Abstract
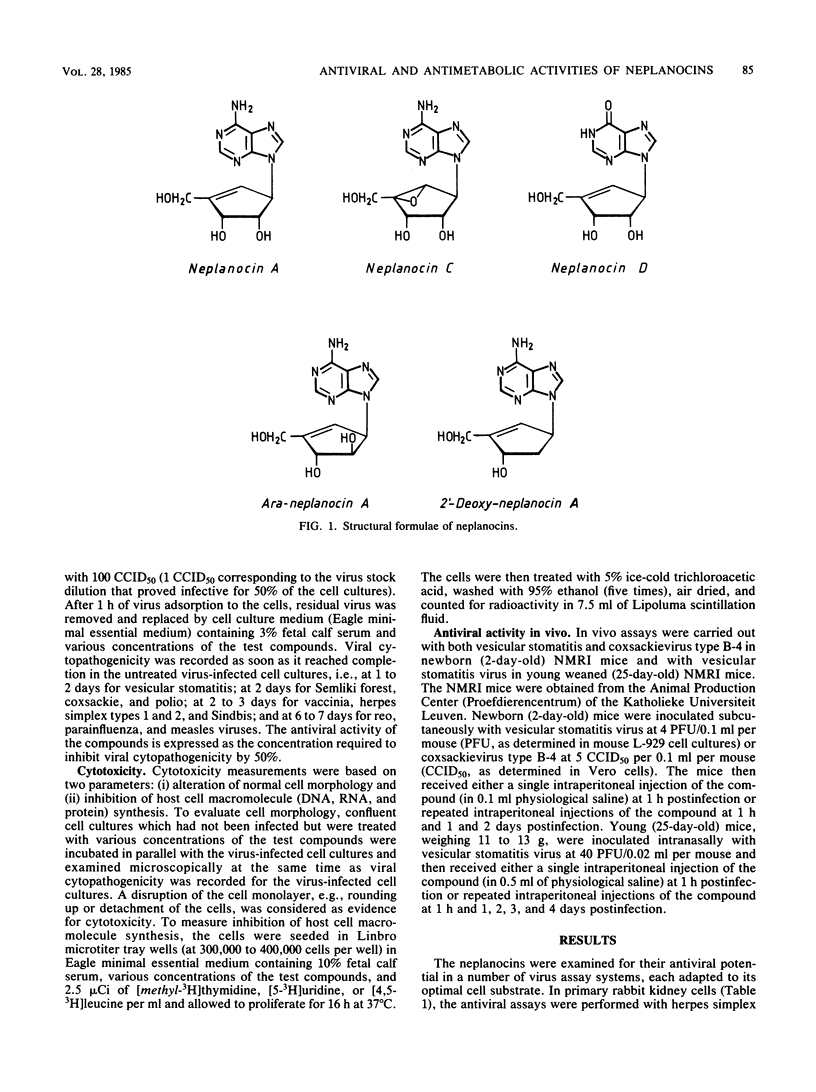
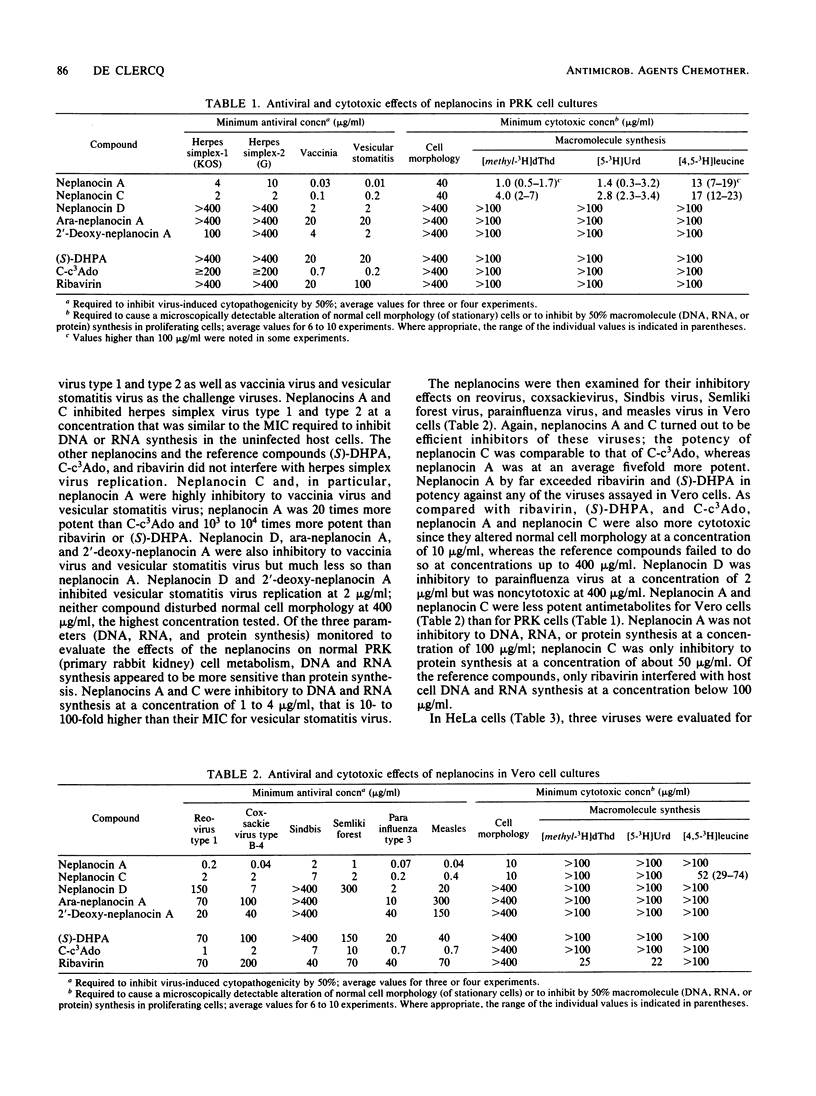
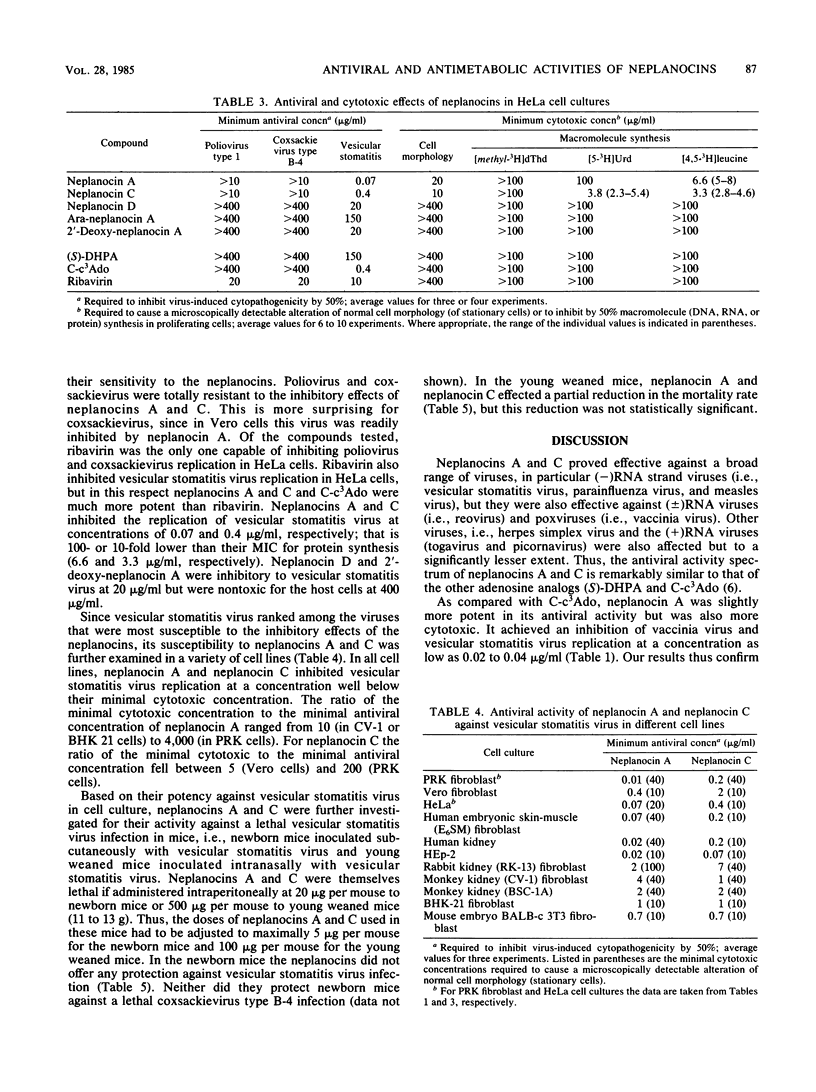
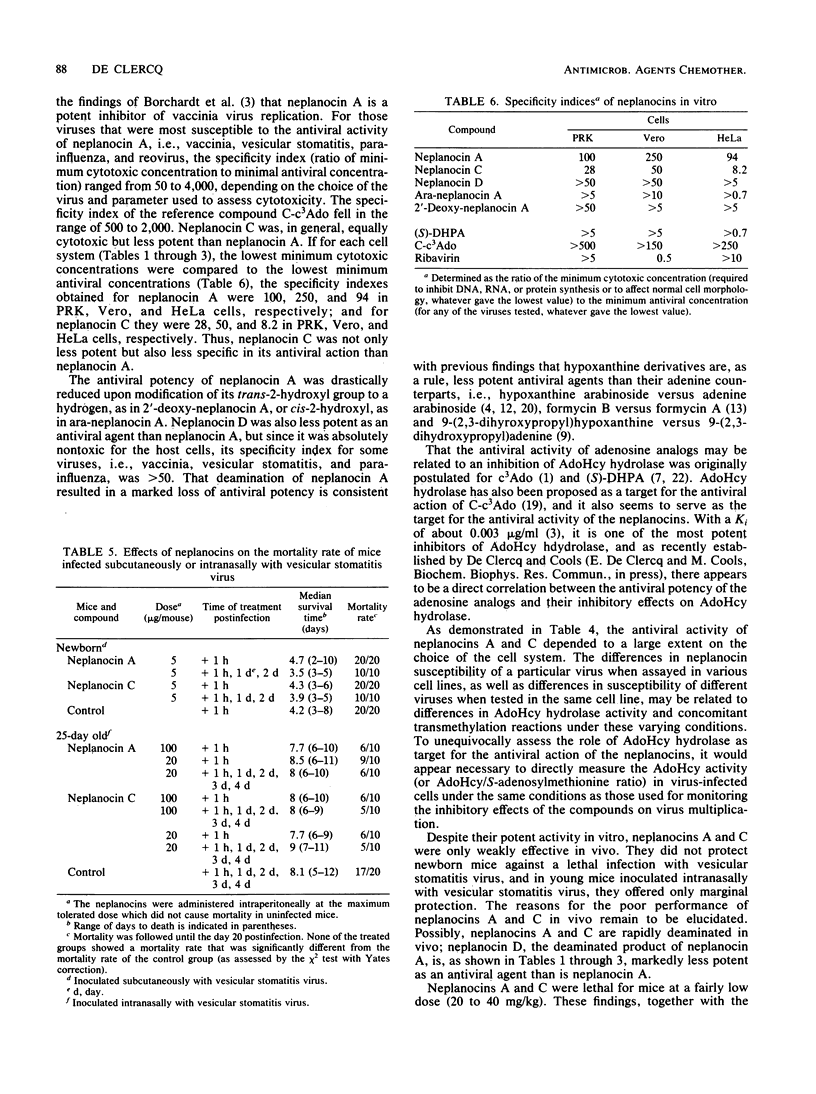
Of a series of carbocyclic analogs of adenosine, in which the ribose moiety was replaced by a cyclopentenyl ring, neplanocin A, or (-)-9-[trans-2, trans-3-dihydroxy-4-(hydroxymethyl)cyclopent-4-enyl]adenine proved particularly effective in inhibiting the multiplication of DNA viruses (i.e., vaccinia), (-)RNA viruses (i.e., parainfluenza, measles, and vesicular stomatitis), and double-stranded RNA viruses (i.e., reo) in vitro in cell culture. Depending on the cells used, the MIC of neplanocin A for these viruses ranged from 0.01 to 4 micrograms/ml, and depending on the parameter used to assess toxicity for the host cell, the specificity index of neplanocin A ranged from 50 to 4,000. As postulated before for other adenosine analogs, neplanocin A may owe its antiviral action to inhibition of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase, hence perturbation of transmethylation reactions. In vivo, neplanocin A afforded only marginal protection against a lethal infection of mice with vesicular stomatitis virus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bader J. P., Brown N. R., Chiang P. K., Cantoni G. L. 3-Deazaadenosine, an inhibitor of adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase, inhibits reproduction of Rous sarcoma virus and transformation of chick embryo cells. Virology. 1978 Sep;89(2):494–505. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodner A. J., Cantoni G. L., Chiang P. K. Anti-viral activity of 3-deazaadenosine and 5'-deoxy-5'-isobutylthio-3-deazaadenosine (3-deaza-SIBA). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Jan 30;98(2):476–481. