Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (239.8 KB).
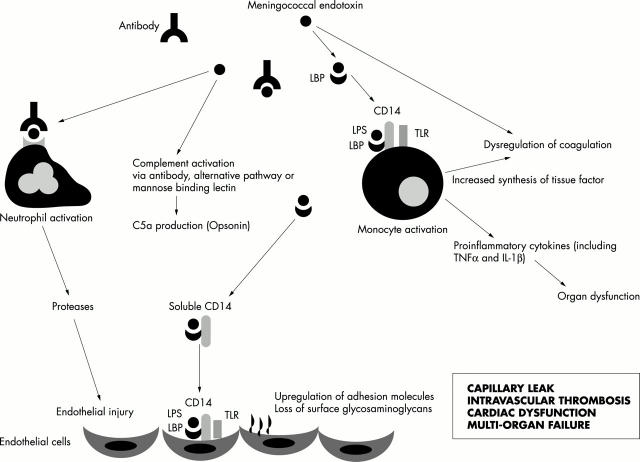
Figure 1.
The inflammatory cascade in meningococcal septicaemia.
Figure 2.
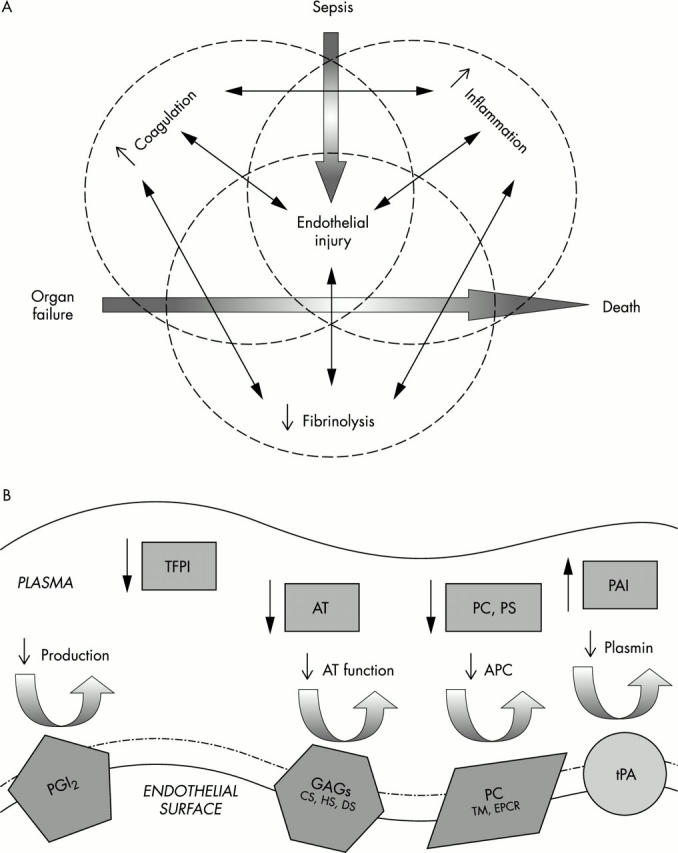
(A) The inflammatory, coagulation, and fibrinolytic pathways are linked at many levels, leading to organ failure and eventually death. (B) The coagulation and fibrinolytic pathways rely on the function of endothelial proteins and protein complexes. Dysfunctional regulatory mechanisms in meningococcal disease include endothelial (protein C pathway) and plasma (TFPI, antithrombin, PAI) factors.
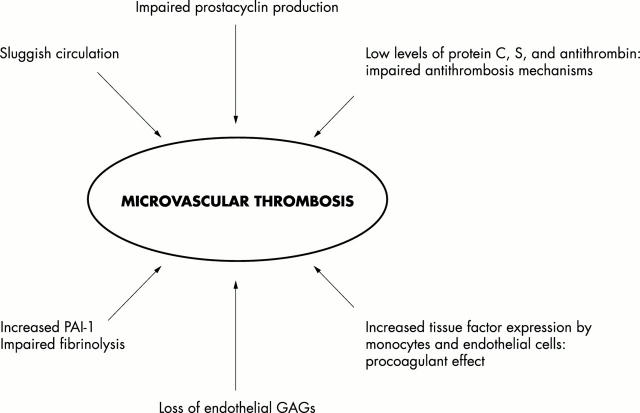
Figure 3.
