Abstract
Background—There have been conflicting reports concerning the use of cardia biopsies in screening patients for gastro-oesophageal disease.
Aim—To define the histopathological changes in the gastric cardia of patients with and without gastro-oesophageal disease.
Methods—Topographically mapped gastric biopsy specimens were obtained from patients with gastro-oesophageal disease and from controls. Biopsies were scored on a visual analogue scale of 0 to 5 for Helicobacter pylori, intestinal metaplasia, pancreatic metaplasia, foveolar hyperplasia, and active inflammation. The presence or absence of cardiac glands was recorded.
Results—Sixty five patients with gastro-oesophageal disease and 71 controls were examined. Intestinal metaplasia was present in cardia biopsies of 10 patients with gastro-oesophageal disease and 11 controls. Only two patients with gastro-oesophageal disease and intestinal metaplasia in the cardia had no evidence of exposure to H pylori. Intestinal metaplasia was not found in the cardia of those with long segment Barrett's oesophagus. Carditis was strongly associated with active H pylori infection (p = 0.000) and resolved after treatment of the infection. A negative association was present between gastro-oesophageal disease and the presence of cardiac glands in cardiac biopsies (p = 0.003). Pancreatic metaplasia was found in 15 of 65 and foveolar hyperplasia in 19 of 65 cases but neither was related to gastro-oesophageal disease.
Conclusion—Intestinal metaplasia in the cardia is uncommon in gastro-oesophageal disease in the absence of H pylori infection. With chronic H pylori infection the junction between the cardia and corpus expands in a cardia–corpal direction.
Key Words: Barrett's oesophagus • gastro-oesophageal disease • cardia • Helicobacter pylori
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (139.4 KB).
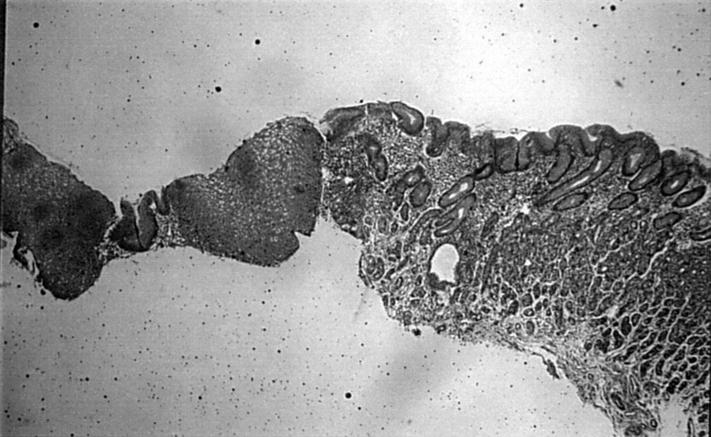
Figure 1 The cardia is a small structure varying from 0–10 mm in length. El-Zimaity triple stain. Original magnification, x4.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonioli D. A., Goldman H. Changes in the location and type of gastric adenocarcinoma. Cancer. 1982 Aug 15;50(4):775–781. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19820815)50:4<775::aid-cncr2820500425>3.0.co;2-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blot W. J., Devesa S. S., Kneller R. W., Fraumeni J. F., Jr Rising incidence of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and gastric cardia. JAMA. 1991 Mar 13;265(10):1287–1289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalasani N., Wo J. M., Hunter J. G., Waring J. P. Significance of intestinal metaplasia in different areas of esophagus including esophagogastric junction. Dig Dis Sci. 1997 Mar;42(3):603–607. doi: 10.1023/a:1018863529777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craanen M. E., Blok P., Dekker W., Tytgat G. N. Helicobacter pylori and early gastric cancer. Gut. 1994 Oct;35(10):1372–1374. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.10.1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craanen M. E., Dekker W., Blok P., Ferwerda J., Tytgat G. N. Time trends in gastric carcinoma: changing patterns of type and location. Am J Gastroenterol. 1992 May;87(5):572–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doglioni C., Laurino L., Dei Tos A. P., De Boni M., Franzin G., Braidotti P., Viale G. Pancreatic (acinar) metaplasia of the gastric mucosa. Histology, ultrastructure, immunocytochemistry, and clinicopathologic correlations of 101 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1993 Nov;17(11):1134–1143. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199311000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekström A. M., Signorello L. B., Hansson L. E., Bergström R., Lindgren A., Nyrén O. Evaluating gastric cancer misclassification: a potential explanation for the rise in cardia cancer incidence. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999 May 5;91(9):786–790. doi: 10.1093/jnci/91.9.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Serag H. B., Sonnenberg A. Ethnic variations in the occurrence of gastroesophageal cancers. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1999 Mar;28(2):135–139. doi: 10.1097/00004836-199903000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Serag H. B., Sonnenberg A., Jamal M. M., Kunkel D., Crooks L., Feddersen R. M. Characteristics of intestinal metaplasia in the gastric cardia. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999 Mar;94(3):622–627. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.00924.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Zimaity H. M., Graham D. Y. Evaluation of gastric mucosal biopsy site and number for identification of Helicobacter pylori or intestinal metaplasia: role of the Sydney System. Hum Pathol. 1999 Jan;30(1):72–77. