Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (100.3 KB).
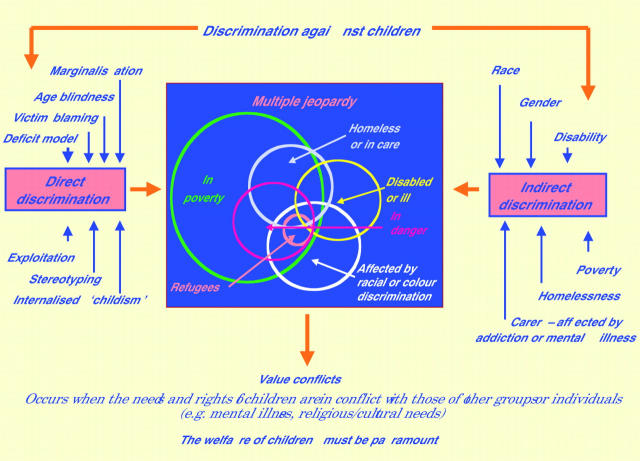
Figure 1.
Discrimination against children.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aynsley-Green A., Barker M., Burr S., Macfarlane A., Morgan J., Sibert J., Turner T., Viner R., Waterston T., Hall D. Who is speaking for children and adolescents and for their health at the policy level? BMJ. 2000 Jul 22;321(7255):229–232. doi: 10.1136/bmj.321.7255.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bariciak Erika D., Plint Amy C., Gaboury Isabelle, Bennett Sue. Dating of bruises in children: an assessment of physician accuracy. Pediatrics. 2003 Oct;112(4):804–807. doi: 10.1542/peds.112.4.804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler-Sloss Elizabeth, Hall Ananda. Expert witnesses, courts and the law. J R Soc Med. 2002 Sep;95(9):431–434. doi: 10.1258/jrsm.95.9.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland J. G., Van Ginneken J. K. Maternal education and child survival in developing countries: the search for pathways of influence. Soc Sci Med. 1988;27(12):1357–1368. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(88)90201-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conroy S., Choonara I., Impicciatore P., Mohn A., Arnell H., Rane A., Knoeppel C., Seyberth H., Pandolfini C., Raffaelli M. P. Survey of unlicensed and off label drug use in paediatric wards in European countries. European Network for Drug Investigation in Children. BMJ. 2000 Jan 8;320(7227):79–82. doi: 10.1136/bmj.320.7227.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David T. J., Hershman D. A., McFarlane A. E. Pretrial liaison between doctors in alleged child abuse. Arch Dis Child. 1998 Sep;79(3):205–206. doi: 10.1136/adc.79.3.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. M. George Armstrong MD (1719-1789) and his dispensary for the infant poor. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2002 Nov;87(3):F228–F231. doi: 10.1136/fn.87.3.F228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrington D. P. The Twelfth Jack Tizard Memorial Lecture. The development of offending and antisocial behaviour from childhood: key findings from the Cambridge Study in Delinquent Development. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1995 Sep;36(6):929–964. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1995.tb01342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khanna R., Kumar A., Vaghela J. F., Sreenivas V., Puliyel J. M. Community based retrospective study of sex in infant mortality in India. BMJ. 2003 Jul 19;327(7407):126–126. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7407.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langlois N. E., Gresham G. A. The ageing of bruises: a review and study of the colour changes with time. Forensic Sci Int. 1991 Sep;50(2):227–238. doi: 10.1016/0379-0738(91)90154-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffitt T. E., Caspi A. Childhood predictors differentiate life-course persistent and adolescence-limited antisocial pathways among males and females. Dev Psychopathol. 2001 Spring;13(2):355–375. doi: 10.1017/s0954579401002097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munang L. A., Leonard P. A., Mok J. Y. Q. Lack of agreement on colour description between clinicians examining childhood bruising. J Clin Forensic Med. 2002 Dec;9(4):171–174. doi: 10.1016/s1353-1131(02)00097-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts I., Coggan C. Blaming children for child pedestrian injuries. Soc Sci Med. 1994 Mar;38(5):749–753. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(94)90465-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell-Eggitt I. M., Thompson D. A., Khair K., Liesner R., Hann I. M. Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome presenting with subdural haematoma and retinal haemorrhages in infancy. J R Soc Med. 2000 Nov;93(11):591–592. doi: 10.1177/014107680009301110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanz Emilio J. Concordance and children's use of medicines. BMJ. 2003 Oct 11;327(7419):858–860. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7419.858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloper P., Lightfoot J. Involving disabled and chronically ill children and young people in health service development. Child Care Health Dev. 2003 Jan;29(1):15–20. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2214.2003.00315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth R. L. Research with children. Paediatric practice needs better evidence--gained in collaboration with parents and children. BMJ. 2001 Jun 9;322(7299):1377–1378. doi: 10.1136/bmj.322.7299.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson T., Bialas Y. Estimation of the age of bruising. Arch Dis Child. 1996 Jan;74(1):53–55. doi: 10.1136/adc.74.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe Alastair G. Testing new pharmaceutical products in children. BMJ. 2003 Jan 11;326(7380):64–65. doi: 10.1136/bmj.326.7380.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischler V., Vostanis P., Bellerby T., Cumella S. Evaluation of a mental health outreach service for homeless families. Arch Dis Child. 2002 Mar;86(3):158–163. doi: 10.1136/adc.86.3.158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker N. E., Doyon T. 'Fairness and reasonableness of the child's decision:' a proposed legal standard for children's participation in medical decision making. Behav Sci Law. 2001;19(5-6):611–636. doi: 10.1002/bsl.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall N. Judicial attitudes to expert evidence in children's cases. Arch Dis Child. 1997 Jun;76(6):485–487. doi: 10.1136/adc.76.6.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb E. Health services: who are the best advocates for children? Arch Dis Child. 2002 Sep;87(3):175–177. doi: 10.1136/adc.87.3.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb E., Naish J., MacFarlane A. Planning and commissioning of health services for children and young people. J Public Health Med. 1996 Jun;18(2):217–220. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.pubmed.a024482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb E., Shankleman J., Evans M. R., Brooks R. The health of children in refuges for women victims of domestic violence: cross sectional descriptive survey. BMJ. 2001 Jul 28;323(7306):210–213. doi: 10.1136/bmj.323.7306.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber W. Experimentelle Untersuchungen zu Schädelbruchverletzungen des Säuglings. Z Rechtsmed. 1984;92(2):87–94. doi: 10.1007/BF02116216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber W. Prädilektionsstellen infantiler Kalottenfrakturen nach stumpfer Gewalt. Z Rechtsmed. 1987;98(2):81–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00200464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber W. Zur biomechanischen Fragilität des Säuglingsschädels. Z Rechtsmed. 1985;94(2):93–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00198677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. Expert evidence in cases of child abuse. Arch Dis Child. 1993 May;68(5):712–714. doi: 10.1136/adc.68.5.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young Bridget, Dixon-Woods Mary, Windridge Kate C., Heney David. Managing communication with young people who have a potentially life threatening chronic illness: qualitative study of patients and parents. BMJ. 2003 Feb 8;326(7384):305–305. doi: 10.1136/bmj.326.7384.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]