Factors involved in intravascular thrombosis and purpura fulminans.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen B. M. Endotoxin release from neisseria meningitidis. Relationship between key bacterial characteristics and meningococcal disease. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1989;64:1–43. doi: 10.3109/inf.1989.21.suppl-64.01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard G. R., Vincent J. L., Laterre P. F., LaRosa S. P., Dhainaut J. F., Lopez-Rodriguez A., Steingrub J. S., Garber G. E., Helterbrand J. D., Ely E. W. Efficacy and safety of recombinant human activated protein C for severe sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2001 Mar 8;344(10):699–709. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200103083441001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucek M. M., Boerth R. C., Artman M., Graham T. P., Jr, Boucek R. J., Jr Myocardial dysfunction in children with acute meningococcemia. J Pediatr. 1984 Oct;105(4):538–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80416-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Joø G. B., Brusletto B., Kierulf P. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 and 2, alpha-2-antiplasmin, plasminogen, and endotoxin levels in systemic meningococcal disease. Thromb Res. 1990 Jan 15;57(2):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(90)90326-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Kierulf P., Gaustad P., Skulberg A., Bruun J. N., Halvorsen S., Sørensen E. Plasma endotoxin as a predictor of multiple organ failure and death in systemic meningococcal disease. J Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;159(2):195–204. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.2.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Sandset P. M., Joø G. B., Ovstebø R., Abildgaard U., Kierulf P. The quantitative association of plasma endotoxin, antithrombin, protein C, extrinsic pathway inhibitor and fibrinopeptide A in systemic meningococcal disease. Thromb Res. 1989 Aug 15;55(4):459–470. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(89)90054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britto J., Nadel S., Habibi P., Levin M. Gastrointestinal perforation complicating meningococcal disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1995 May;14(5):393–394. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199505000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T., Ding W., Yasuhiro K., Gu J. M., Ferrell G., Regan L. M., Stearns-Kurosawa D. J., Kurosawa S., Mather T., Laszik Z. The protein C pathway: new insights. Thromb Haemost. 1997 Jul;78(1):70–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust S. N., Levin M., Harrison O. B., Goldin R. D., Lockhart M. S., Kondaveeti S., Laszik Z., Esmon C. T., Heyderman R. S. Dysfunction of endothelial protein C activation in severe meningococcal sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2001 Aug 9;345(6):408–416. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200108093450603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fijen C. A., Kuijper E. J., Tjia H. G., Daha M. R., Dankert J. Complement deficiency predisposes for meningitis due to nongroupable meningococci and Neisseria-related bacteria. Clin Infect Dis. 1994 May;18(5):780–784. doi: 10.1093/clinids/18.5.780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finne J., Bitter-Suermann D., Goridis C., Finne U. An IgG monoclonal antibody to group B meningococci cross-reacts with developmentally regulated polysialic acid units of glycoproteins in neural and extraneural tissues. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4402–4407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fourrier F., Lestavel P., Chopin C., Marey A., Goudemand J., Rime A., Mangalaboyi J. Meningococcemia and purpura fulminans in adults: acute deficiencies of proteins C and S and early treatment with antithrombin III concentrates. Intensive Care Med. 1990;16(2):121–124. doi: 10.1007/BF02575306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardin E., Grau G. E., Dayer J. M., Roux-Lombard P., Lambert P. H. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in the serum of children with severe infectious purpura. N Engl J Med. 1988 Aug 18;319(7):397–400. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198808183190703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschneider I., Gotschlich E. C., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. I. The role of humoral antibodies. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1307–1326. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschneider I., Gotschlich E. C., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. II. Development of natural immunity. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1327–1348. