Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (244.1 KB).
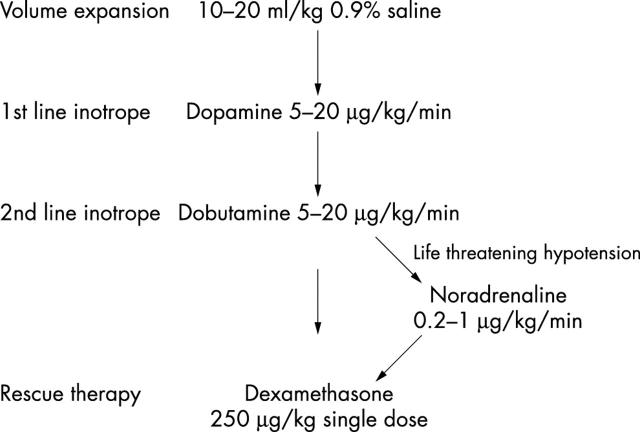
Figure 1 .
Flow chart for management of hypotension in the very low birthweight infant.
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourchier D., Weston P. J. Randomised trial of dopamine compared with hydrocortisone for the treatment of hypotensive very low birthweight infants. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1997 May;76(3):F174–F178. doi: 10.1136/fn.76.3.f174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Costeloe K. L. Measuring intramucosal pH in very low birth weight infants. Pediatr Res. 2001 Sep;50(3):398–404. doi: 10.1203/00006450-200109000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Van Aerde J. E., Cheung P. Y., Mayes D. C. Tonometry to estimate intestinal perfusion in newborn piglets. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1999 Sep;81(2):F105–F109. doi: 10.1136/fn.81.2.f105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dammann Olaf, Allred Elizabeth N., Kuban Karl C. K., Van Marter Linda J., Pagano Marcello, Sanocka Ulana, Leviton Alan, Developmental Epidemiology Network Systemic hypotension and white-matter damage in preterm infants. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2002 Feb;44(2):82–90. doi: 10.1017/s0012162201001724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellagrammaticas H. D., Wilson A. J. Clinical evaluation of the Dinamap non-invasive blood pressure monitor in pre-term neonates. Clin Phys Physiol Meas. 1981 Nov;2(4):271–276. doi: 10.1088/0143-0815/2/4/003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitriou G., Greenough A., Mantagos J., Skinner S. Metabolic acidosis, core-peripheral temperature difference and blood pressure response to albumin infusion in hypotensive, very premature infants. J Perinat Med. 2001;29(5):442–445. doi: 10.1515/JPM.2001.061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diprose G. K., Evans D. H., Archer L. N., Levene M. I. Dinamap fails to detect hypotension in very low birthweight infants. Arch Dis Child. 1986 Aug;61(8):771–773. doi: 10.1136/adc.61.8.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll W., Thurin S., Carrion V., Steinhorn R. H., Morin F. C., 3rd Effect of methylene blue on refractory neonatal hypotension. J Pediatr. 1996 Dec;129(6):904–908. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(96)70036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery E. F., Greenough A., Gamsu H. R. Randomised controlled trial of colloid infusions in hypotensive preterm infants. Arch Dis Child. 1992 Oct;67(10 Spec No):1185–1188. doi: 10.1136/adc.67.10_spec_no.1185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler B., Whitehouse C., Wenzel F., Wraith J. E. Methionine and serine formation in control and mutant human cultured fibroblasts: evidence for methyl trapping and characterization of remethylation defects. Pediatr Res. 1997 Jan;41(1):145–151. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199701000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaissmaier R. E., Pohlandt F. Single-dose dexamethasone treatment of hypotension in preterm infants. J Pediatr. 1999 Jun;134(6):701–705. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(99)70284-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill A. B., Weindling A. M. Randomised controlled trial of plasma protein fraction versus dopamine in hypotensive very low birthweight infants. Arch Dis Child. 1993 Sep;69(3 Spec No):284–287. doi: 10.1136/adc.69.3_spec_no.284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heckmann M., Wudy S. A., Haack D., Pohlandt F. Serum cortisol concentrations in ill preterm infants less than 30 weeks gestational age. Acta Paediatr. 2000 Sep;89(9):1098–1103. doi: 10.1080/713794576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegyi T., Anwar M., Carbone M. T., Ostfeld B., Hiatt M., Koons A., Pinto-Martin J., Paneth N. Blood pressure ranges in premature infants: II. The first week of life. Pediatrics. 1996 Mar;97(3):336–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegyi T., Carbone M. T., Anwar M., Ostfeld B., Hiatt M., Koons A., Pinto-Martin J., Paneth N. Blood pressure ranges in premature infants. I. The first hours of life. J Pediatr. 1994 Apr;124(4):627–633. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)83146-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel R., Hensel D., Brune T., Rabe H., Jorch G. Impact on blood pressure and intestinal perfusion of dobutamine or dopamine in hypotensive preterm infants. Biol Neonate. 1995;68(5):318–324. doi: 10.1159/000244252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaber L., Gabriel R., Merlob P. Meconium aspiration and otitis media in children. Eur J Pediatr. 1993 Feb;152(2):164–165. doi: 10.1007/BF02072497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawczynski P., Piotrowski A. Circulatory and diuretic effects of dopexamine infusion in low-birth-weight infants with respiratory failure. Intensive Care Med. 1996 Jan;22(1):65–70. doi: 10.1007/BF01728334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimble K. J., Darnall R. A., Jr, Yelderman M., Ariagno R. L., Ream A. K. An automated oscillometric technique for estimating mean arterial pressure in critically ill newborns. Anesthesiology. 1981 May;54(5):423–425. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198105000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klarr J. M., Faix R. G., Pryce C. J., Bhatt-Mehta V. Randomized, blind trial of dopamine versus dobutamine for treatment of hypotension in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome. J Pediatr. 1994 Jul;125(1):117–122. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(94)70137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluckow M., Evans N. Relationship between blood pressure and cardiac output in preterm infants requiring mechanical ventilation. J Pediatr. 1996 Oct;129(4):506–512. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(96)70114-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kluckow M., Evans N. Superior vena cava flow in newborn infants: a novel marker of systemic blood flow. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2000 May;82(3):F182–F187. doi: 10.1136/fn.82.3.F182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J., Rajadurai V. S., Tan K. W. Blood pressure standards for very low birthweight infants during the first day of life. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1999 Nov;81(3):F168–F170. doi: 10.1136/fn.81.3.f168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low J. A., Froese A. B., Galbraith R. S., Smith J. T., Sauerbrei E. E., Derrick E. J. The association between preterm newborn hypotension and hypoxemia and outcome during the first year. Acta Paediatr. 1993 May;82(5):433–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1993.tb12717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miall-Allen V. M., Whitelaw A. G. Response to dopamine and dobutamine in the preterm infant less than 30 weeks gestation. Crit Care Med. 1989 Nov;17(11):1166–1169. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198911000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miall-Allen V. M., de Vries L. S., Whitelaw A. G. Mean arterial blood pressure and neonatal cerebral lesions. Arch Dis Child. 1987 Oct;62(10):1068–1069. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.10.1068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moïse A. A., Wearden M. E., Kozinetz C. A., Gest A. L., Welty S. E., Hansen T. N. Antenatal steroids are associated with less need for blood pressure support in extremely premature infants. Pediatrics. 1995 Jun;95(6):845–850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng P. C., Lam C. W., Fok T. F., Lee C. H., Ma K. C., Chan I. H., Wong E. Refractory hypotension in preterm infants with adrenocortical insufficiency. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2001 Mar;84(2):F122–F124. doi: 10.1136/fn.84.2.F122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuntnarumit P., Yang W., Bada-Ellzey H. S. Blood pressure measurements in the newborn. Clin Perinatol. 1999 Dec;26(4):981-96, x. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padbury J. F., Agata Y., Baylen B. G., Ludlow J. K., Polk D. H., Goldblatt E., Pescetti J. Dopamine pharmacokinetics in critically ill newborn infants. J Pediatr. 1987 Feb;110(2):293–298. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80176-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panerai R. B., Kelsall A. W., Rennie J. M., Evans D. H. Cerebral autoregulation dynamics in premature newborns. Stroke. 