Abstract
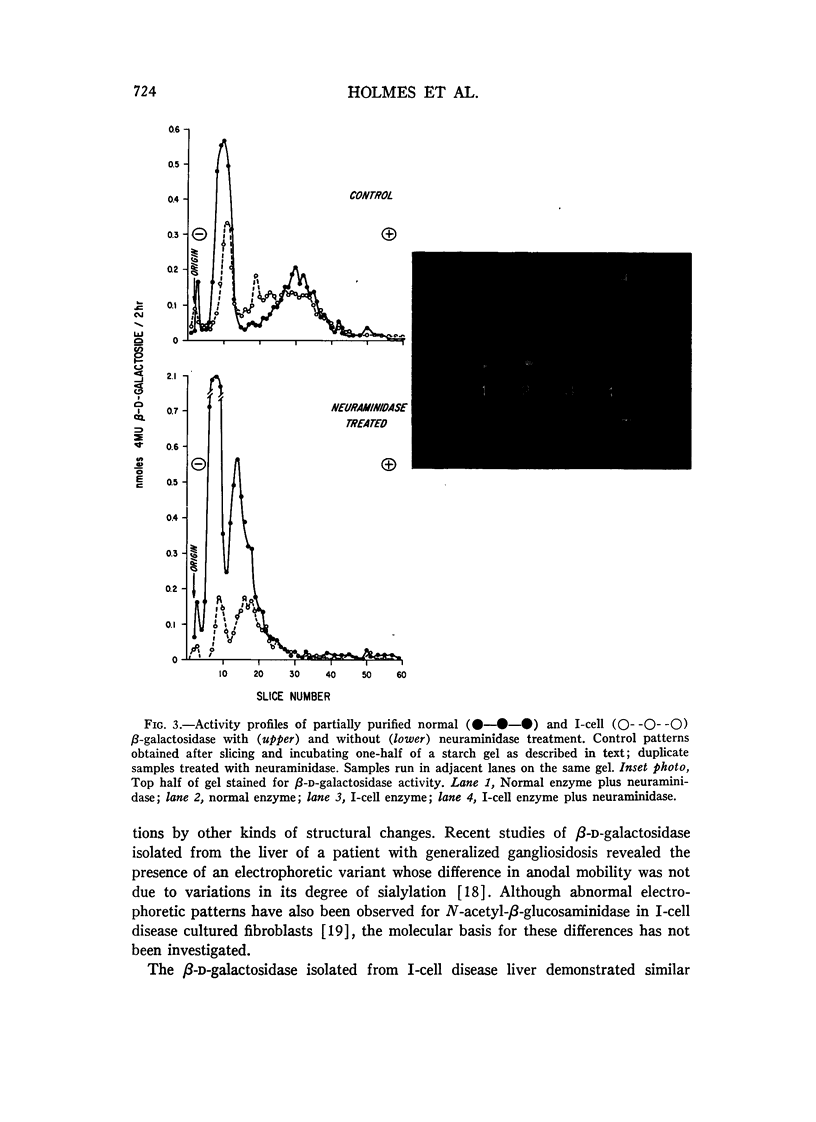
The residual beta-D-galactosidase activity (10% of normal) present in an autopsy sample of liver derived from an I-cell patient has been characterized. The pH optima for both I-cell and normal acid 4-methylumbelliferyl beta-D-galactoside activities were 4.35. The adsorption and elution profiles of the I-cell enzyme from Con A-Sepharose were similar to those of normal liver beta-D-galactosidase. Although starch gel electrophoresis revealed the presence of beta-D-galactosidase A and B in I-cell disease liver, the A band was more diffuse and migrated less anodally than the A band from normal liver. The electrophoretic mobilities of both I-cell and normal beta-D-galactosidase A appeared to decrease after treatment with neuraminidase. Kinetic studies of the I-cell and normal level beta-D-galactosidase demonstrated similar apparent Km values with respect to the 4-methylumbelliferyl beta-D-galactoside and Gm1 ganglioside, whereas the Vmax values obtained for the I-cell enzyme were 10- to 12-fold lower than those of the normal enzyme for both substrates.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker M. A., Kostel P. J., Meyer L. J., Seegmiller J. E. Human phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase: increased enzyme specific activity in a family with gout and excessive purine synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2749–2752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland W. W. The statistical analysis of enzyme kinetic data. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1967;29:1–32. doi: 10.1002/9780470122747.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Den Tandt W. R., Lassila E., Philippart M. Leroy's l-cell disease: markedly increased activity of plasma acid hydrolases. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Mar;83(3):403–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanai J., Leroy J., O'Brien J. S. Ultrastructure of cultured fibroblasts in I-cell disease. Am J Dis Child. 1971 Jul;122(1):34–38. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1971.02110010070011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman S., Neufeld E. F. A hypothesis for I-cell disease: defective hydrolases that do not enter lysosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 15;49(4):992–999. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickman S., Shapiro L. J., Neufeld E. F. A recognition marker required for uptake of a lysosomal enzyme by cultured fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Mar 15;57(1):55–61. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80356-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho M. W., O'Brien J. S. Differential effect of chloride ions on -galactosidase isoenzymes: a method for separate assay. Clin Chim Acta. 1971 May;32(3):443–450. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(71)90446-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy J. G., Demars R. I. Mutant enzymatic and cytological phenotypes in cultured human fibroblasts. Science. 1967 Aug 18;157(3790):804–806. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3790.804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy J. G., Ho M. W., MacBrinn M. C., Zielke K., Jacob J., O'Brien J. S. I-cell disease: biochemical studies. Pediatr Res. 1972 Oct;6(10):752–757. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197210000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy J. G., Spranger J. W., Feingold M., Opitz J. M., Crocker A. C. I-cell disease: a clinical picture. J Pediatr. 1971 Sep;79(3):360–365. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80142-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lie K. K., Thomas G. H., Taylor H. A., Sensenbrenner J. A. Analysis of N-acetyl- -D-glucosaminidase in mucolipidosis II (I-cell disease). Clin Chim Acta. 1973 May 18;45(3):243–248. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90433-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightbody J., Wiesmann U., Hadorn B., Herschkowitz N. I-cell disease: multiple lysosomal-enzyme defect. Lancet. 1971 Feb 27;1(7696):451–451. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92435-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luchsinger U., Bühler E. M., Méhes K., Hirt H. R. Correspondence. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jun 11;282(24):1374–1375. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197006112822413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden A. G., O'Brien J. S. Binding of human liver beta-galactosidases to plant lectins insolubilized on agarose. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jan;56(1):193–198. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden A. G., O'Brien J. S. Ganglioside GM1 beta-galactosidase: studies in human liver and brain. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Nov;159(1):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90465-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES O. An improved procedure for starch-gel electrophoresis: further variations in the serum proteins of normal individuals. Biochem J. 1959 Mar;71(3):585–587. doi: 10.1042/bj0710585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tondeur M., Vamos-Hurwitz E., Mockel-Pohl S., Dereume J. P., Cremer N., Loeb H. Clinical, biochemical, and ultrastructural studies in a case of chondrodystrophy presenting the I-cell phenotype in tissue culture. J Pediatr. 1971 Sep;79(3):366–378. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