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90864-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borchardt R. T., Keller B. T., Patel-Thombre U. Neplanocin A. A potent inhibitor of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase and of vaccinia virus multiplication in mouse L929 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4353–4358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryson Y. J., Connor J. D. In vitro susceptibility of varicella zoster virus to adenine arabinoside and hypoxanthine arabinoside. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Mar;9(3):540–543. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.3.540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang P. K., Guranowski A., Segall J. E. Irreversible inhibition of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase by nucleoside analogs. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Mar;207(1):175–184. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE Clercq E., Descamps J., DE Somer P., Holyacute A. (S)-9-(2,3-Dihydroxypropyl)adenine: An Aliphatic Nucleoside Analog with Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Activity. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):563–565. doi: 10.1126/science.200.4341.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Cercq E., Luczak M. Fluoroimidazoles as antiviral agents and inhibitors of polynucleotide biosynthesis. Life Sci. 1975 Jul 15;17(2):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90502-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Bergstrom D. E., Holy A., Montgomery J. A. Broad-spectrum antiviral activity of adenosine analogues. Antiviral Res. 1984 Jun;4(3):119–133. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(84)90012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Descamps J., Verhelst G., Walker R. T., Jones A. S., Torrence P. F., Shugar D. Comparative efficacy of antiherpes drugs against different strains of herpes simplex virus. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):563–574. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E., Holy A. Antiviral activity of aliphatic nucleoside analogues: structure-function relationship. J Med Chem. 1979 May;22(5):510–513. doi: 10.1021/jm00191a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gephart J. F., Lerner A. M. Comparison of the effects of arabinosyladenine, arabinosylhypoxanthine, and arabinosyladenine 5'-monophosphate against herpes simplex virus, varicella-zoster virus, and cytomegalovirus with their effects on cellular deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jan;19(1):170–178. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.1.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giziewicz J., De Clercq E., Luczak M., Shugar D. Antiviral and antimetabolic activities of formycin and its N1-, N2-, 2'-O- and 3'-O-methylated derivatives. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Oct 1;24(19):1813–1817. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90462-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guranowski A., Montgomery J. A., Cantoni G. L., Chiang P. K. Adenosine analogues as substrates and inhibitors of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 6;20(1):110–115. doi: 10.1021/bi00504a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M., Yaginuma S., Muto N., Tsujino M. Structures of neplanocins, new antitumor antibiotics. