Abstract
Aim—To re-examine the previously reported in vitro interaction of insulin with Burkholderia pseudomallei, in the light of a suggestion that the interaction may have resulted from the presence of the preservative m-cresol in commercial preparations.
Methods—Broth culture studies of B pseudomallei were performed with and without the addition of m-cresol and various preparations of insulin.
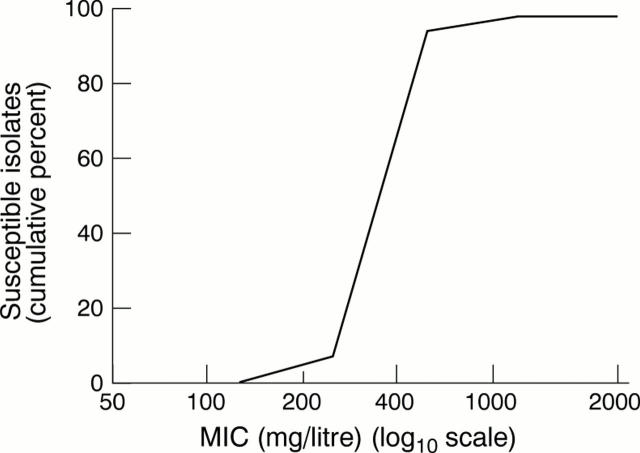
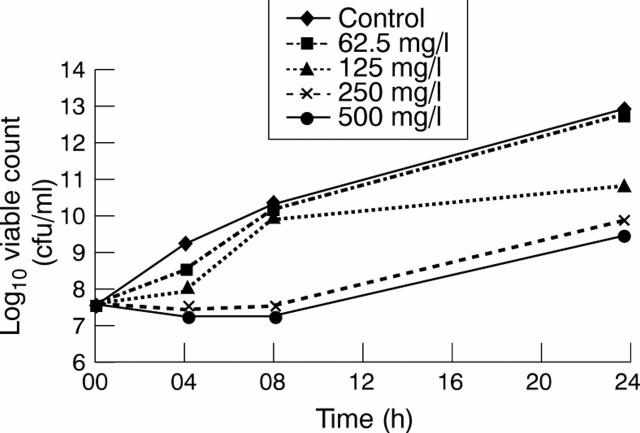
Results—Growth of B pseudomallei was inhibited by m-cresol at the concentrations found in pharmaceutical insulin preparations, and by the insulin preparation Humulin R, but not by pure insulin.
Conclusions—The results of previous experiments may have been confounded by the presence of the preservative m-cresol.
Key Words: Burkholderia pseudomallei • melioidosis • insulin • cresol
Full Text
The Full Text of this article is available as a PDF (93.5 KB).
Figure 1 Cumulative percentage of Burkholderia pseudomallei isolates (n = 100) susceptible to increasing concentrations of m-cresol.
Figure 2 Effects of different concentrations of m-cresol on growth of Burkholderia pseudomallei.
Figure 3 Optical densities during growth of Burkholderia pseudomallei in the presence of insulin or m-cresol. (Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals.)