1995 Jan;26(1):74–80. doi: 10.1161/01.str.26.1.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryds O., Edwards A. D. Cerebral blood flow in the newborn infant. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1996 Jan;74(1):F63–F69. doi: 10.1136/fn.74.1.f63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju N. V., Maisels M. J., Kring E., Schwarz-Warner L. Capillary refill time in the hands and feet of normal newborn infants. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1999 Mar;38(3):139–144. doi: 10.1177/000992289903800303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozé J. C., Tohier C., Maingueneau C., Lefèvre M., Mouzard A. Response to dobutamine and dopamine in the hypotensive very preterm infant. Arch Dis Child. 1993 Jul;69(1 Spec No):59–63. doi: 10.1136/adc.69.1_spec_no.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott S. M., Watterberg K. L. Effect of gestational age, postnatal age, and illness on plasma cortisol concentrations in premature infants. Pediatr Res. 1995 Jan;37(1):112–116. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199501000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seri I., Abbasi S., Wood D. C., Gerdes J. S. Regional hemodynamic effects of dopamine in the sick preterm neonate. J Pediatr. 1998 Dec;133(6):728–734. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(98)70141-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seri I. Cardiovascular, renal, and endocrine actions of dopamine in neonates and children. J Pediatr. 1995 Mar;126(3):333–344. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(95)70445-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seri I., Tan R., Evans J. Cardiovascular effects of hydrocortisone in preterm infants with pressor-resistant hypotension. Pediatrics. 2001 May;107(5):1070–1074. doi: 10.1542/peds.107.5.1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stopfkuchen H., Queisser-Luft A., Vogel K. Cardiovascular responses to dobutamine determined by systolic time intervals in preterm infants. Crit Care Med. 1990 Jul;18(7):722–724. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199007000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet D. G., Halliday H. L. A risk-benefit assessment of drugs used for neonatal chronic lung disease. Drug Saf. 2000 May;22(5):389–404. doi: 10.2165/00002018-200022050-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tantivit P., Subramanian N., Garg M., Ramanathan R., deLemos R. A. Low serum cortisol in term newborns with refractory hypotension. J Perinatol. 1999 Jul-Aug;19(5):352–357. doi: 10.1038/sj.jp.7200202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibby S. M., Hatherill M., Murdoch I. A. Capillary refill and core-peripheral temperature gap as indicators of haemodynamic status in paediatric intensive care patients. Arch Dis Child. 1999 Feb;80(2):163–166. doi: 10.1136/adc.80.2.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji M., Saul J. P., du Plessis A., Eichenwald E., Sobh J., Crocker R., Volpe J. J. Cerebral intravascular oxygenation correlates with mean arterial pressure in critically ill premature infants. Pediatrics. 2000 Oct;106(4):625–632. doi: 10.1542/peds.106.4.625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardle S. P., Yoxall C. W., Weindling A. M. Determinants of cerebral fractional oxygen extraction using near infrared spectroscopy in preterm neonates. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000 Feb;20(2):272–279. doi: 10.1097/00004647-200002000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardle S. P., Yoxall C. W., Weindling A. M. Peripheral oxygenation in hypotensive preterm babies. Pediatr Res. 1999 Mar;45(3):343–349. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199903000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins A. M., West C. R., Cooke R. W. Blood pressure and cerebral haemorrhage and ischaemia in very low birthweight infants. Early Hum Dev. 1989 May;19(2):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(89)90120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weindling A. M. Blood pressure monitoring in the newborn. Arch Dis Child. 1989 Apr;64(4 Spec No):444–447. doi: 10.1136/adc.64.4_spec_no.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]