Abstract
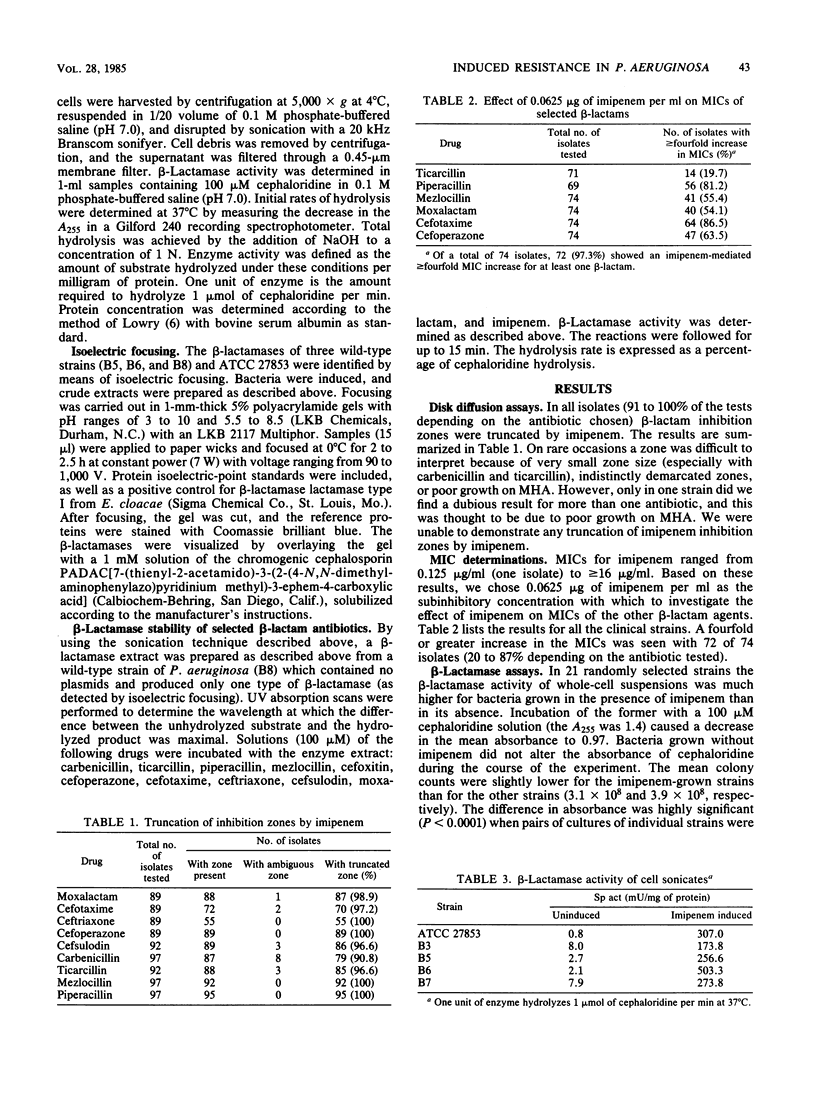
Using clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, we studied the ability of imipenem to antagonize the activity of nine other antipseudomonal beta-lactam antimicrobial agents. Imipenem caused truncation of the zones of inhibition in a disk diffusion test for 91 to 100% of the strains, depending on the beta-lactam tested. Addition of subinhibitory concentrations of imipenem caused a fourfold or greater increase in MICs for 72 of 74 isolates and in 20 to 87% of the tests, again depending on the antibiotic tested. beta-Lactamase assays with both whole-cell suspensions and cell sonicates showed that exposure to subinhibitory concentrations of imipenem resulted in a beta-lactamase production supported the hypothesis that induction of beta-lactamase was responsible for antagonism. In hydrolysis studies with a beta-lactamase extract, most of the antagonized drugs were either not hydrolyzed or only poorly hydrolyzed. We conclude that imipenem induces significantly elevated levels of beta-lactamase in P. aeruginosa. This increase in beta-lactamase is associated with increased resistance of the organism to many other beta-lactam agents.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertram M. A., Young L. S. Imipenem antagonism of the in vitro activity of piperacillin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):272–274. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gootz T. D., Sanders C. C. Characterization of beta-lactamase induction in Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jan;23(1):91–97. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuck N. A., Testa R. T., Forbes M. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial effects of combinations of beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Apr;19(4):634–638. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.4.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livermore D. M. Kinetics and significance of the activity of the Sabath and Abrahams' beta-lactamase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa against cefotaxime and cefsulodin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Feb;11(2):169–179. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.2.169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livermore D. M., Williams R. J., Williams J. D. Comparison of the beta-lactamase stability and the in-vitro activity of cefoperazone, cefotaxime, cefsulodin, ceftazidime, moxalactam and ceftriaxone against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Oct;8(4):323–331. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.4.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami S., Yotsuji A., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Induction of beta-lactamase by various beta-lactam antibiotics in Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Sep;18(3):382–385. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.3.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Labthavikul P. Comparative in vitro activity of N-formimidoyl thienamycin against gram-positive and gram-negative aerobic and anaerobic species and its beta-lactamase stability. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jan;21(1):180–187. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicas T. I., Hancock R. E. Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane permeability: isolation of a porin protein F-deficient mutant. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):281–285. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.281-285.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Luckey M., Rosenberg E. Y. Nonspecific and specific diffusion channels in the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. J Supramol Struct. 1980;13(3):305–313. doi: 10.1002/jss.400130304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Rosenberg E. Y., Foulds J. Porin channels in Escherichia coli: studies with beta-lactams in intact cells. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):232–240. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.232-240.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preheim L. C., Penn R. G., Sanders C. C., Goering R. V., Giger D. K. Emergence of resistance to beta-lactam and aminoglycoside antibiotics during moxalactam therapy of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Dec;22(6):1037–1041. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.6.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer L. G., Stratton C. W., Reller L. B. Minimum inhibitory and bactericidal concentrations of 44 antimicrobial agents against three standard control strains in broth with and without human serum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jun;19(6):1050–1055. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.6.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their possible physiological role. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;9:31–88. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr Emergence of resistance to cefamandole: possible role of cefoxitin-inducible beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jun;15(6):792–797. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.6.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr, Goering R. V. In vitro antagonism of beta-lactam antibiotics by cefoxitin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jun;21(6):968–975. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.6.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeberg A. H., Tolxdorff-Neutzling R. M., Wiedemann B. Chromosomal beta-lactamases of Enterobacter cloacae are responsible for resistance to third-generation cephalosporins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jun;23(6):918–925. doi: 10.1128/aac.23.6.918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes R. B., Matthew M. The beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria and their role in resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1976 Jun;2(2):115–157. doi: 10.1093/jac/2.2.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Then R. L., Angehrn P. Trapping of nonhydrolyzable cephalosporins by cephalosporinases in Enterobacter cloacae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a possible resistance mechanism. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 May;21(5):711–717. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.5.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston D. J., Barnes R. C., Ho W. G., Young L. S., Champlin R. E., Gale R. P. Moxalactam plus piperacillin versus moxalactam plus amikacin in febrile granulocytopenic patients. Am J Med. 1984 Sep;77(3):442–450. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu D. H., Baltch A. L., Smith R. P., Conley P. E. Effect of aztreonam in combination with azlocillin or piperacillin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Oct;26(4):519–521. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.4.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Nikaido H. Diffusion of beta-lactam antibiotics through the porin channels of Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):84–92. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