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halstensen A., Ceska M., Brandtzaeg P., Redl H., Naess A., Waage A. Interleukin-8 in serum and cerebrospinal fluid from patients with meningococcal disease. J Infect Dis. 1993 Feb;167(2):471–475. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.2.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans P. W., Hibberd M. L., Booy R., Daramola O., Hazelzet J. A., de Groot R., Levin M. 4G/5G promoter polymorphism in the plasminogen-activator-inhibitor-1 gene and outcome of meningococcal disease. Meningococcal Research Group. Lancet. 1999 Aug 14;354(9178):556–560. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(99)02220-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyderman R. S., Klein N. J., Daramola O. A., Hammerschmidt S., Frosch M., Robertson B. D., Levin M., Ison C. A. Induction of human endothelial tissue factor expression by Neisseria meningitidis: the influence of bacterial killing and adherence to the endothelium. Microb Pathog. 1997 May;22(5):265–274. doi: 10.1006/mpat.1996.0112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyderman R. S., Klein N. J., Shennan G. I., Levin M. Deficiency of prostacyclin production in meningococcal shock. Arch Dis Child. 1991 Nov;66(11):1296–1299. doi: 10.1136/adc.66.11.1296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyderman R. S., Klein N. J., Shennan G. I., Levin M. Reduction of the anticoagulant activity of glycosaminoglycans on the surface of the vascular endothelium by endotoxin and neutrophils: evaluation by an amidolytic assay. Thromb Res. 1992 Sep 15;67(6):677–685. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(92)90071-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibberd M. L., Sumiya M., Summerfield J. A., Booy R., Levin M. Association of variants of the gene for mannose-binding lectin with susceptibility to meningococcal disease. Meningococcal Research Group. Lancet. 1999 Mar 27;353(9158):1049–1053. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(98)08350-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis G. A., Vedros N. A. Sialic acid of group B Neisseria meningitidis regulates alternative complement pathway activation. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):174–180. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.174-180.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Wass C. A., Cross A. S. Blood-brain barrier permeability during the development of experimental bacterial meningitis in the rat. Exp Neurol. 1997 May;145(1):253–257. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1997.6458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein N. J., Ison C. A., Peakman M., Levin M., Hammerschmidt S., Frosch M., Heyderman R. S. The influence of capsulation and lipooligosaccharide structure on neutrophil adhesion molecule expression and endothelial injury by Neisseria meningitidis. J Infect Dis. 1996 Jan;173(1):172–179. doi: 10.1093/infdis/173.1.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein N. J., Shennan G. I., Heyderman R. S., Levin M. Alteration in glycosaminoglycan metabolism and surface charge on human umbilical vein endothelial cells induced by cytokines, endotoxin and neutrophils. J Cell Sci. 1992 Aug;102(Pt 4):821–832. doi: 10.1242/jcs.102.4.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornelisse R. F., Hazelzet J. A., Savelkoul H. F., Hop W. C., Suur M. H., Borsboom A. N., Risseeuw-Appel I. M., van der Voort E., de Groot R. The relationship between plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and proinflammatory and counterinflammatory mediators in children with meningococcal septic shock. J Infect Dis. 1996 May;173(5):1148–1156. doi: 10.1093/infdis/173.5.1148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Brar R., Wang P., Dee L., Skorupa G., Khadour F., Schulz R., Parrillo J. E. Role of nitric oxide and cGMP in human septic serum-induced depression of cardiac myocyte contractility. Am J Physiol. 1999 Jan;276(1 Pt 2):R265–R276. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1999.276.1.R265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Thota V., Dee L., Olson J., Uretz E., Parrillo J. E. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1beta are responsible for in vitro myocardial cell depression induced by human septic shock serum. J Exp Med. 1996 Mar 1;183(3):949–958. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.3.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi M., de Jonge E., van der Poll T., ten Cate H. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb Haemost. 1999 Aug;82(2):695–705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin M., Quint P. A., Goldstein B., Barton P., Bradley J. S., Shemie S. D., Yeh T., Kim S. S., Cafaro D. P., Scannon P. J. Recombinant bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein (rBPI21) as adjunctive treatment for children with severe meningococcal sepsis: a randomised trial. rBPI21 Meningococcal Sepsis Study Group. Lancet. 