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(99)90303-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Zimaity H. M., Ota H., Scott S., Killen D. E., Graham D. Y. A new triple stain for Helicobacter pylori suitable for the autostainer: carbol fuchsin/Alcian blue/hematoxylin-eosin. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1998 Aug;122(8):732–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eloubeidi M. A., Provenzale D. Does this patient have Barrett's esophagus? The utility of predicting Barrett's esophagus at the index endoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999 Apr;94(4):937–943. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.990_m.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk G. W. Reflux disease and Barrett's esophagus. Endoscopy. 1999 Jan;31(1):9–16. doi: 10.1055/s-1999-13643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genta R. M., Hamner H. W., Graham D. Y. Gastric lymphoid follicles in Helicobacter pylori infection: frequency, distribution, and response to triple therapy. Hum Pathol. 1993 Jun;24(6):577–583. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(93)90235-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genta R. M., Hamner H. W. The significance of lymphoid follicles in the interpretation of gastric biopsy specimens. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1994 Jul;118(7):740–743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genta R. M., Robason G. O., Graham D. Y. Simultaneous visualization of Helicobacter pylori and gastric morphology: a new stain. Hum Pathol. 1994 Mar;25(3):221–226. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90191-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblum J. R., Vicari J. J., Falk G. W., Rice T. W., Peek R. M., Easley K., Richter J. E. Inflammation and intestinal metaplasia of the gastric cardia: the role of gastroesophageal reflux and H. pylori infection. Gastroenterology. 1998 Apr;114(4):633–639. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(98)70576-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackelsberger A., Günther T., Schultze V., Labenz J., Roessner A., Malfertheiner P. Prevalence and pattern of Helicobacter pylori gastritis in the gastric cardia. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997 Dec;92(12):2220–2224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackelsberger A., Günther T., Schultze V., Manes G., Dominguez-Muñoz J. E., Roessner A., Malfertheiner P. Intestinal metaplasia at the gastro-oesophageal junction: Helicobacter pylori gastritis or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease? Gut. 1998 Jul;43(1):17–21. doi: 10.1136/gut.43.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henihan R. D., Stuart R. C., Nolan N., Gorey T. F., Hennessy T. P., O'Morain C. A. Barrett's esophagus and the presence of Helicobacter pylori. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998 Apr;93(4):542–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.162_b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota W. K., Loughney T. M., Lazas D. J., Maydonovitch C. L., Rholl V., Wong R. K. Specialized intestinal metaplasia, dysplasia, and cancer of the esophagus and esophagogastric junction: prevalence and clinical data. Gastroenterology. 1999 Feb;116(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(99)70123-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Integlia M. J., Krishnamurthy S., Berhane R., Grand R. J., Dayal Y. Pancreatic metaplasia of the gastric mucosa in pediatric patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997 Sep;92(9):1553–1556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura K. Chronological transition of the fundic-pyloric border determined by stepwise biopsy of the lesser and greater curvatures of the stomach. Gastroenterology. 1972 Oct;63(4):584–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause W. J., Ivey K. J., Baskin W. N., MacKercher P. A. Morphological observations on the normal human cardiac glands. Anat Rec. 1978 Sep;192(1):59–71. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091920106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai T., Malaty H. M., Graham D. Y., Hosogaya S., Misawa K., Furihata K., Ota H., Sei C., Tanaka E., Akamatsu T. Acquisition versus loss of Helicobacter pylori infection in Japan: results from an 8-year birth cohort study. J Infect Dis. 1998 Sep;178(3):717–721. doi: 10.1086/515376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luque-Barona R. J., Pereda-Salguero T., Fernández-Alonso J. So-called pancreatic acinar metaplasia of the gastric mucosa in two infants: a post-mortem study. Eur J Pediatr. 1999 Mar;158(3):267–268. doi: 10.1007/pl00022926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyagawa Y. The Exact Distribution of the Gastric Glands in Man and in Certain Animals. J Anat. 1920 Oct;55(Pt 1):56–67. