Abstract
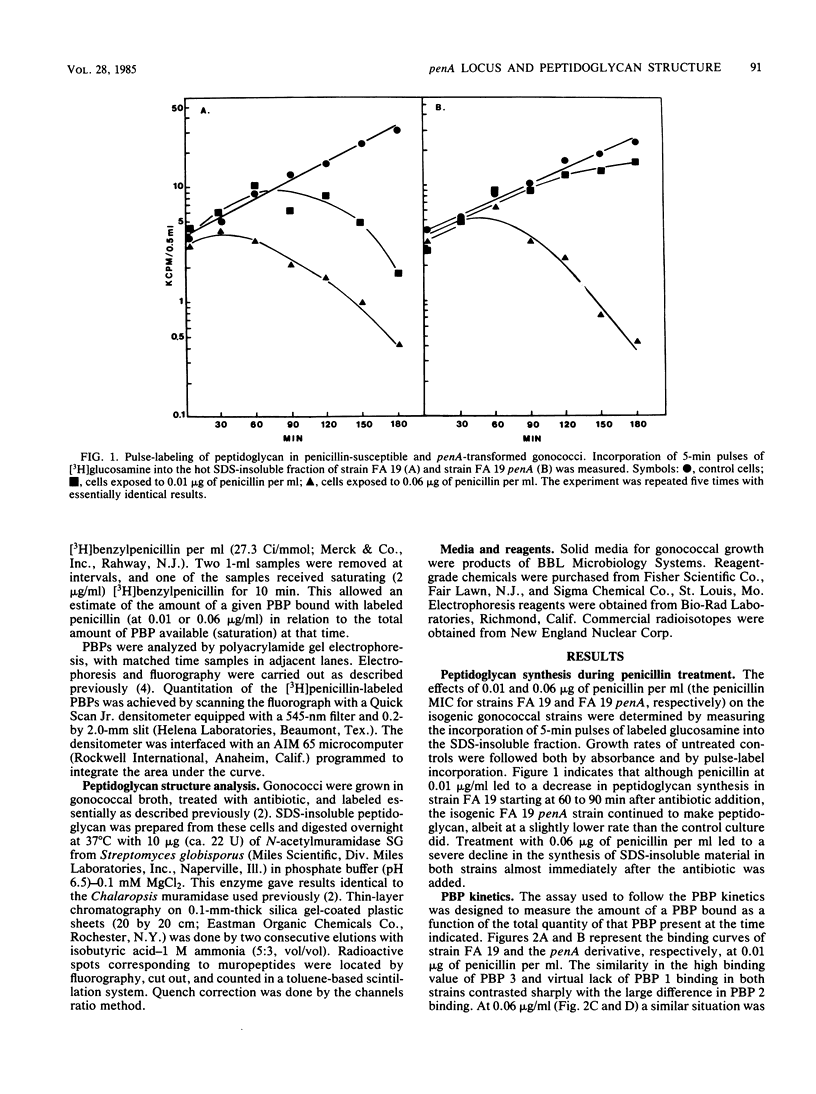
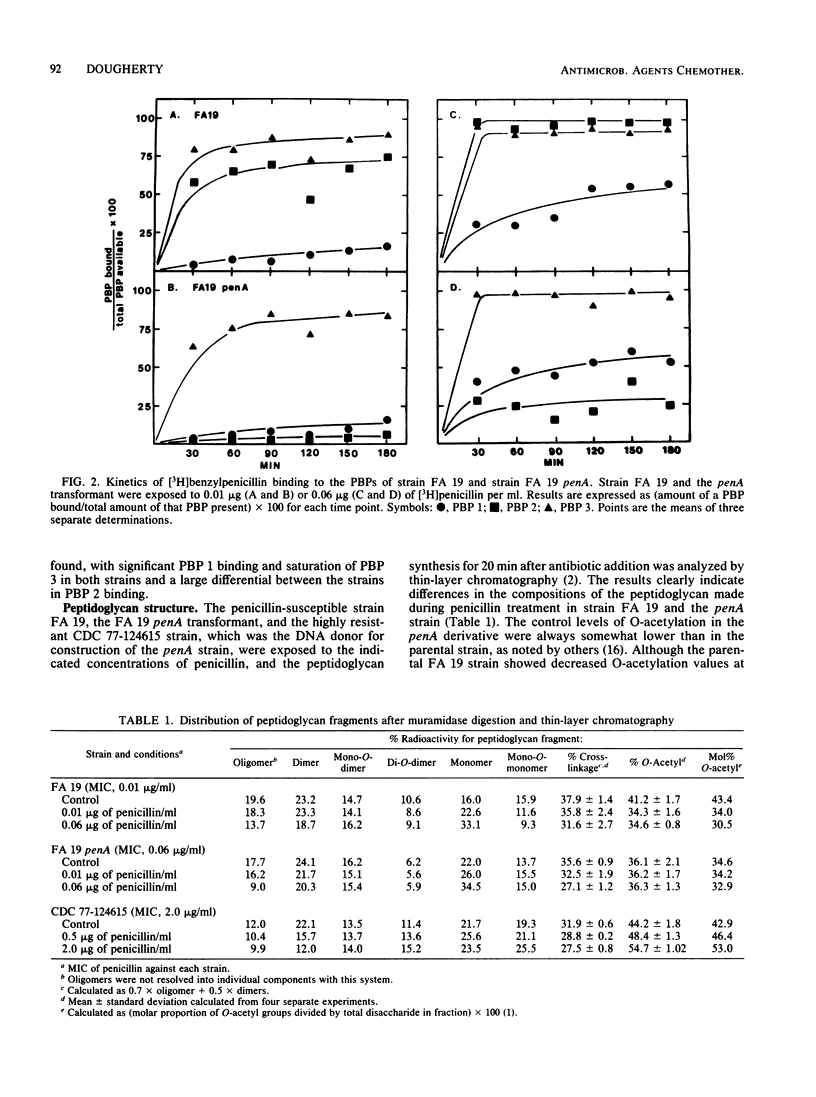
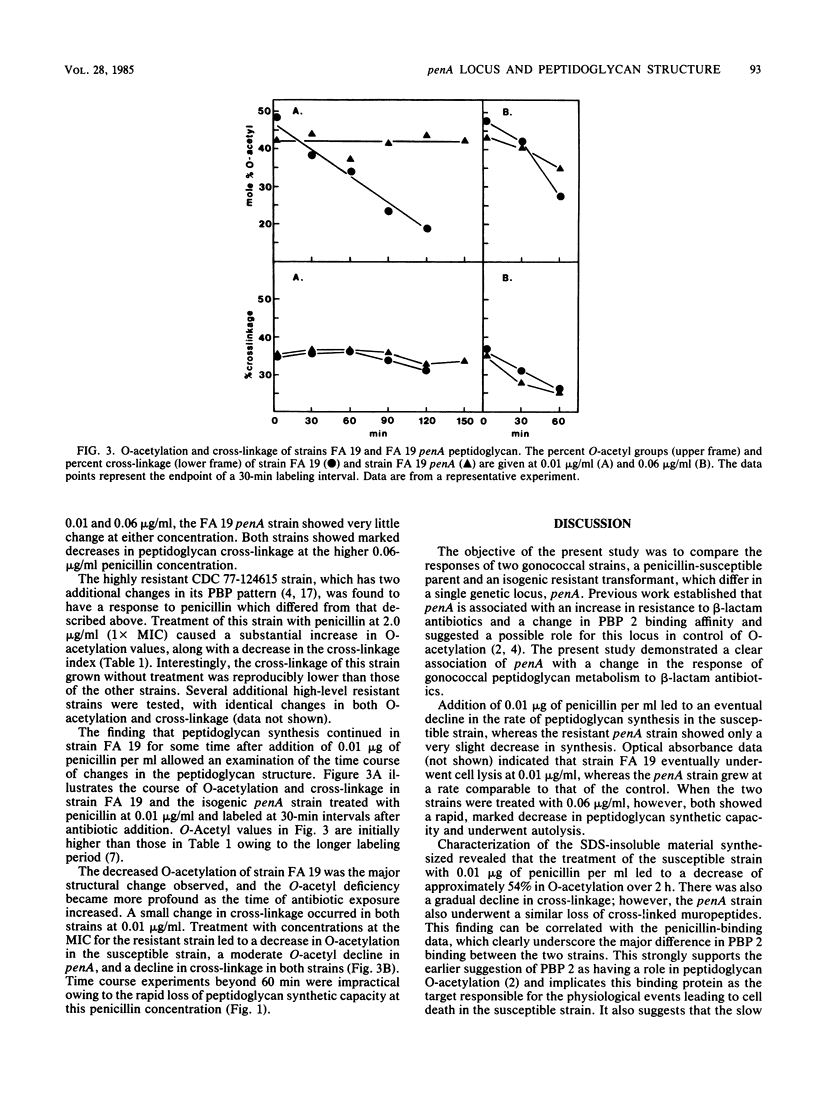
A penicillin-susceptible gonococcus and its low-level resistant penA transformant were examined with regard to their penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) and their peptidoglycan structures. Treatment of the susceptible strain with its MIC of penicillin (0.01 microgram/ml) led to significant binding to PBPs 2 and 3 and a substantial decrease in the O-acetyl modification on the peptidoglycan. Peptidoglycan synthesis gradually ceased over an extended time. When the penA strain was treated with the same concentration of penicillin, only binding to PBP 3 was observed and there was no O-acetylation decrease, with continued peptidoglycan synthesis. This suggested that PBP 2 was the primary target in penicillin-susceptible gonococci and that this protein participated in the O-acetylation of peptidoglycan. Penicillin concentrations representing the MIC for the penA transformant (0.06 microgram/ml) caused significant binding to PBPs 1, 2, and 3 in the susceptible strain and PBPs 1 and 3 in the penA strain. In both strains the rate of peptidoglycan synthesis and the cross-linkage of the peptidoglycan made declined sharply, suggesting that significant inhibition of PBP 1 interfered with transpeptidation. A model for low-level resistance is proposed in which a decreased PBP 2 affinity leads to assumption of the role of primary target in the resistant transformant by PBP 1. The differences observed in peptidoglycan metabolism are a direct consequence of this change.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blundell J. K., Perkins H. R. Effects of beta-lactam antibiotics on peptidoglycan synthesis in growing Neisseria gonorrhoeae, including changes in the degree of O-acetylation. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):633–641. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.633-641.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty T. J., Koller A. E., Tomasz A. Competition of beta-lactam antibiotics for the penicillin-binding proteins of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jul;20(1):109–114. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty T. J., Koller A. E., Tomasz A. Penicillin-binding proteins of penicillin-susceptible and intrinsically resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):730–737. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty T. J. Peptidoglycan biosynthesis in Neisseria gonorrhoeae strains sensitive and intrinsically resistant to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):429–435. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.429-435.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell E. W., Fazio M., Tomasz A. Effect of benzylpenicillin on the synthesis and structure of the cell envelope of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Mar;13(3):514–526. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.3.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lear A. L., Perkins H. R. Degrees of O-acetylation and cross-linking of the peptidoglycan of Neisseria gonorrhoeae during growth. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Mar;129(3):885–888. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-3-885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier T. W., Zubrzycki L., Coyle M. B., Chila M., Warner P. Genetic analysis of drug resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: production of increased resistance by the combination of two antibiotic resistance loci. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):834–842. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.834-842.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin H. H., Gmeiner J. Modification of peptidoglycan structure by penicillin action in cell walls of Proteus mirabilis. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr;95(3):487–495. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarubbi F. A., Jr, Sparling P. F., Blackman E., Lewis E. Loss of low-level antibiotic resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae due to env mutations. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):750–756. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.750-756.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha R. K., Rosenthal R. S. Release of soluble peptidoglycan from growing conococci: demonstration of anhydro-muramyl-containing fragments. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):914–925. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.914-925.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling P. F., Sarubbi F. A., Jr, Blackman E. Inheritance of low-level resistance to penicillin, tetracycline, and chloramphenicol in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):740–749. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.740-749.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Penicillin-binding proteins and the future of beta-lactam antibiotics. The Seventh Fleming Lecture. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 May;129(5):1247–1260. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-5-1247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XII. Colony color and opacity varienats of gonococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):320–331. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.320-331.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swim S. C., Gfell M. A., Wilde C. E., 3rd, Rosenthal R. S. Strain distribution in extents of lysozyme resistance and O-acetylation of gonococcal peptidoglycan determined by high-performance liquid chromatography. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):446–452. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.446-452.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner P. F., Zubrzycki L. J., Chila M. Polygenes and modifier genes for tetracycline and penicillin resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Mar;117(1):103–110. doi: 10.1099/00221287-117-1-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Strominger J. L. Penicillin-binding proteins and the mechanism of action of beta-lactam antibiotics. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:825–869. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.004141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener W. S., Hebeler B. H., Morse S. A. Cell envelope of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: relationship between autolysis in buffer and the hydrolysis of peptidoglycan. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):210–219. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.210-219.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



