Abstract
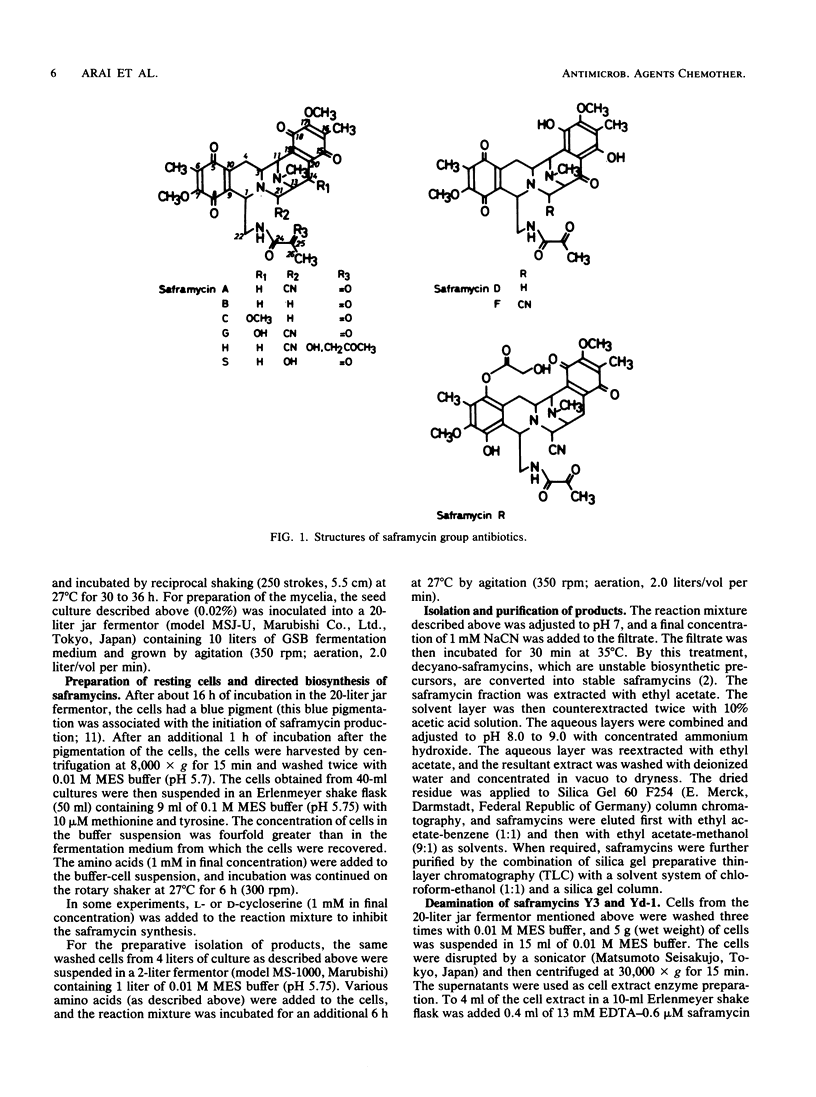
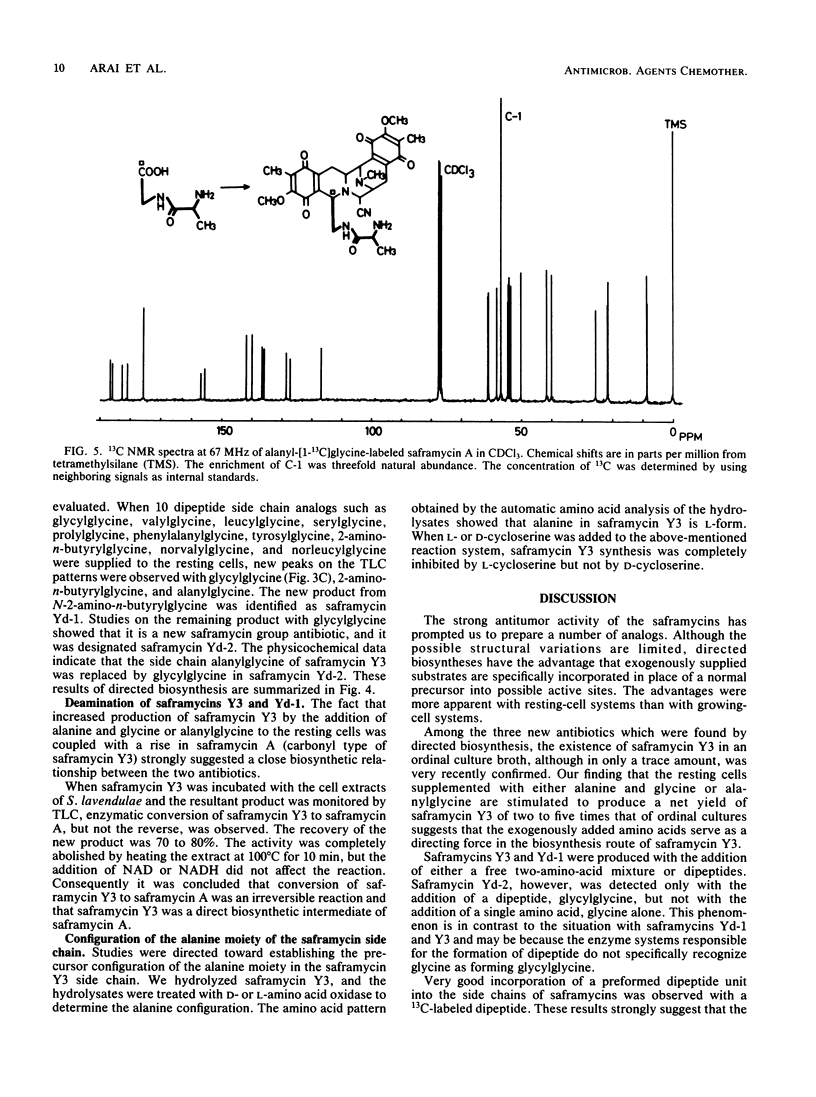
Saframycin A is an antitumor antibiotic produced by Streptomyces lavendulae 314 which falls into the category of the N-heterocyclic quinone group. Biosynthetically the quinone ring is derived from two tyrosine molecules which condense to generate the basic ring system of saframycin A. The side chain also has been found to derive from two amino acids, i.e., glycine and alanine. Supplementation by various amino acid analogs of the side chain produced three new saframycin derivatives with a replaced side chain. These three saframycins, designated Yd-1, Yd-2, and Y3, contained 2-amino-n-butyric acid, glycine, and alanine residues, respectively. in place of the normal N-terminal pyruvic acid in the side chain of saframycin A. Feeding experiments with 13C-labeled dipeptide indicated that the amino acids are probably incorporated in the side chain as a dipeptide unit. It was also found that saframycin A is produced from saframycin Y3 by an enzymatic deamination reaction. Based on these results, saframycin biosynthesis in S. lavendulae is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai T., Takahashi K., Ishiguro K., Mikami Y. Some chemotherapeutic properties of two new antitumor antibiotics, saframycins A and C. Gan. 1980 Dec;71(6):790–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai T., Takahashi K., Ishiguro K., Yazawa K. Increased production of saframycin A and isolation of saframycin S. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1980 Sep;33(9):951–960. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.33.951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai T., Takahashi K., Kubo A. New antibiotics saframycins A, B, C, D and E. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1977 Nov;30(11):1015–1018. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.30.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asaoka T., Yazawa K., Mikami Y., Arai T., Takahashi K. A new saframycin, saframycin R. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1982 Dec;35(12):1708–1710. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.35.1708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good N. E., Winget G. D., Winter W., Connolly T. N., Izawa S., Singh R. M. Hydrogen ion buffers for biological research. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):467–477. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro K., Takahashi K., Yazawa K., Sakiyama S., Arai T. Binding of saframycin A, a heterocyclic quinone anti-tumor antibiotic to DNA as revealed by the use of the antibiotic labeled with [14C]tyrosine or [14C]cyanide. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2162–2167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishi K., Yazawa K., Takahashi K., Mikami Y., Arai T. Structure-activity relationships of saframycins. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1984 Aug;37(8):847–852. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.37.847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lown J. W., Hanstock C. C., Joshua A. V., Arai T., Takahashi K. Structure and conformation of saframycin R determined by high field 1H and 13C NMR and its interactions with DNA in solution. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1983 Sep;36(9):1184–1194. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.36.1184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lown J. W., Joshua A. V., Lee J. S. Molecular mechanisms of binding and single-strand scission of deoxyribonucleic acid by the antitumor antibiotics saframycins A and C. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 2;21(3):419–428. doi: 10.1021/bi00532a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikami Y., Takahashi K., Yazawa K., Arai T., Namikoshi M., Iwasaki S., Okuda S. Biosynthetic studies on saframycin A, a quinone antitumor antibiotic produced by Streptomyces lavendulae. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):344–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