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morales T. G., Sampliner R. E., Bhattacharyya A. Intestinal metaplasia of the gastric cardia. Am J Gastroenterol. 1997 Mar;92(3):414–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandurkar S., Talley N. J., Martin C. J., Ng T. H., Adams S. Short segment Barrett's oesophagus: prevalence, diagnosis and associations. Gut. 1997 Jun;40(6):710–715. doi: 10.1136/gut.40.6.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberg S., Peters J. H., DeMeester T. R., Chandrasoma P., Hagen J. A., Ireland A. P., Ritter M. P., Mason R. J., Crookes P., Bremner C. G. Inflammation and specialized intestinal metaplasia of cardiac mucosa is a manifestation of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Surg. 1997 Oct;226(4):522–532. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199710000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pera M., Cameron A. J., Trastek V. F., Carpenter H. A., Zinsmeister A. R. Increasing incidence of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and esophagogastric junction. Gastroenterology. 1993 Feb;104(2):510–513. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90420-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira A. D., Suspiro A., Chaves P., Saraiva A., Glória L., de Almeida J. C., Leitão C. N., Soares J., Mira F. C. Short segments of Barrett's epithelium and intestinal metaplasia in normal appearing oesophagogastric junctions: the same or two different entities? Gut. 1998 May;42(5):659–662. doi: 10.1136/gut.42.5.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokkas T., Filipe M. I., Sladen G. E. Detection of an increased incidence of early gastric cancer in patients with intestinal metaplasia type III who are closely followed up. Gut. 1991 Oct;32(10):1110–1113. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.10.1110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva S., Filipe M. I., Pinho A. Variants of intestinal metaplasia in the evolution of chronic atrophic gastritis and gastric ulcer. A follow up study. Gut. 1990 Oct;31(10):1097–1104. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.10.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spechler S. J., Zeroogian J. M., Antonioli D. A., Wang H. H., Goyal R. K. Prevalence of metaplasia at the gastro-oesophageal junction. Lancet. 1994 Dec 3;344(8936):1533–1536. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90349-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachura J., Konturek J., Urbańczyk K., Bogdal J., Domschke W. Pancreatic metaplasia of the human gastric mucosa is associated with high expression of transforming growth factor alpha but not of epidermal growth factor. Histopathology. 1995 Dec;27(6):509–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1995.tb00321.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takubo K., Mafune K., Tanaka Y., Sasajima K. [Pathology of the cardia]. Nihon Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 1998 Sep;99(9):547–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voutilainen M., Färkkilä M., Juhola M., Nuorva K., Mauranen K., Mäntynen T., Kunnamo I., Mecklin J. P., Sipponen P. Specialized columnar epithelium of the esophagogastric junction: prevalence and associations. The Central Finland Endoscopy Study Group. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999 Apr;94(4):913–918. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.986_i.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. H., Zeroogian J. M., Spechler S. J., Goyal R. K., Antonioli D. A. Prevalence and significance of pancreatic acinar metaplasia at the gastroesophageal junction. Am J Surg Pathol. 1996 Dec;20(12):1507–1510. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199612000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston A. P., Krmpotich P. T., Cherian R., Dixon A., Topalovski M. Prospective evaluation of intestinal metaplasia and dysplasia within the cardia of patients with Barrett's esophagus. Dig Dis Sci. 1997 Mar;42(3):597–602. doi: 10.1023/a:1018811512939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Serag H. B., Sonnenberg A. Opposing time trends of peptic ulcer and reflux disease. Gut. 1998 Sep;43(3):327–333. doi: 10.1136/gut.43.3.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Zimaity H. M., Graham D. Y., al-Assi M. T., Malaty H., Karttunen T. J., Graham D. P., Huberman R. M., Genta R. M. Interobserver variation in the histopathological assessment of Helicobacter pylori gastritis. Hum Pathol. 1996 Jan;27(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(96)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Zimaity H. M., al-Assi M. T., Genta R. M., Graham D. Y. Confirmation of successful therapy of Helicobacter pylori infection: number and site of biopsies or a rapid urease test. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995 Nov;90(11):1962–1964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]