Abstract
Objective: To assess various aspects of visual function at school age in children with neonatal cerebral infarction.
Patients and methods: Sixteen children born at term, who had cerebral infarction of perinatal onset on neonatal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were assessed using a battery of visual tests. This included measures of crowding acuity (Cambridge Crowding Cards), stereopsis (TNO test), and visual fields. The results of the visual assessment were compared with the type and the extent of the lesion observed on neonatal MRI.
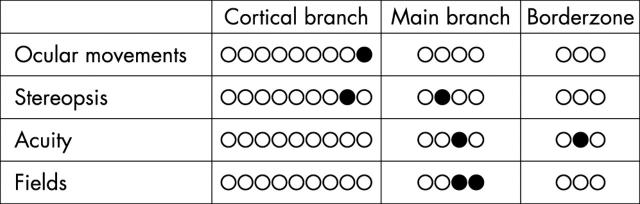
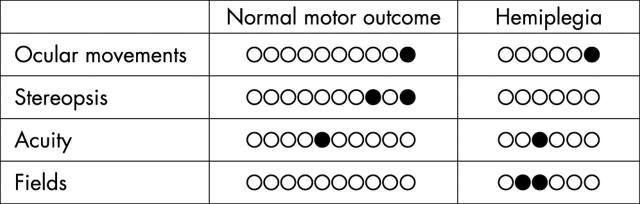
Results: Only six of the 16 children (28%) had some abnormalities of visual function on these tests. Visual abnormalities were more common in children with more extensive lesions involving the main branch of the middle cerebral artery and were less often associated with lesions in the territory of one of the cortical branches of the middle cerebral artery. The presence of visual abnormalities was not always associated with the involvement of optic radiations or occipital primary visual cortex. Abnormal visual fields were only found in children who also developed hemiplegia.
Conclusions: Abnormality of visual function is not common in children who had neonatal infarction and, when present, tends to be associated with hemiplegia and more extensive lesions.
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (213.8 KB).
Figure 1 .
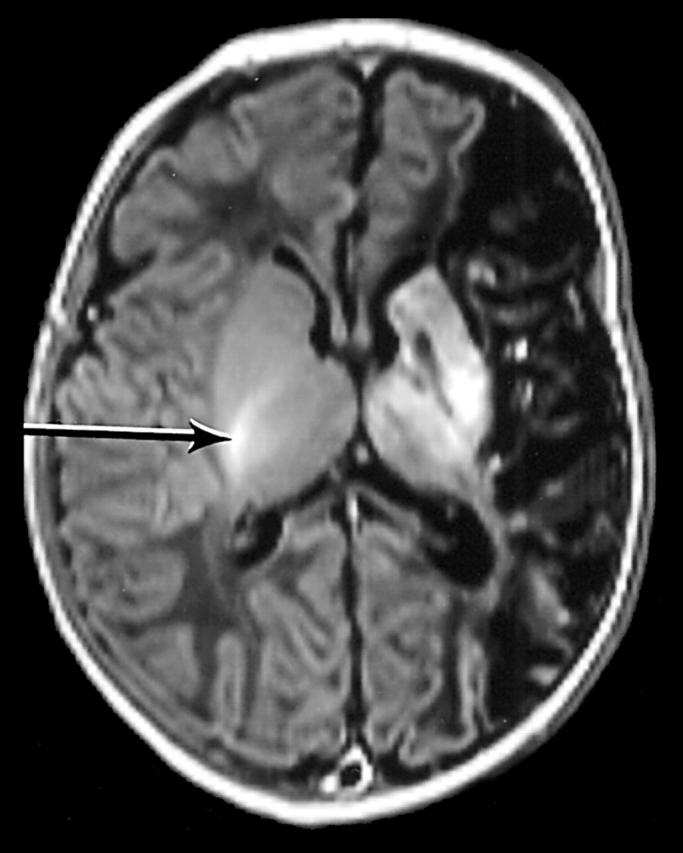
Inversion recovery sequence (IR 3800/30/950). Infant aged 14 days (case No 12). There is a large infarct involving the left hemisphere. There are additional abnormal high and low signal intensities within the basal ganglia, thalamus, and optic radiation on the left.
Figure 2 .
Comparison of visual and magnetic resonance imaging findings.
Figure 3 .
Comparison of visual and motor outcome.
Figure 4 .
