II. Kinetic and structural properties. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2049–2053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swallow D. M., Stokes D. C., Corney G., Harris H. Differences between the N-acetyl hexosaminidase isozymes in serum and tissues. Ann Hum Genet. 1974 Jan;37(3):287–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1974.tb01836.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallman J. F., Brady R. O., Quirk J. M., Villalba M., Gal A. E. Isolation and relationship of human hexosaminidases. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3489–3499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. H., Taylor H. A., Miller C. S., Axelman J., Migeon B. R. Genetic complementation after fusion of Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff cells. Nature. 1974 Aug 16;250(467):580–582. doi: 10.1038/250580a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


