Abstract
Aims: To study the effect of gluten-free diet on growth and diabetic control of children with type 1 diabetes mellitus and coeliac disease.
Methods: Twenty one children (mean age 7.5 years, range 1.6–12.9) with type 1 diabetes, primarily initially identified on the basis of symptoms and consecutively diagnosed with coeliac disease by biopsy over a 10 year period, were matched by sex, age at onset, and duration of diabetes with two diabetic controls without coeliac disease. Weight, height, haemoglobin A1c, and insulin requirements were measured before and for 12 months after the diagnosis and treatment of coeliac disease. Dietary awareness and adherence were assessed by structured questionnaire.
Results: A gluten-free diet resulted in a significant increase in weight-for-age z scores at 12 months after diagnosis (mean increase in z score 0.33) and in BMI (mean increase in z score 0.32). Increases in height did not achieve statistical significance. Controls showed no significant changes in weight, height, or BMI over the same period. Insulin dosage at diagnosis was less in coeliacs than in controls (mean difference 0.16 units/kg/day), but was similar to controls once a gluten-free diet had been established. Questionnaires were obtained in 20 patients. There appeared to be a relation between dietary awareness/adherence and growth parameters, but the small number of patients with "poor/fair" dietary adherence prevented meaningful analysis of this group.
Conclusion: Identification and dietary treatment of coeliac disease in children with diabetes improved growth and influenced diabetic control. Evaluation of the outcome of treatment of coeliac disease in diabetics should include assessments of gluten intake.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (229.4 KB).
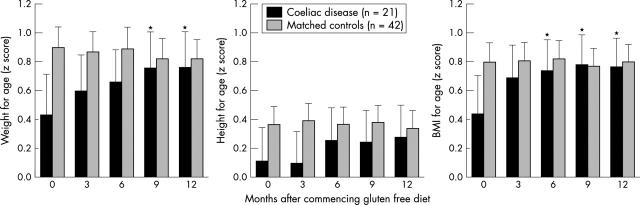
Figure 1.
Weight, height, and BMI standard deviation scores for age after diagnosis of coeliac disease in type 1 diabetics and in matched diabetic controls without coeliac disease. There were statistically significant increases in weight-for-age at 9 and 12 months and in BMI at 6, 9, and 12 months. *p < 0.05 compared to parameter at diagnosis.
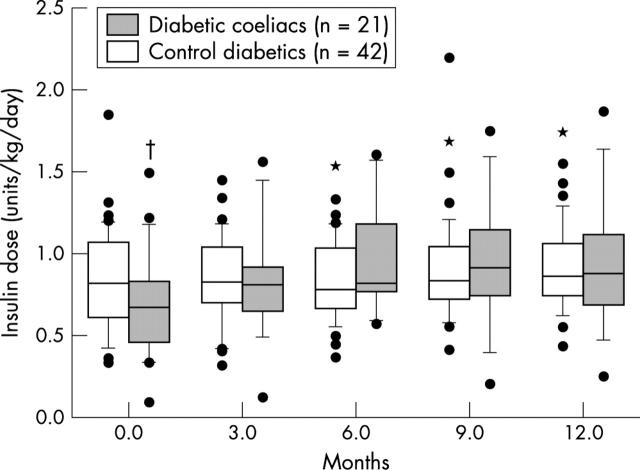
Figure 2.
Insulin dose after diagnosis of coeliac disease compared to controls. Insulin dosage increased significantly after diagnosis of coeliac disease. *p < 0.05 compared to insulin dose at diagnosis; †p = 0.05 compared to control.
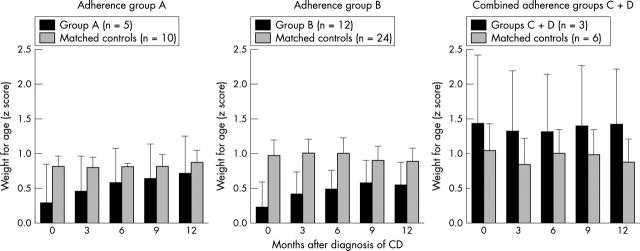
Figure 3.