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1980;(8):s65–s67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M., Yaginuma S., Yoshioka H., Nakatsu K. Studies on neplanocin A, new antitumor antibiotic. II. Structure determination. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1981 Jun;34(6):675–680. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.34.675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery J. A., Clayton S. J., Thomas H. J., Shannon W. M., Arnett G., Bodner A. J., Kion I. K., Cantoni G. L., Chiang P. K. Carbocyclic analogue of 3-deazaadenosine: a novel antiviral agent using S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase as a pharmacological target. J Med Chem. 1982 Jun;25(6):626–629. doi: 10.1021/jm00348a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipman C., Jr, Smith S. H., Carlson R. H., Drach J. C. Antiviral activity of arabinosyladenine and arabinosylhypoxanthine in herpes simplex virus-infected KB cells: selective inhibition of viral deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in synchronized suspension cultures. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Jan;9(1):120–127. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaginuma S., Muto N., Tsujino M., Sudate Y., Hayashi M., Otani M. Studies on neplanocin A, new antitumor antibiotic. I. Producing organism, isolation and characterization. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1981 Apr;34(4):359–366. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.34.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Clercq E., Montgomery J. A. Broad-spectrum antiviral activity of the carbocyclic analog of 3-deazaadenosine. Antiviral Res. 1983 Mar;3(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(83)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