Comparison of early and late visual assessments.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson J., Anker S., Evans C., Hall R., Pimm-Smith E. Visual acuity testing of young children with the Cambridge Crowding Cards at 3 and 6 m. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1988 Oct;66(5):505–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1988.tb04371.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braddick O., Atkinson J., Hood B., Harkness W., Jackson G., Vargha-Khadem F. Possible blindsight in infants lacking one cerebral hemisphere. Nature. 1992 Dec 3;360(6403):461–463. doi: 10.1038/360461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estan J., Hope P. Unilateral neonatal cerebral infarction in full term infants. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1997 Mar;76(2):F88–F93. doi: 10.1136/fn.76.2.f88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. Psychological aspects of hemiplegia. Arch Dis Child. 1997 Mar;76(3):177–178. doi: 10.1136/adc.76.3.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunn Alison, Cory Elizabeth, Atkinson Janette, Braddick Oliver, Wattam-Bell John, Guzzetta Andrea, Cioni Giovanni. Dorsal and ventral stream sensitivity in normal development and hemiplegia. Neuroreport. 2002 May 7;13(6):843–847. doi: 10.1097/00001756-200205070-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzzetta A., Fazzi B., Mercuri E., Bertuccelli B., Canapicchi R., van Hof-van Duin J., Cioni G. Visual function in children with hemiplegia in the first years of life. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2001 May;43(5):321–329. doi: 10.1017/s0012162201000603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongmans M., Mercuri E., Henderson S., de Vries L., Sonksen P., Dubowitz L. Visual function of prematurely born children with and without perceptual-motor difficulties. Early Hum Dev. 1996 Jul 5;45(1-2):73–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(95)01722-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercuri E., Atkinson J., Braddick O., Anker S., Cowan F., Rutherford M., Pennock J., Dubowitz L. Basal ganglia damage and impaired visual function in the newborn infant. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1997 Sep;77(2):F111–F114. doi: 10.1136/fn.77.2.f111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercuri E., Atkinson J., Braddick O., Anker S., Cowan F., Rutherford M., Pennock J., Dubowitz L. Visual function in full-term infants with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Neuropediatrics. 1997 Jun;28(3):155–161. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-973693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercuri E., Atkinson J., Braddick O., Anker S., Nokes L., Cowan F., Rutherford M., Pennock J., Dubowitz L. Visual function and perinatal focal cerebral infarction. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1996 Sep;75(2):F76–F81. doi: 10.1136/fn.75.2.f76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercuri E., Rutherford M., Cowan F., Pennock J., Counsell S., Papadimitriou M., Azzopardi D., Bydder G., Dubowitz L. Early prognostic indicators of outcome in infants with neonatal cerebral infarction: a clinical, electroencephalogram, and magnetic resonance imaging study. Pediatrics. 1999 Jan;103(1):39–46. doi: 10.1542/peds.103.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercuri E., Spanò M., Bruccini G., Frisone M. F., Trombetta J. C., Blandino A., Longo M., Guzzetta F. Visual outcome in children with congenital hemiplegia: correlation with MRI findings. Neuropediatrics. 1996 Aug;27(4):184–188. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-973784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda F. C., Apt L., Wanter B. S. Evaluation of the TNO -random-dot stereogram test. Am Orthopt J. 1977;27:124–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike M. G., Holmstrom G., de Vries L. S., Pennock J. M., Drew K. J., Sonksen P. M., Dubowitz L. M. Patterns of visual impairment associated with lesions of the preterm infant brain. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1994 Oct;36(10):849–862. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1994.tb11776.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thal D. J., Marchman V., Stiles J., Aram D., Trauner D., Nass R., Bates E. Early lexical development in children with focal brain injury. Brain Lang. 1991 May;40(4):491–527. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(91)90145-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verfaellie M., Rapcsak S. Z., Heilman K. M. Impaired shifting of attention in Balint's syndrome. Brain Cogn. 1990 Mar;12(2):195–204. doi: 10.1016/0278-2626(90)90015-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries L. S., Groenendaal F., Eken P., van Haastert I. C., Rademaker K. J., Meiners L. C. Infarcts in the vascular distribution of the middle cerebral artery in preterm and fullterm infants. Neuropediatrics. 1997 Apr;28(2):88–96. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-973679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hof-van Duin J., Heersema D. J., Groenendaal F., Baerts W., Fetter W. P. Visual field and grating acuity development in low-risk preterm infants during the first 2 1/2 years after term. Behav Brain Res. 1992 Jul 31;49(1):115–122. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(05)80201-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]