Weight-for-age after diagnosis of coeliac disease by dietary adherence. "A" represented excellent adherence, "B" good adherence, and "CD" was assessed as poor to fair.
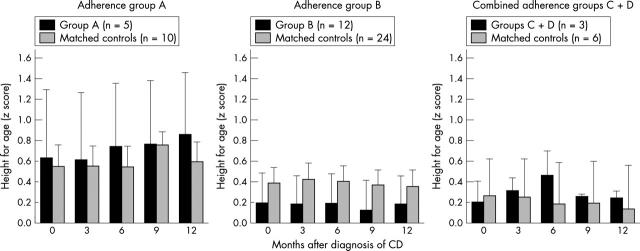
Figure 4.
Height-for-age after diagnosis of coeliac disease by dietary adherence. "A" represented excellent adherence, "B" good adherence, and "CD" was assessed as poor to fair.
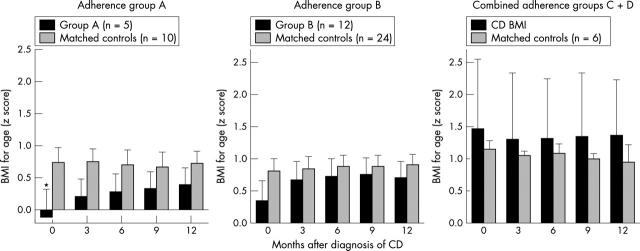
Figure 5.
BMI-for-age after diagnosis of coeliac disease by dietary adherence. "A" represented excellent adherence, "B" good adherence, and "CD" was assessed as poor to fair. *p < 0.05 compared to controls.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acerini C. L., Ahmed M. L., Ross K. M., Sullivan P. B., Bird G., Dunger D. B. Coeliac disease in children and adolescents with IDDM: clinical characteristics and response to gluten-free diet. Diabet Med. 1998 Jan;15(1):38–44. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9136(199801)15:1<38::AID-DIA520>3.0.CO;2-L. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amin Rakesh, Murphy Nuala, Edge Julie, Ahmed Marion L., Acerini Carlo L., Dunger David B. A longitudinal study of the effects of a gluten-free diet on glycemic control and weight gain in subjects with type 1 diabetes and celiac disease. Diabetes Care. 2002 Jul;25(7):1117–1122. doi: 10.2337/diacare.25.7.1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barera G., Bianchi C., Calisti L., Cerutti F., Dammacco F., Frezza E., Illeni M. T., Mistura L., Pocecco M., Prisco F. Screening of diabetic children for coeliac disease with antigliadin antibodies and HLA typing. Arch Dis Child. 1991 Apr;66(4):491–494. doi: 10.1136/adc.66.4.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buyken A. E., Toeller M., Heitkamp G., Irsigler K., Holler C., Santeusanio F., Stehle P., Fuller J. H. Carbohydrate sources and glycaemic control in Type 1 diabetes mellitus. EURODIAB IDDM Complications Study Group. Diabet Med. 2000 May;17(5):351–359. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.2000.00283.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colaco J., Egan-Mitchell B., Stevens F. M., Fottrell P. F., McCarthy C. F., McNicholl B. Compliance with gluten free diet in coeliac disease. Arch Dis Child. 1987 Jul;62(7):706–708. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.7.706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronin C. C., Shanahan F. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and coeliac disease. Lancet. 1997 Apr 12;349(9058):1096–1097. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)09153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vitis I., Ghirlanda G., Gasbarrini G. Prevalence of coeliac disease in type I diabetes: a multicentre study. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1996 May;412:56–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1996.tb14253.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickey W., Hughes D. F., McMillan S. A. Disappearance of endomysial antibodies in treated celiac disease does not indicate histological recovery. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000 Mar;95(3):712–714. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.01838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadd S., Kamath K. R., Silink M., Skerritt J. H. Co-existence of coeliac disease and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in children: screening sera using an ELISA test for gliadin antibody. Aust N Z J Med. 1992 Jun;22(3):256–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1992.tb02121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffenberg E. J., Bao F., Eisenbarth G. S., Uhlhorn C., Haas J. E., Sokol R. J., Rewers M. Transglutaminase antibodies in children with a genetic risk for celiac disease. J Pediatr. 2000 Sep;137(3):356–360. doi: 10.1067/mpd.2000.107582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes G. K. Celiac disease and malignancy. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1997 May;24(5):S20–S24. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199700001-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes G. K., Prior P., Lane M. R., Pope D., Allan R. N. Malignancy in coeliac disease--effect of a gluten free diet. Gut. 1989 Mar;30(3):333–338. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.3.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iafusco D., Rea F., Prisco F. Hypoglycemia and reduction of the insulin requirement as a sign of celiac disease in children with IDDM. Diabetes Care. 1998 Aug;21(8):1379–1381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P. T., Glasgow J. F., Thom R. Parents' understanding of coeliac disease and diet. Arch Dis Child. 1985 Jul;60(7):672–674. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.7.672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaukinen K., Salmi J., Lahtela J., Siljamäki-Ojansuu U., Koivisto A. M., Oksa H., Collin P. No effect of gluten-free diet on the metabolic control of type 1 diabetes in patients with diabetes and celiac disease. Retrospective and controlled prospective survey. Diabetes Care. 1999 Oct;22(10):1747–1748. doi: 10.2337/diacare.22.10.1747a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemppainen T., Kröger H., Janatuinen E., Arnala I., Kosma V. M., Pikkarainen P., Julkunen R., Jurvelin J., Alhava E., Uusitupa M. Osteoporosis in adult patients with celiac disease. Bone. 1999 Mar;24(3):249–255. doi: 10.1016/s8756-3282(98)00178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar P. J., Walker-Smith J., Milla P., Harris G., Colyer J., Halliday R. The teenage coeliac: follow up study of 102 patients. Arch Dis Child. 1988 Aug;63(8):916–920. doi: 10.1136/adc.63.8.916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljungman G., Myrdal U. Compliance in teenagers with coeliac disease--a Swedish follow-up study. Acta Paediatr. 1993 Mar;82(3):235–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1993.tb12649.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M., Greco L., Troncone R., Auricchio S., Marsh M. N. Compliance of adolescents with coeliac disease with a gluten free diet. Gut. 1991 Aug;32(8):881–885. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.8.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peña A. S., Garrote J. A., Crusius J. B. Advances in the immunogenetics of coeliac disease. Clues for understanding the pathogenesis and disease heterogeneity. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1998;225:56–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocecco M., Ventura A. Coeliac disease and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a causal association? Acta Paediatr. 1995 Dec;84(12):1432–1433. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1995.tb13583.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saukkonen T., Savilahti E., Reijonen H., Ilonen J., Tuomilehto-Wolf E., Akerblom H. K. Coeliac disease: frequent occurrence after clinical onset of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Childhood Diabetes in Finland Study Group. Diabet Med. 1996 May;13(5):464–470. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9136(199605)13:5<464::AID-DIA101>3.0.CO;2-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savilahti E., Simell O., Koskimies S., Rilva A., Akerblom H. K. Celiac disease in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Pediatr. 1986 May;108(5 Pt 1):690–693. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)81042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigurs N., Johansson C., Elfstrand P. O., Viander M., Lanner A. Prevalence of coeliac disease in diabetic children and adolescents in Sweden. Acta Paediatr. 1993 Sep;82(9):748–751. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1993.tb12551.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdimarsson T., Löfman O., Toss G., Ström M. Reversal of osteopenia with diet in adult coeliac disease. Gut. 1996 Mar;38(3):322–327. doi: 10.1136/gut.38.3.322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker-Smith J. A., Vines R., Grigor W. Coeliac disease and diabetes. Lancet. 1969 Sep 20;2(7621):650–650. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90363-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westman E., Ambler G. R., Royle M., Peat J., Chan A. Children with coeliac disease and insulin dependent diabetes mellitus--growth, diabetes control and dietary intake. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 1999 May-Jun;12(3):433–442. doi: 10.1515/jpem.1999.12.3.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]