2000 Sep 16;356(9234):961–967. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(00)02712-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. A., Silverman H. J. Gram-negative sepsis and the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Jun;14(6):1213–1228. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.6.1213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavrommatis A. C., Theodoridis T., Orfanidou A., Roussos C., Christopoulou-Kokkinou V., Zakynthinos S. Coagulation system and platelets are fully activated in uncomplicated sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2000 Feb;28(2):451–457. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200002000-00027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulks M. H., Plaut A. G., Feldman H. A., Frangione B. IgA proteases of two distinct specificities are released by Neisseria meningitidis. J Exp Med. 1980 Nov 1;152(5):1442–1447. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.5.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oragui E. E., Nadel S., Kyd P., Levin M. Increased excretion of urinary glycosaminoglycans in meningococcal septicemia and their relationship to proteinuria. Crit Care Med. 2000 Aug;28(8):3002–3008. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200008000-00054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathan Nazima, Sandiford Colin, Harding Sian E., Levin Michael. Characterization of a myocardial depressant factor in meningococcal septicemia. Crit Care Med. 2002 Oct;30(10):2191–2198. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200210000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poltorak A., Ricciardi-Castagnoli P., Citterio S., Beutler B. Physical contact between lipopolysaccharide and toll-like receptor 4 revealed by genetic complementation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Feb 29;97(5):2163–2167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.040565397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quagliarello V., Scheld W. M. Bacterial meningitis: pathogenesis, pathophysiology, and progress. N Engl J Med. 1992 Sep 17;327(12):864–872. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199209173271208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock F. L., Hardiman G., Timans J. C., Kastelein R. A., Bazan J. F. A family of human receptors structurally related to Drosophila Toll. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jan 20;95(2):588–593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.2.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimura M., Wada H., Wakita Y., Nakase T., Hiyoyama K., Nagaya S., Mori Y., Shiku H. Plasma tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitor levels in patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation. Am J Hematol. 1996 Jul;52(3):165–170. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8652(199607)52:3<165::AID-AJH5>3.0.CO;2-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöholm A. G., Braconier J. H., Söderström C. Properdin deficiency in a family with fulminant meningococcal infections. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Nov;50(2):291–297. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens D. S., Farley M. M. Pathogenic events during infection of the human nasopharynx with Neisseria meningitidis and Haemophilus influenzae. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Jan-Feb;13(1):22–33. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiru Y., Pathan N., Bignall S., Habibi P., Levin M. A myocardial cytotoxic process is involved in the cardiac dysfunction of meningococcal septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2000 Aug;28(8):2979–2983. doi: 10.1097/00003246-200008000-00049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunkel A. R., Scheld W. M. Pathogenesis and pathophysiology of bacterial meningitis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1993 Apr;6(2):118–136. doi: 10.1128/cmr.6.2.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch S. B., Nadel S. Treatment of meningococcal infection. Arch Dis Child. 2003 Jul;88(7):608–614. doi: 10.1136/adc.88.7.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J., Mathison J. C. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1431–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.1698311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deuren M., van der Ven-Jongekrijg J., Bartelink A. K., van Dalen R., Sauerwein R. W., van der Meer J. W. Correlation between proinflammatory cytokines and antiinflammatory mediators and the severity of disease in meningococcal infections. J Infect Dis. 1995 Aug;172(2):433–439. doi: 10.1093/infdis/172.2.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]